| Issue |
A&A
Volume 538, February 2012
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A109 | |
| Number of page(s) | 12 | |
| Section | The Sun | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201117842 | |
| Published online | 10 February 2012 | |
Horizontal flow fields observed in Hinode G-band images
II. Flow fields in the final stages of sunspot decay
1 Leibniz-Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP), An der Sternwarte 16, 14482 Potsdam, Germany
e-mail: mverma@aip.de; hbalthasar@aip.de; cdenker@aip.de
2 New Jersey Institute of Technology, Space Weather Research Laboratory, 323 Martin Luther King Blvd., Newark, NJ 07102, USA
e-mail: nd7@njit.edu; chang.liu@njit.edu; haimin.wang@njit.edu
3 California State University Northridge, Physics and Astronomy Department, 18111 Nordhoff St., Northridge, CA 91330, USA
4 Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, 3-1-1 Yoshinodai, Chuo-ku, Sagamihara, 252-5210 Kanagawa, Japan
e-mail: shimizu.toshifumi@isas.jaxa.jp
Received: 6 August 2011
Accepted: 2 December 2011
Context. Generation and dissipation of magnetic fields is a fundamental physical process on the Sun. In comparison to flux emergence and the initial stages of sunspot formation, the demise of sunspots still lacks a comprehensive description.
Aims. The evolution of sunspots is most commonly discussed in terms of their intensity and magnetic field. Here, we present additional information about the three-dimensional flow field in the vicinity of sunspots towards the end of their existence.
Methods. We present a subset of multi-wavelengths observations obtained with the Japanese Hinode mission, the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), and the Vacuum Tower Telescope (VTT) at Observatorio del Teide, Tenerife, Spain during the time period 2010 November 18−23. Horizontal proper motions were derived from G-band and Ca ii H images, whereas line-of-sight velocities were extracted from VTT echelle Hα λ656.28 nm spectra and Fe i λ630.25 nm spectral data of the Hinode/Spectro-Polarimeter, which also provided three-dimensional magnetic field information. The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager on board SDO provided continuum images and line-of-sight magnetograms, in addition to the high-resolution observations for the entire disk passage of the active region.
Results. We perform a quantitative study of photospheric and chromospheric flow fields in and around decaying sunspots. In one of the trailing sunspots of active region NOAA 11126, we observe moat flow and moving magnetic features (MMFs), even after its penumbra had decayed. We also detect a superpenumbral structure around this pore. We find that MMFs follow well-defined, radial paths from the spot all the way to the border of a supergranular cell surrounding the spot. In contrast, flux emergence near the other sunspot prevents the establishment of similar well ordered flow patterns, which could be discerned around a tiny pore of merely 2 Mm diameter. After the disappearance of the sunspots/pores, a coherent patch of abnormal granulation remained at their location, which was characterized by more uniform horizontal proper motions, low divergence values, and smaller photospheric Doppler velocities. This region, thus, differs significantly from granulation and other areas covered by G-band bright points. We conclude that this peculiar flow pattern is a signature of sunspot decay and the dispersal of magnetic flux.
Key words: methods: data analysis / Sun: chromosphere / Sun: photosphere / Sun: surface magnetism / sunspots / techniques: image processing
© ESO, 2012
1. Introduction
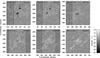 |
Fig. 1 Calibrated Hinode G-band images showing the decay of active region NOAA 11126 observed during the period 2010 November 18 − 23 (from top-left to bottom-right). The FOV is 111″ × 111″. The annotation of the axes refers to heliocentric coordinates given in seconds of arc. Brighter areas delineated by vertical black lines correspond to regions, which were covered by spectral scans obtained with the VTT echelle spectrograph. The intensity scale to the right applies to these regions, while areas not covered by echelle data are displayed with an offset of 0.1I0. On 2010 November 23, only few Hinode G-band images were available. The limb darkening was subtracted from the G-band images, which were then normalized so that the mean of the quiet Sun intensity distribution corresponds to unity. |
Sunspots are a thought-provoking aspect of solar activity because of the close interaction between plasma motions and magnetic fields. Recent progress in magnetothermodynamics (MHD) simulations (e.g., Rempel 2011) has provided a comprehensive framework for the interpretation of high-resolution sunspot observations. The formation of a penumbra around a sunspot occurs rapidly, i.e., within a few hours a sunspot can develop a penumbra (Leka & Skumanich 1998; Yang et al. 2003), and this rapidity is intimately linked to the more inclined magnetic field lines and the onset of the Evershed flow. Schlichenmaier et al. (2010) observed the growth of a penumbra where only the newly formed penumbra contributed to the increase in spot size while the umbra remained stable. The formation of a penumbra, which would surround the entire spot, was hindered by continuous flux emergence between the spots of the bipolar region.
In contrast, the decay of a sunspot is a slow process. The decay rates of stable leading sunspots and irregular follower spots are different (Martínez Pillet 2002). A number of decay laws have been proposed such as a linear decay law described by Bumba (1963) and a parabolic decay law proposed by Petrovay & van Driel-Gesztelyi (1997). Martínez Pillet (2002) critically reviewed various diffusion models, concluding that they explain well how flux is spread over larger areas while the spot is decaying, but fail to satisfactorily describe the flux removal process. The initial stages of sunspot decay, i.e., when the spot loses its penumbra, are described in great detail by Bellot Rubio et al. (2008), who discovered finger-like structures that are related neither to penumbral filaments nor the Evershed flow. These features might be penumbral field lines that rise to the chromosphere, thus contribute to the decay of the sunspot penumbra. When a sunspot loses its penumbra, its decay reaches a critical point. Magnetic field lines become more vertical and convective motions in its vicinity begin to change. These ideas of a critical inclination angle and convective motions were developed by Rucklidge et al. (1995), who explained in a simple model why small sunspots can have a penumbra while larger pores do not.
The moat flow is a large-scale flow pattern commonly observed around sunspots (Meyer et al. 1974). However, flux removal and dispersal can only be understood in the context of the moat flow’s fine structure. Moving magnetic features (MMFs) play a major role in the flux dispersal process and are only associated with decaying sunspots (Harvey & Harvey 1973). The total flux carried by MMFs is several times higher than the flux contained within the sunspot itself. Thus, the polarity of MMFs has to be considered to ensure a balance of the net flux. The MMFs move radially outward with a velocity of 1 km s-1 before they reach and dissolve within the network, i.e., at the boundaries of the supergranular cell containing the sunspot. Zuccarello et al. (2009) presented evidence that MMFs and moat flow exist even in the vicinity of pores, i.e., in the absence of penumbral filaments and the Evershed flow (cf., Cabrera Solana et al. 2006). Deng et al. (2007) also detected a persistent moat flow after the penumbra around a spot had disappeared leaving only a pore. Even though the moat flow might not be closely tied to the Evershed flow, the sub-photospheric interaction of magnetic field lines and flows can still produce the observed flow patterns.
Verma & Denker (2011) described a local correlation tracking (LCT) method to measure horizontal flows based on Hinode G-band images. In present paper, we describe a case study that places these such horizontal flow fields in the context of other photospheric and chromospheric data. In particular, we are interested in the final stages of sunspot decay. In Sect. 2, we present a subset of multi-wavelengths observations obtained within the scope of Hinode Operation Plan (HOP) 0176. The temporal evolution of active region NOAA 11126 in terms of intensity, morphology, and flow as well as magnetic fields is described in Sect. 3 and discussed in Sect. 4.
Observing characteristics and physical parameters.
2. Observations
The disk passage of active region NOAA 11126 started on 2010 November 12 and ended on November 24. The sunspot group NOAA 11126 was classified as a β-region, while it crossed the solar disk. No major flaring was associated with the region. Only a few B-class events were reported on 2010 November 15. As part of HOP 0176 “High-resolution multi-wavelength study of small-scale jets on the solar disk”, we observed the decay of two small follower sunspots in the active region for five days from 2010 November 18–22. A time-series of Hinode G-band images is shown in Fig. 1, where we have labeled the northern and southern spots A and B, respectively. In the following, we simply refer to these magnetic features as spots, even if the proper classification should be pores, i.e., sunspots lacking a penumbra. Spectral scans with different field-of-views (FOVs) and cadences were observed for three hours every day. Since we focus only on the general properties of sunspot decay, we chose the first scan on the given day, which covered the largest FOV. The settings for the Vacuum Tower Telescope (VTT) echelle data and data of Hinode/Spectro-Polarimeter- were chosen as to ensure the optimal spatial and spectral match. The general observing characteristics are listed in Table 1.
2.1. SDO/HMI full-disk images
The discussion of the temporal evolution and morphology of the active region NOAA 11126 is based on full-disk images and line-of-sight (LOS) magnetograms obtained with the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI, Schou et al. 2012; Couvidat et al. 2012; Wachter et al. 2012) on board the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Since the Hinode FOV is too small to cover the entire active region and provide an overview of the magnetic field topology, we show in Fig. 2 the limb-darkening corrected HMI continuum image and magnetogram for November 18.
We selected from the SDO/HMI database one image/magnetogram with 4096 × 4096 pixels every 15 min for the period from 2010 November 13 − 23, i.e., a total of 1056 full-disk images. The image scale is about 0.5′′ pixel-1, so that even finer details of penumbra and umbra can be captured. The average limb-darkening function was computed for this time interval and subtracted from the full-disk images to yield contrast-enhanced images (see e.g., Denker et al. 1999), which can then be used for feature identification. The photometric temporal evolution for the entire active region shown in Fig. 2 is depicted in Fig. 3. The corresponding changes in the magnetic flux are shown in Fig. 4. Since HMI data cover the whole solar disk, it is straightforward to compute the heliocentric angle μ on a pixel-by-pixel basis. Thus, a geometrical correction is applied to the measured areas and the flux values of Figs. 3 and 4, which are discussed in detail in Sects. 3.1 and 3.5, respectively.
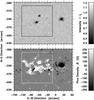 |
Fig. 2 Limb-darkening corrected HMI continuum image (top) and magnetogram (bottom) of active region NOAA 11126 on November 18. The square box in both images shows the FOV covered by Hinode/BFI. The axes are labeled in heliographic coordinates. |
2.2. Hinode G-band and Ca ii H images
 |
Fig. 3 Temporal evolution of the area covered by active region NOAA 11126 as it crossed the solar disk. The area enclosed by umbral cores and pores is displayed with a dashed line. Dashed dot dot line refers to the penumbra, whereas the solid line denotes the total area. Some smoothing was applied to the time-series to suppress features on temporal scales shorter than one hour. The vertical gray bars refer to the observing periods of HOP 0176 (2010 November 18 − 22). The labels indicate different stages of active region evolution, which are explained in Sect. 3.1. |
 |
Fig. 4 Temporal evolution of the magnetic flux contained in active region NOAA 11126 while it crossed the solar disk. The solid, dashed dot dot, and dashed lines refer to the total, positive, and negative flux, respectively. |
We applied LCT (for details see Verma & Denker 2011) to image sequences captured in G-band λ430.5 nm and Ca ii H λ396.8 nm to compare horizontal flows in the photosphere and chromosphere. The Ca ii H images do not purely represent the chromosphere, but contain contributions from both the upper photosphere and lower chromosphere. These observations were carried out by the Broad-band Filter Imager (BFI) of the Solar Optical Telescope (SOT, Tsuneta et al. 2008) on board Hinode (Kosugi et al. 2007). Data sequences were captured every day from 09:00 UT to 12:00 UT with an average time cadence of 120 s (with some jumps in the data sequences). At both wavelengths the images are 2 × 2-pixel binned with an image scale of 0.11′′ pixel-1. Images have a size of 1024 × 1024 pixels and a FOV of 111″ × 111″.
After basic data calibration, the images were corrected for geometrical foreshortening and resampled onto a regular grid of 80 km × 80 km. The signature of the five-minute oscillation was removed from the images by using a three-dimensional Fourier filter with a cut-off velocity of 8 km s-1 corresponding roughly to the photospheric sound speed. To measure horizontal proper motions, we applied the LCT algorithm described in Verma & Denker (2011), which computes cross-correlations over 32 × 32-pixel regions with a Gaussian kernel having a FWHM of 15 pixels (1200 km) corresponding to the typical size of a granule. In two aspects, we deviated from the aforementioned algorithm, the time cadence was Δt = 120 s and the flow maps were averaged over ΔT = 3 h.
2.3. Hα echelle spectra
The observations in Hαλ656.28 nm and Fe i λ656.92 nm were carried out with the VTT echelle spectrograph. Spectral data were acquired with a slit width of 80 μm and an exposure time of 300 ms. The image-scale of the spectrograph is 8.99″ mm-1. We did not use a predisperser, hence, to suppress overlapping in spectral orders, we placed a broad-band interference filter directly behind the spectrograph slit. The infrared grating with a blaze angle of 51.6° and 200 grooves mm-1 was used to record spectra in the 12th order. In this configuration, we achieved a dispersion of 0.60 pm pixel-1. The spectra covered a wavelength range of 1.2 nm from λ655.9 nm to λ657.1 nm. We employed a PCO.4000 CCD camera that has a quantum efficiency of about 30% at Hα. After 2 × 2-pixel binning the images have a size of 2004 × 1336 pixels. The pixel size of the CCD detector is 9 μm × 9 μm. The echelle data were intended to match the Hinode observations, which was mostly achieved except for a few interruptions caused by deteriorating seeing conditions. The two-dimensional FOV was scanned with a spatial step of 0.32′′ and 200 − 250 spectra were recorded in a sequence. A sequence of 240 spatial steps were taken over about 12 min and covered a FOV of 72.0″ × 182.6″.
The common FOVs of the G-band images and Hα echelle spectra are shown in Fig. 1 for each observing day. We first matched the image scale of the echelle data to that of the Hinode data. We then aligned Hinode G-band images and continuum images derived from echelle spectra. After this procedure, the heliocentric coordinates of the G-band images and Hα spectra differ by less than 1′′ in the periphery of the FOV. Furthermore, the Echelle scan direction is not perfectly aligned with the Hinode BFI detector. Hence, we computed an offset angle (smaller than ± 2°) for each date and applied it to the spectral data. On 2010 November 20, the time difference between G-band images and Echelle spectra was about five hours.
2.4. Hinode spectro-polarimeter
The photospheric magnetic topology and evolution of the active region were studied using high-resolution spectral data from the Hinode/Spectro-Polarimeter (SP, Ichimoto et al. 2008), which uses two magnetically sensitive Fe i lines at λ630.15 nm and λ630.25 nm and the nearby continuum (Tsuneta et al. 2008) to obtain Stokes IQUV spectral profiles. We used spectral data captured in the fast mapping mode with a FOV of 58″ × 122″ and an average scan time of 12 min. On November 18, we also used ten continuous high cadence scans with a FOV of 32″ × 123″ and a scan time of 7 min. The dispersion is about 2.155 pm pixel-1. The region was scanned with a spatial step of about 0.3′′ and image scale of 0.32′′ pixel-1. The basic data reduction steps such as subtraction of dark current, flat fielding, polarization, and wavelength correction were performed using procedures available in SolarSoft (SSW, Bentley & Freeland 1998; Freeland & Handy 1998).
3. Results
In the following sections, we present the evolution of the decaying sunspots in the photosphere and chromosphere, discuss the horizontal proper motions and line-of-sight velocities in their surroundings, and study changes of the magnetic fields with special emphasis on MMFs.
3.1. Photospheric evolution
Contrast-enhanced HMI full-disk continuum images were used to study the evolution and decay of the active region NOAA 11126 during its disk passage. The curves in Fig. 3 correspond to the areas of umbral cores/pores, penumbrae, and the sum of both types of features. These strong magnetic features are identified according to intensity thresholds of 75% and 92%, respectively, where the quiet Sun intensity was normalized to unity. Some spatial smoothing and minimum-size criteria were applied to binary masks of identified features using morphological image processing techniques, thus ensuring unwrinkled boundaries and contiguous structures. This algorithm only provides a rough estimate of the above areas. Some (small) features can be misclassified. In particular, the borders of pores are classified as penumbra.
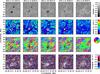 |
Fig. 5 G-band images (top) after correction of geometrical foreshortening tracing the photospheric evolution of the central part of active region NOAA 11126 (from left to right 2010 November 18 − 22). The horizontal flow speeds (2nd row) are given by the velocity scale to the right. The direction of the horizontal flows (3rd row) are displayed according to the color-wheel and arrows for which a velocity of 1 km s-1 corresponds to exactly the grid spacing. The divergence of the horizontal flow field (bottom) are presented according to the scale on the right, where gray indicates divergence values close to zero. All G-band images and LCT maps were aligned so that the center of the panels coincides with a latitude of 31.9° south. The white and black contours outline the location of the small sunspot/pores. Times refer to the first image of the time-series, which was used to compute the flow maps. |
The most important ten stages of the active region evolution are labeled in Fig. 3 and we now describe each one: (a) initially, two tightly spaced sunspots of positive polarity were present early on November 13. The leading spot was larger and had a well-established penumbra; (b) new flux emerged towards the south-east of these spots at 8:30 UT on November 14. Numerous (more than ten) magnetic knots and pores appeared to the south-west forming a bipolar magnetic region; (c) the umbral core of a leading sunspot of the new group was established at 2:00 UT on November 15; (d) the leading sunspot of the new group continuously grew by advecting magnetic knots and small pores. The umbral cores/pores occupied the largest area at 2:20 UT on November 16; (e) the penumbra of the leading spot reached its maximum about nine hours later. At this time, the active region NOAA 11126 started its decay phase; (f) some additional flux emergence occurred in the trailing part of the region at about 16:00 UT on November 17, which strengthened spot B and produced thin elongated dark lanes. These typical features of flux emergence (see e.g., Strous et al. 1996) were labeled erroneously as penumbrae by the thresholding algorithm. HOP 0176 focused on the two trailing spots/pores, of which the northern one (spot A) was already decaying, while the southern one (spot B) had just reached its maximum. This sunspot also showed strong indications of rotation; (g) this spot then fragmented into numerous magnetic knots until about 19:30 UT on November 19. At this time, the fragments started to converge again (h) forming a small sunspot, which reached its maximum at 8:00 UT on November 20. Interestingly, the northern pore faded away in parallel to this growth spurt; (i) most of the penumbra in the leading spot had disappeared by 5:00 UT on November 21; (j) finally, on November 23, all spots, pores, and magnetic knots had vanished, and only a bright plage region remained until it rotated off the visible hemisphere.
In summary and neglecting all details of active region evolution, active region decay rates can be computed using a linear fit to the time periods when the area-coverage reached its maximum to the point when the area fell below 5 Mm2. The overall decay rate of the active region is 72.6 Mm2 per day. The values for penumbrae and umbral cores/pores are 48.3 and 25.1 Mm2 per day, respectively. Similarly, we computed the growth rate of umbrae and penumbrae starting at 21:00 UT on November 14. The values are 171.4 and 104.8 Mm2 per day, respectively. This is about four times faster than the corresponding decay times but less than one half of the penumbral growth rate of about 400 Mm2 per day presented by Schlichenmaier et al. (2010).
Hinode G-band images allowed us to zoom into the two trailing spots. The region-of-interest (ROI) is shown in the top row of Fig. 5. The data of 2010 November 18–22 are corrected for geometrical foreshortening and the center-to-limb variation. The ROI with a size of 756 × 756 pixels or 60 Mm × 60 Mm was centered on a heliographic latitude of S31.9°. The first G-band image of the daily observing sequences was used as a reference to align all other data.
Various solar features were identified using intensity thresholds and morphological image processing. We indiscriminately used a fixed intensity threshold of Imag = 0.8I0 for strong magnetic features and an adaptive threshold for G-band bright points of Ibp = (1.37 − 0.08μ)I0, where μ is the cosine of the heliocentric angle θ, and I0 refers to the average quiet Sun intensity. Intensity values between Ibp and Imag consequently corresponds to granulation. The measured spot areas for HMI and Hinode agree with each other, and the remaining differences can be attributed to different spectral characteristics of the observed passbands, image scales, and threshold/selection criteria. In general, the temporal evolution within the ROI follows the same trend as discussed in the context of SDO observations (Fig. 3). The areas, velocities, and other physical quantities based on high-resolution data are included in Table 1.
In the following, we present a chronology of the important phases of sunspot decay based on the high-spatial resolution G-band images. On November 18, the two trailing sunspots were embedded in a network of G-band bright points,which are indicative of widely dispersed, weak magnetic fields. Both spots were filled with numerous umbral dots. Spot A consisted of three umbral cores separated by faint light bridges and a small penumbral segment pointing westward. Spot B had two umbral cores with a few associated magnetic knots. It possessed curved penumbral filaments pointing eastwards, which are indicative of twisted magnetic field lines. These non-radial penumbral filaments are frequently observed in flaring sunspots with horizontal shear flows (Denker et al. 2007; Deng et al. 2006). On November 19, the faint light-bridges had disappeared and the penumbra had vanished leaving only a single pore, which was filled with conglomerates of umbral dots. Spot B also lost its penumbra leaving four umbral cores separated by faint light-bridges, which, however, were more pronounced in comparison to the previous day. Magnetic knots still surrounded spot B. Spot A had decayed on November 20 with only two faint magnetic knots remaining at its location. At this point of time, spot B started to grow in area with hints of a penumbral filament being visible on its western side. It consisted of three umbral cores, which had been separated by strong light-bridges that divided the spot into two halves along its north-south axis. The presence of strong light-bridges suggests that this corresponds to the initiation of the spot’s decay phase (see Sobotka et al. 1993). Once spot A had disappeared on November 21, it did not leave any significant trace within the network of G-band bright points. By this time, spot B had dissolved into multiple tiny pores and magnetic knots, which roughly covered the same region as on the previous day. By November 22, only two tiny pores were left of spot B, which disappeared on November 23, leaving merely the G-band bright points at its point of disappearance. Two observations are noteworthy: (1) the area covered by the G-band bright points remained almost constant during the disk passage of the active region, which suggests that the flux decayed more or less in place and was not redistributed over a larger area. The time scale of flux removal or dispersal extends well beyond the photometric decay time of strong magnetic features such as sunspots, pores, and magnetic knots; (2) the two trailing spots have different histories of flux emergence and decay.
3.2. Chromospheric evolution
Our description of the chromospheric evolution is based on Hinode Ca ii H (top row of Fig. 6) and echelle Hα line core intensity maps (top row of Fig. 8). The Ca ii H images were averaged over three hours to highlight some of the long-lived chromospheric features. On November 18, the lower quarter of the Ca ii H image showed the undisturbed pattern of inverse granulation (Rutten et al. 2004). The Ca ii H brightenings cover a larger area, because their filling factor is significantly greater than that of the G-band bright points. Spot A was encircled by individual brightenings at a radial distance of 5 Mm. These individual brightenings coalesced into a wagon-wheel-like Ca ii H intensity structure in the three-hour average image pointing to the presence of MMFs. A similar feature was noticeable around a much smaller pore with a diameter of about 2 Mm located to the west of spot A. This conspicuous Ca ii intensity structure was first described by Shine et al. (1996), who identified the bright ridges with azimuthal convergence regions, whereas the dark regions between the spokes correspond to azimuthal divergence zones. Spot A resided in the middle of a supergranular cell with a diameter of about 20 Mm. In contrast, spot B was embedded in an area of much more pronounced Ca ii H brightenings. The exterior tips of its penumbral filaments appeared to be bright because a low-level B-class flare occurred at the time of observations.
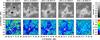 |
Fig. 6 Ca ii H average images tracing the evolution of active region NOAA 11126 in the chromosphere. The horizontal proper motions were derived from time-sequences of Ca ii H images. Otherwise, the data processing and display are the same as in Fig. 5. |
On November 19, the average Ca ii H image showed evidence that the moat flow around spot A survived the initial stages of sunspot decay, even after its penumbra had disappeared (see e.g., Deng et al. 2007). Spot A had completely dissolved by November 20. Assuming that spot A was located at the center of a supergranular cell as indicated by the surrounding Ca ii H brightenings on November 18 and 19, we conclude that this supergranular cell ceased to exist on November 20, when the strong magnetic fields of spot A where no longer present. The Ca ii H brightenings had been squeezed together by two supergranular cells to east and to the west, which could already be identified on November 19 and remained visible until November 22.
At the time when spot A vanished, spot B had already fragmented into two umbral cores, which were separated by a strong light-bridge with a noticeable dark lane along its axis (Rouppe van der Voort et al. 2010). This dark core was even more clearly discernible in the three-hour average Ca ii H image. The presence of strong light-bridge can be taken as a first indication of the spot entering the decay phase. During the next two days of November 21–22, spot B decayed yet further.
The Hα line core intensity map of November 18 exposed a radial pattern of fibrils around spot A that is reminiscent of a superpenumbra. Strong brightenings in the Hα line core in the vicinity of spot B are related to the aforementioned small B-class flare. We did not notice any significant Hα intensity features on the following days, except that after the decay of both spots the Hα plage became more prominent. By the end of our observations with the echelle spectrograph, only a very compact plage region with a length of about 8 Mm remained within ROI.
3.3. Horizontal proper motions
The LCT flow maps displayed in Figs. 5 and 6 were computed using the time-sequence of Hinode G-band and Ca ii H images. As mentioned in Sect. 3.1, we distinguished various solar features (e.g., G-band bright points, granulation, strong magnetic features, and sunspot penumbrae) by applying some morphological and adaptive thresholding. For comparison, we referred to the typical flow speeds of granulation vgran = 0.47 ± 0.27 km s-1 and G-band bright points vbp = 0.23 ± 0.15 km s-1 as reported by Verma & Denker (2011), who also presented values for longer time intervals ΔT (Table 1 therein) and cadences Δt (Fig. 3 therein). Their values for granulation are in very good agreement with the mean values 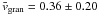 km s-1 of the present study. The mean values for bright points
km s-1 of the present study. The mean values for bright points 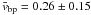 km s-1 in the neighborhood of active region NOAA 11126 are within the range of expected values. Daily values of flow speeds for granulation and G-band bright points are given in Table 1. The standard deviation in the aforementioned horizontal flow speeds refers to the variance in the data for a particular solar feature rather than to a formal error. The intrinsic error in the LCT algorithm is 50 m s-1 and 15° for flow speed and direction, respectively (see Verma & Denker 2011).
km s-1 in the neighborhood of active region NOAA 11126 are within the range of expected values. Daily values of flow speeds for granulation and G-band bright points are given in Table 1. The standard deviation in the aforementioned horizontal flow speeds refers to the variance in the data for a particular solar feature rather than to a formal error. The intrinsic error in the LCT algorithm is 50 m s-1 and 15° for flow speed and direction, respectively (see Verma & Denker 2011).
We computed the flow vectors for strong magnetic elements, i.e., spots A and B. We identified spots by smoothing the geometrically corrected G-band images using a Gaussian kernel with a FWHM of 1280 km and subsequently applied an intensity threshold of 0.83I0. We plotted contours based on these binary masks in Figs. 5 and 6 to provide some visual guidance in identifying the spot positions in the physical maps. The mean flow speeds 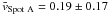 km s-1 and
km s-1 and 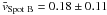 km s-1 are virtually identical for both spots. While computing the mean velocity
km s-1 are virtually identical for both spots. While computing the mean velocity 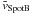 for spot B, we discarded the data acquired on November 22, because on that day only a tiny pore with a diameter of 4 Mm was left at the location of spot B. Therefore, adjacent regions with G-band bright points and granulation could bias the flow speed towards higher values. The overall flow pattern for the Ca ii H data is very similar to that for the G-band data, and the average values
for spot B, we discarded the data acquired on November 22, because on that day only a tiny pore with a diameter of 4 Mm was left at the location of spot B. Therefore, adjacent regions with G-band bright points and granulation could bias the flow speed towards higher values. The overall flow pattern for the Ca ii H data is very similar to that for the G-band data, and the average values 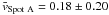 km s-1 and
km s-1 and 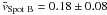 km s-1 are virtually identical with a tendency to be slightly lower on individual days.
km s-1 are virtually identical with a tendency to be slightly lower on individual days.
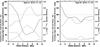 |
Fig. 7 Radial dependence of parameters characterizing the flow fields of spots A (left) and B (right). Radial distances are measured from the outer boundary of the spots, i.e., 0.0 Mm marks the transition from penumbra to granulation. The thick black curves indicate the average angle of horizontal flow vectors with respect to the outward radial direction. High values refer to inward flows and low values indicate outward flow vectors. Fractions of in-/out-ward flow vectors as defined in the text are shown as dash-dotted and dashed lines, respectively. The horizontal straight lines denotes the 100%level. The average flow speed is displayed as a dash-dot-dot-dotted line. |
The moat flow around sunspots and pores reveals itself as radially, outward-directed vectors in flow maps, which point to a ring-like structure with kernels of elevated flow speeds. In the speed and azimuth maps on November 18 and 19 (Figs. 5 and 6), indications of moat flow were visible around spot A and a small pore located to the west of spot A. No clear signature of the moat flow could be detected around spot B. To express the characteristics of the moat flow in more quantitative terms, we plotted in Fig. 7 the angle of the flow vectors, the fraction of in- and outward flow vectors, and the horizontal velocities for spots A and B. These quantities are radial averages and the zero point of the radial distance was placed at the penumbra/granulation boundary of the spots. We considered a flow vector to point either inward or outward depending on whether, if the tip of the arrow aims in-/out-ward and the angle with the radial direction is less than 20°. Therefore, the fractions of in-/outward flow vectors presented in Fig. 7 do not add up to 100%, since more tangential flows are neglected. At a radial distance of 6 ± 2 Mm from the boundary of spot A, more than 50% of the flow vectors point outward. The average flow speed in this region is about 0.5 km s-1. The region with high-speed outward flows marks the location where the moat flow around spot A terminates. An exact determination of where the moat flow starts and where it ends depends strongly on the underlying criteria, e.g., photometric or magnetic features, or horizontal proper motions. In Sect. 3.5, we discuss some properties of the moat flow based on the proper motions of MMFs. Sobotka & Roudier (2007) determined that the moat radius is independent of the spot size. However, Balthasar & Muglach (2010) found that the moat flow terminates at a distance of four times the spot radius – in contrast to three times the spot radius in the present study. Extended statistical studies will help us to clarify this issue.
We created two ring-like structures by performing morphological dilation of width 4 Mm that encircled both spots at a distance of 2 Mm. This ring-like structure starts, where inflows turn to outflows 2 Mm beyond the boundary of spot A, and terminates where the outflows reach the highest speed. We used these templates to calculate the flows in the immediate neighborhood of spots A and B. These regions were labeled rings A and B. The velocities in these regions are included in Table 1. The flow speed vRing A was more than double than that of vSpot A because of the suppressed convective motions in the spot’s interior. The flow speeds in the immediate vicinity of spot B was higher by 30–40% on November 18 and 19. However, on November 22 during the final decay stage of spot B, no major difference between the spot and its closest surroundings was observed.
 |
Fig. 8 VTT Echelle spectra were used to study the chromospheric evolution of active region NOAA 11126 during the period from 2010 November 18 − 22. The chromospheric fibril structure surrounding the decaying sunspots can be traced in Hαλ656.28 nm line core intensity (top) and LOS velocity (middle) maps. In addition, photospheric LOS velocities (bottom) were derived from Hinode/SP Fe i λ630.25 nm spectra. The FOV matches those of Figs. 5 and 6. Regions not covered by the spectral data are shown in medium gray. The times above the panels refers to the start of a spectral scan. |
To effectively visualize the plasma motions, we presented high resolution maps of flow speed and azimuth (see Figs. 5 and 6). The speed maps of G-band and Ca ii H images are virtually same. The region with G-band bright points exhibits had systematically smaller velocities in both cases. The regions around spot A and the small pore to the west are surrounded by a ring of systematically large velocities (around 0.5 km s-1) where the ordered moat flow terminates. In the azimuth maps of November 18 and 19, outward plasma motions are traceable in these regions. In addition, to gain more insight into inflows and outflows around the spots we computed the divergence of the flow field. The divergence maps are included in the bottom row of Fig. 5. The positive values of divergence refer to outflows, whereas negative values indicate inflows. Negative divergence values are encountered within the boundaries of the sunspots. In contrast, small patches of positive divergence encircle the spots. This is indicative of inflows in the sunspots and outflows at their periphery. The area with low divergence values increases in size as the active region decays. The presence of a low divergence region could be a signature of the final stages of decay.
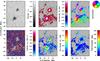 |
Fig. 9 Maps of physical parameters derived using SIR-code for Hinode/SP scan on 2010 November 18 (from top-left to bottom-right) normalized intensity I/I0, vertical component of magnetic flux density Bz, magnetic field azimuth φ, Doppler velocity vLOS, horizontal component of magnetic flux density Bhor, and magnetic field inclination γ. |
3.4. Line-of-sight velocities
The LOS velocities were derived using Hinode/SP Fe i spectral data and Hα spectra of the VTT Echelle spectrograph. The LOS velocities for the Fe i spectral line were calculated using the Fourier phase method (Schmidt et al. 1999). This method uses the entire line profile, is less sensitive to noise, and takes into account the spectral line asymmetry. To compute the LOS velocity for Hα spectra, we calculated shifts using parabola fits to the central 50 pixels (0.03 nm), because the Hα spectral line is too wide to identify the real continuum. The calculated shifts in both cases were converted to velocities using the Doppler formula. The average photospheric velocity of dark umbral cores was used as the frame of reference. The Fe i λ656.92 nm line served as the reference for the Hα velocities. The Doppler velocity maps are displayed in the bottom and middle rows of Fig. 8. Redshifts in these maps are positive and blueshifts are negative, hence areas moving away from the observer are bright, while areas moving toward the observer are dark.
To compute velocities for various solar features, we used an intensity mask generated using G-band images. The values are compiled in Table 1. On November 18 and 20 in the Fe i Doppler velocity maps, strong photospheric downflows were observed at the edges of spot B. The average downflow velocity in these regions is about 2.5 km s-1. In all maps, a gray patch of near zero velocity was observed in the central FOV, which became more prominent on the last two days of observation. We identify this region with abnormal granulation (see e.g., de Boer & Kneer 1992), in which convection is still strongly inhibited by the presence of (dispersed) magnetic fields.
In case of Hα LOS velocities, no conspicuous features were visible in the velocity maps, except on November 18 when we observed a radial filamentary structure around spot A in Hα line core intensity maps, which resembled a superpenumbra. At the footpoints of the dark Hα filaments, we measured downflows from about 3.5 up to 4.5 km s-1, which we interpreted as an inverse Evershed flow (Maltby 1975). Tightly wound superpenumbral spirals are only predicted for spots with radii larger than 8 Mm, whereas spot A was compact with a radius of 4 Mm. The downward chromospheric velocities at the edge of spot A are compatible with the MHD model of superpenumbral flows presented by Peter (1996).
3.5. Magnetic fields
In addition to the photometric evolution shown in Fig. 3, we also computed the flux contained in the active region as shown in Fig. 4. Since only HMI LOS magnetograms were available (processing of the vector magnetograms is still under way). We took the measured magnetic field strength at face value and only carried out a geometrical correction to yield the proper average values of the magnetic flux. The geometrical correction only applies to the surface area covered by a pixel, which can simply be achieved by dividing the magnetic field strength by μ = cosθ. Signatures of geometric projection effects can be seen when the active region was close to the east limb, and the angle between LOS and shallow penumbral field lines causes an apparent polarity reversal. Consequently, the positive and negative flux gradients have opposite signs, while the total flux remained almost constant for the first 30 h until projection effects become less severe. To compute the temporal evolution of magnetic flux, we created a binary template, which only contained pixels above/below ± 50 Gauss in the HMI magnetograms. Morphological erosion with a 1-Mm kernel was applied to the template three times to eliminate small, isolated flux concentrations. Finally, we used morphological dilation with a 5-Mm kernel to include the strong magnetic fields in the immediate neighborhood of active region NOAA 11126. In this way, we avoided any bias being introduced by weak magnetic fields, which do not belong to the active region but are contained within the FOV shown in Fig. 2.
The growth rates of the magnetic flux are 2.66, 1.98, and 1.09 × 1013 Wb day-1 for the total, positive, and negative flux, respectively. The negative flux underwent a monotonic rise until about 06:00 UT on November 16, whereas the positive flux increased with a slope twice as steep, stopped a day earlier, and turned to a shallower slope until the end of November 17. On average the positive flux was three times higher than the negative one. However, using adaptive thresholding and morphological image processing tools, we only measured the flux in the immediate vicinity of the sunspots. The missing negative flux required for flux balance has to be contained in flux concentration beyond the immediate neighborhood of the sunspots. The decay rates of the magnetic flux are four to five times lower than the growth rates and amount to 0.66, 0.47, and 0.23 × 1013 Wb day-1 for the total, positive, and negative flux, respectively. A linear fit to the data was used and despite some deviations from a linear trend, there is no indication of a parabolic (or any other) decay law. The decay rates of the present study agree with those of Kubo et al. (2008), who reported rates on the order of 1013 Wb day-1 and discussed the magnetic-flux loss rate in a decaying active region.
The SIR(Stokes Inversion based on Response functions)-code developed by Ruiz Cobo & del Toro Iniesta (1992) was used to invert the Hinode/SP spectra. We restricted ourselves to the more sensitive line Fe iλ630.25 nm (geff = 2.5). The starting model covered the optical depth range + 1.0 ≤ log τ ≤ − 4.4. A limb-darkening factor was considered according to Eq. (10) of Pierce & Slaughter (1977). We assumed a constant macroturbulence of 1 km s-1 and a fixed straylight contribution of one percent. The inversions delivered the temperature stratification with four nodes T(τ), the total magnetic flux density Btot, the magnetic inclination γ and azimuth φ, and the Doppler velocity vLOS that is constant with height (one node for each of these physical parameters).
The magnetic azimuth ambiguity had to be solved after the inversions. For the first two days when we observed two major pores/small sunspots, we assumed two azimuth centers (see Balthasar 2006). For the other days, it was sufficient to assume that there is one azimuth center away from the pores in the direction of the disk center. The magnetic field in these small pores is more or less vertical to the solar surface such that on these days the field was sufficiently inclined with respect to the LOS for such an assumption to be justified. If the expected azimuth φ deviated by more than 90° and less than 270° from the calculated one, we corrected it by 180°. Finally, we rotated the magnetic vector with respect to the local solar frame. For a few locations, there was a sudden change in the sign of the cartesian components of the magnetic vector. This problem was solved by an additional correction to the LOS-azimuth. To be on the safe side, we applied to the data of November 18 the code provided by Leka et al. (2009), which minimizes |Jz| + |∇B| to solve the azimuth ambiguity. Pixels for which the integrated circular and the integrated linear polarization were below 0.006, were excluded from any further analysis of the magnetic field. We finally used the magnetic vector field in the local solar frame. The results of the SIR-inversion for November 18 are depicted in Fig. 9.
The vertical magnetic flux density Bz in the ROI was predominantly positive and pointed outwards. The only significant patches of negative polarity were found on November 18 on the eastern side of spot B. Penumbral filaments connected spot B to several magnetic knots of negative polarity. In addition, we measured Evershed flows with velocities vLOS > 2 km s-1. On smaller spatial scales, we found MMFs in the vicinity of spot A. They were mostly of type II (unipolar with the same polarity as the spot) but a few scattered U-shaped type I MMFs (bipolar with the inner footpoint of opposite polarity of the spot) were observed as well. No type I MMFs were observed near spot B.
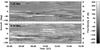 |
Fig. 10 Space-time slices showing the temporal evolution of the magnetic flux along annuli with radii of 5.75 Mm (bottom) and 7.25 Mm (top), respectively, which are centered on spot A. HMI magnetograms with a cadence of 45 s covered a period of 12 h starting at 04:00 UT on 2010 November 18. The annulus with a width of 0.5 Mm was cut open in the east and then transformed to a straight line such that the southern part of the spot was mapped to the lower half of the space-time map. The heliographic direction is indicated on the axis to the right. |
Since the time cadence of Hinode/SP scans is about 12 min, we used SDO/HMI magnetograms with a cadence of 45 s to study the dynamics of MMFs. Space-time slices were a possible option for visualizing local changes in the magnetic flux in a time-series. The continuous coverage of HMI magnetograms allowed us to depict in Fig. 10 the temporal evolution of the magnetic flux around spot A during a 12-h period on 2010 November 18. The magnetic flux changes were recorded within two 0.5-Mm wide annuli of 5.75 Mm (bottom panel) and 7.25 nm (top panel) radius, respectively. The linear scale of the the ordinate in Fig. 10 is 38 Mm and 47 Mm for the inner and outer rings, respectively. The inner ring corresponds to the location, where the strongest outflows were observed (see Fig. 7). The outer ring marks the site, where the largest fraction (about 8%) of the annulus was covered by negative-polarity features.
Within a radial distance of 4–10 Mm from the center of spot A, only about 5% of the magnetic flux observed during a 12-h period was of negative polarity. Negative-polarity MMFs were weaker by about 20% compared to MMFs of opposite polarity. Negative flux elements were most prominent in the southern half of spot A and absent in the northern half. The most notable difference between positive- and negative-polarity features was in terms of their morphology. Negative-polarity features can be tracked in space-time slices for only about 15 − 30 min, i.e., they were strongly localized. Time-lapse movies show that these negative-polarity features were mostly type I MMFs. The positive polarity appeared first in the space-time slices (to the left) followed by the negative polarity. The appearances of the positive-polarity features were very different. Horizontal striation could be seen for several hours. They at times abruptly (dis-)appeared and in a few cases we detected merging as well as splitting of the striae. In time-lapse movies, type II MMFs can be seen moving away from spot A along radial paths on top of a background of positive flux.
The temporal variation in the magnetic flux above/below the local background is given by Bvar = ⟨ |B − ⟨ B ⟩ | ⟩ , where ⟨ ... ⟩ indicates a temporal average. To compute the temporal average in Fig. 11, we used the same 12-h time-series of HMI magnetograms that was used to create Fig. 10. The strongest changes occur at the periphery of spot A, where the horizontal magnetic field Bhor was also at its strongest as can be seen in Fig. 9. This correspondence also applied to the strong horizontal field to the north-east of spot A, which belongs to the (chromospheric) network. The most notable features in Fig. 11 are, however, several spoke-like structures with a length of about 10 Mm that extend from spot A all the way out to the border of the supergranule surrounding the spot. These elongated structures are the signatures of MMFs streaming from the spot along identical paths (Harvey & Harvey 1973) towards the supergranular boundary. However, the distance traveled is much shorter as Harvey & Harvey (1973) observed for mature sunspots. Therefore, we conclude that the preferred paths of MMFs are a phenomenon that can be observed even in the final stages of sunspot decay. The traces left by MMFs in the variance in the magnetic field around its background Bvar are most prominent on the eastern side of the spot. They also match the wagon-wheel structure discussed in the context of the time-averaged Ca ii H images in Sect. 3.2. Finally, the preference of MMFs for distinct radial channels connecting the sunspots’ magnetic fields to the strong network fields was also noticed by Hagenaar & Shine (2005).
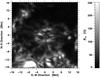 |
Fig. 11 Local, background-subtracted variation in the magnetic flux Bvar around spot A on 2010 November 18. |
Maps similar to Fig. 9 were computed for each day so that we could study the evolution of the magnetic field. The strongest horizontal magnetic flux densities Bhor were observed in the immediate surroundings of spots A and B as long as the spots were compact (November 18 and 19). They symmetrically enclose the entire boundary of the spots. Once spot A had disappeared and spot B had started to fragment, this symmetry was clearly broken most on November 20, when strong horizontal fields were present at the western side of spot B. This corresponds to a time when a rudimentary penumbra was present. Whenever indications of penumbral filaments were observed during the decay of the sunspots, inclined magnetic field lines and Evershed flows were present at the same time (cf., Leka & Skumanich 1998; Yang et al. 2003).
The magnetic field lines spread out symmetrically from the center of the spots on November 18 and 19. Similar well-defined azimuth centers could still be found in the later decay stages of spot B. Nevertheless these region were no longer circular and become elongated. Smaller azimuth centers were also observed to the east of spot B on November 19. These centers were associated with several magnetic knots.
The Doppler velocity vLOS was clearly smaller in the presence of strong magnetic features. From November 20, the velocity pattern associated with the magnetic fields started to change. Positive Doppler velocities occupied more and more of the magnetic region. This coherent pattern was also observed in the divergence maps (bottom row of Fig. 5) and the horizontal flow maps (Figs. 5 and 6). Since the region was approaching the limb, some of the Doppler velocities can be interpreted as a coherent proper motion of the magnetic region towards the south-west (cf. the azimuth maps of the horizontal proper motions). In summary, during the final stages of sunspot decay, the three-dimensional flow field, in regions previously occupied by strong magnetic fields, differed significantly from granular flow patterns or regions of reduced velocities in the presence of G-band bright points. Since we have presented only a case study, the question remains whether this intriguing flow pattern is a typical feature of sunspot decay.
4. Conclusions
We have presented a detailed account of the final stages of the decay of the active region NOAA 11126, which did not obey the Hale-Nicholson polarity law (e.g., Zirin 1988). Since only one in ten active regions display such a behavior (Howard 1990) and we have presented only a case study, our results might not be representative of sunspot decay in general. However, space missions such as Hinode and SDO provide data of sufficient coverage, resolution, and cadence to determine the statistical properties of sunspot decay. Furthermore, previous studies of non-Hale regions (e.g., López Fuentes et al. 2000, and references therein) were centered on flux emergence, δ-spots, and strong solar flares. The present study can consequently be considered as an extension of these studies that focuses on a much quieter magnetic field topology, which might be representative of the lower solar activity during cycle No. 24 (Petrovay 2010; Nielsen & Kjeldsen 2011).
The major findings of our study can be summarized as follows. The MMFs were observed in the vicinity of spot A until it decayed. Type II and a few interspersed U-shaped type I MMFs contributed in particular to the observed moat flow, which also left a clear signature in the time-averaged Ca ii H images (Martínez Pillet 2002). Even though penumbral filaments had almost completely disappeared in the photospheric G-band images of spot A on November 18, Hα line core images clearly exhibited a structure reminiscent of a superpenumbra. Thus, filamentary structures including the inverse Evershed flow (Maltby 1975; Georgakilas & Christopoulou 2003) might be more persistent in the chromosphere. We have also observed MMFs in the vicinity of a tiny pore with a diameter of about 2 Mm, which did not show any evidence of penumbral filaments. This observation argues strongly against a close tie between Evershed flows and MMFs (cf., Vargas Domínguez et al. 2008, 2010; Cabrera Solana et al. 2006).
On the basis of MHD simulations of sunspots, Rempel (2011) argued that penumbral flows can be separated into two components, where the shallow one corresponds to the Evershed flow and the deeper one is related to moat flow. The strong rotation and twist that we have detected in spot B might explain why this trailing spot never advected sufficient magnetic flux to establish more than a rudimentary penumbra and remained highly fragmented during its entire life cycle. The photospheric and chromospheric maps of horizontal flows displayed a peculiar pattern, once the last dark feature of the active region had disappeared. In general, the flow field in this region was less structured than regions covered by granulation, i.e., the dispersed magnetic field still significantly affected the convective pattern. Chromospheric flows have increased notably compared to times when spots and pores were still present. Most prominently, a contiguous area of low divergence appeared towards the end of the sunspot decay.
Acknowledgments
Hinode is a Japanese mission developed and launched by ISAS/JAXA, collaborating with NAOJ as a domestic partner, NASA and STFC (UK) as international partners. Scientific operation of the Hinode mission is conducted by the Hinode science team organized at ISAS/JAXA. This team mainly consists of scientists from institutes in the partner countries. Support for the post-launch operation is provided by JAXA and NAOJ (Japan), STFC (UK), NASA, ESA, and NSC (Norway). The SDO/HMI images are provided by the Joint Science Operations Center (JSOC) Science Data Processing (SDP). The Vacuum Tower Telescope at the Spanish Observtorio del Teide of the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias is operated by the German consortium of the Kiepenheuer-Institut für Sonnenphysik in Freiburg, the Leibniz-Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam, and the Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung
in Katlenburg-Lindau. M.V. expresses her gratitude for the generous financial support by the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD) in the form of a PhD scholarship. C.D. was supported by grant DE 787/3-1 of the German Science Foundation (DFG). C.L. and H.W. were supported by NSF grants AGS 08-19662 and AGS 08-49453, and NASA grants NNX 08AQ90G and NNX 08AJ23G. N.D. was supported by NASA grant NNX 08AQ32G. The authors would like to thank Drs. Alexandra Tritschler and Klaus G. Puschmann as well as the referee Dr. Luis Bellot Rubio for carefully reading the manuscript and providing ideas, which significantly enhanced the paper.
References
- Balthasar, H. 2006, A&A, 449, 1169 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Balthasar, H., & Muglach, K. 2010, A&A, 511, A67 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Bellot Rubio, L. R., Tritschler, A., & Martínez Pillet, V. 2008, ApJ, 676, 698 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley, R. D., & Freeland, S. L. 1998, in Crossroads for European Solar and Heliospheric Physics, Recent Achievements and Future Mission Possibilities, ESA Spec. Publ., 417, 225 [Google Scholar]
- Bumba, V. 1963, Bull. Astron. Inst. Czech., 14, 91 [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera Solana, D., Bellot Rubio, L. R., Beck, C., & del Toro Iniesta, J. C. 2006, ApJ, 649, L41 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Couvidat, S., Schou, J., Shine, R. A., et al. 2012, Sol. Phys., 275, 285 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer, C. R., & Kneer, F. 1992, A&A, 264, L24 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Deng, N., Xu, Y., Yang, G., et al. 2006, ApJ, 644, 1278 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Deng, N., Choudhary, D. P., Tritschler, A., et al. 2007, ApJ, 671, 1013 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Denker, C., Johannesson, A., Marquette, W., et al. 1999, Sol. Phys., 184, 87 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Denker, C., Deng, N., Tritschler, A., & Yurchyshyn, V. 2007, Sol. Phys., 245, 219 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Freeland, S. L., & Handy, B. N. 1998, Sol. Phys., 182, 497 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Georgakilas, A. A., & Christopoulou, E. B. 2003, ApJ, 584, 509 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenaar, H. J., & Shine, R. A. 2005, ApJ, 635, 659 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, K., & Harvey, J. 1973, Sol. Phys., 28, 61 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Howard, R. F. 1990, Sol. Phys., 126, 299 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Ichimoto, K., Lites, B., Elmore, D., et al. 2008, Sol. Phys., 249, 233 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kosugi, T., Matsuzaki, K., Sakao, T., et al. 2007, Sol. Phys., 243, 3 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo, M., Lites, B. W., Shimizu, T., & Ichimoto, K. 2008, ApJ, 686, 1447 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Leka, K. D., & Skumanich, A. 1998, ApJ, 507, 454 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Leka, K. D., Barnes, G., Crouch, A. D., et al. 2009, Sol. Phys., 260, 83 [Google Scholar]
- López Fuentes, M., Demoulin, P., Mandrini, C. H., & van Driel-Gesztelyi, L. 2000, ApJ, 544, 540 [Google Scholar]
- Maltby, P. 1975, Sol. Phys., 43, 91 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez Pillet, V. 2002, AN, 323, 342 [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, F., Schmidt, H. U., Wilson, P. R., & Weiss, N. O. 1974, MNRAS, 169, 35 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, M. L., & Kjeldsen, H. 2011, Sol. Phys., 270, 385 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Peter, H. 1996, MNRAS, 278, 821 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovay, K. 2010, Liv. Rev. Sol. Phys., 7, 6 [Google Scholar]
- Petrovay, K., & van Driel-Gesztelyi, L. 1997, Sol. Phys., 176, 249 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce, A. K., & Slaughter, C. D. 1977, Sol. Phys., 51, 25 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Rempel, M. 2011, ApJ, 729, 5 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Rouppe van der Voort, L., Bellot Rubio, L. R., & Ortiz, A. 2010, ApJ, 718, L78 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Rucklidge, A. M., Schmidt, H. U., & Weiss, N. O. 1995, MNRAS, 273, 491 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz Cobo, B., & del ToroIniesta, J. C. 1992, ApJ, 398, 375 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Rutten, R. J., de Wijn, A. G., & Sütterlin, P. 2004, A&A, 416, 333 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Schlichenmaier, R., Rezaei, R., Bello González, N., & Waldmann, T. A. 2010, A&A, 512, L1 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, W., Stix, M., & Wöhl, H. 1999, A&A, 346, 633 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Schou, J., Borrero, J. M., Norton, A. A., et al. 2012, Sol. Phys., 275, 327 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Shine, R. A., Title, A., Frank, Z., & Scharmer, G. 1996, Bull. Am. Astron. Soc., 28, 871 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Sobotka, M., & Roudier, T. 2007, A&A, 472, 277 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Sobotka, M., Bonet, J. A., & Vazquez, M. 1993, ApJ, 415, 832 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Strous, L. H., Scharmer, G., Tarbell, T. D., Title, A. M., & Zwaan, C. 1996, A&A, 306, 947 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuneta, S., Ichimoto, K., Katsukawa, Y., et al. 2008, Sol. Phys., 249, 167 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Vargas Domínguez, S., Rouppe van der Voort, L., Bonet, J. A., et al. 2008, ApJ, 679, 900 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Vargas Domínguez, S., de Vicente, A., Bonet, J. A., & Martínez Pillet, V. 2010, A&A, 516, A91 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Verma, M., & Denker, C. 2011, A&A, 529, A153 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Wachter, R., Schou, J., Rabello-Soares, M. C., et al. 2012, Sol. Phys., 275, 261 [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G., Xu, Y., Wang, H., & Denker, C. 2003, ApJ, 597, 1190 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Zirin, H. 1988, Astrophysics of the Sun [Google Scholar]
- Zuccarello, F., Romano, P., Guglielmino, S. L., et al. 2009, A&A, 500, L5 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
All Tables
All Figures
 |
Fig. 1 Calibrated Hinode G-band images showing the decay of active region NOAA 11126 observed during the period 2010 November 18 − 23 (from top-left to bottom-right). The FOV is 111″ × 111″. The annotation of the axes refers to heliocentric coordinates given in seconds of arc. Brighter areas delineated by vertical black lines correspond to regions, which were covered by spectral scans obtained with the VTT echelle spectrograph. The intensity scale to the right applies to these regions, while areas not covered by echelle data are displayed with an offset of 0.1I0. On 2010 November 23, only few Hinode G-band images were available. The limb darkening was subtracted from the G-band images, which were then normalized so that the mean of the quiet Sun intensity distribution corresponds to unity. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 2 Limb-darkening corrected HMI continuum image (top) and magnetogram (bottom) of active region NOAA 11126 on November 18. The square box in both images shows the FOV covered by Hinode/BFI. The axes are labeled in heliographic coordinates. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 3 Temporal evolution of the area covered by active region NOAA 11126 as it crossed the solar disk. The area enclosed by umbral cores and pores is displayed with a dashed line. Dashed dot dot line refers to the penumbra, whereas the solid line denotes the total area. Some smoothing was applied to the time-series to suppress features on temporal scales shorter than one hour. The vertical gray bars refer to the observing periods of HOP 0176 (2010 November 18 − 22). The labels indicate different stages of active region evolution, which are explained in Sect. 3.1. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 4 Temporal evolution of the magnetic flux contained in active region NOAA 11126 while it crossed the solar disk. The solid, dashed dot dot, and dashed lines refer to the total, positive, and negative flux, respectively. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 5 G-band images (top) after correction of geometrical foreshortening tracing the photospheric evolution of the central part of active region NOAA 11126 (from left to right 2010 November 18 − 22). The horizontal flow speeds (2nd row) are given by the velocity scale to the right. The direction of the horizontal flows (3rd row) are displayed according to the color-wheel and arrows for which a velocity of 1 km s-1 corresponds to exactly the grid spacing. The divergence of the horizontal flow field (bottom) are presented according to the scale on the right, where gray indicates divergence values close to zero. All G-band images and LCT maps were aligned so that the center of the panels coincides with a latitude of 31.9° south. The white and black contours outline the location of the small sunspot/pores. Times refer to the first image of the time-series, which was used to compute the flow maps. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 6 Ca ii H average images tracing the evolution of active region NOAA 11126 in the chromosphere. The horizontal proper motions were derived from time-sequences of Ca ii H images. Otherwise, the data processing and display are the same as in Fig. 5. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 7 Radial dependence of parameters characterizing the flow fields of spots A (left) and B (right). Radial distances are measured from the outer boundary of the spots, i.e., 0.0 Mm marks the transition from penumbra to granulation. The thick black curves indicate the average angle of horizontal flow vectors with respect to the outward radial direction. High values refer to inward flows and low values indicate outward flow vectors. Fractions of in-/out-ward flow vectors as defined in the text are shown as dash-dotted and dashed lines, respectively. The horizontal straight lines denotes the 100%level. The average flow speed is displayed as a dash-dot-dot-dotted line. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 8 VTT Echelle spectra were used to study the chromospheric evolution of active region NOAA 11126 during the period from 2010 November 18 − 22. The chromospheric fibril structure surrounding the decaying sunspots can be traced in Hαλ656.28 nm line core intensity (top) and LOS velocity (middle) maps. In addition, photospheric LOS velocities (bottom) were derived from Hinode/SP Fe i λ630.25 nm spectra. The FOV matches those of Figs. 5 and 6. Regions not covered by the spectral data are shown in medium gray. The times above the panels refers to the start of a spectral scan. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 9 Maps of physical parameters derived using SIR-code for Hinode/SP scan on 2010 November 18 (from top-left to bottom-right) normalized intensity I/I0, vertical component of magnetic flux density Bz, magnetic field azimuth φ, Doppler velocity vLOS, horizontal component of magnetic flux density Bhor, and magnetic field inclination γ. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 10 Space-time slices showing the temporal evolution of the magnetic flux along annuli with radii of 5.75 Mm (bottom) and 7.25 Mm (top), respectively, which are centered on spot A. HMI magnetograms with a cadence of 45 s covered a period of 12 h starting at 04:00 UT on 2010 November 18. The annulus with a width of 0.5 Mm was cut open in the east and then transformed to a straight line such that the southern part of the spot was mapped to the lower half of the space-time map. The heliographic direction is indicated on the axis to the right. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 11 Local, background-subtracted variation in the magnetic flux Bvar around spot A on 2010 November 18. |
| In the text | |
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


