Fig. 8.
Download original image
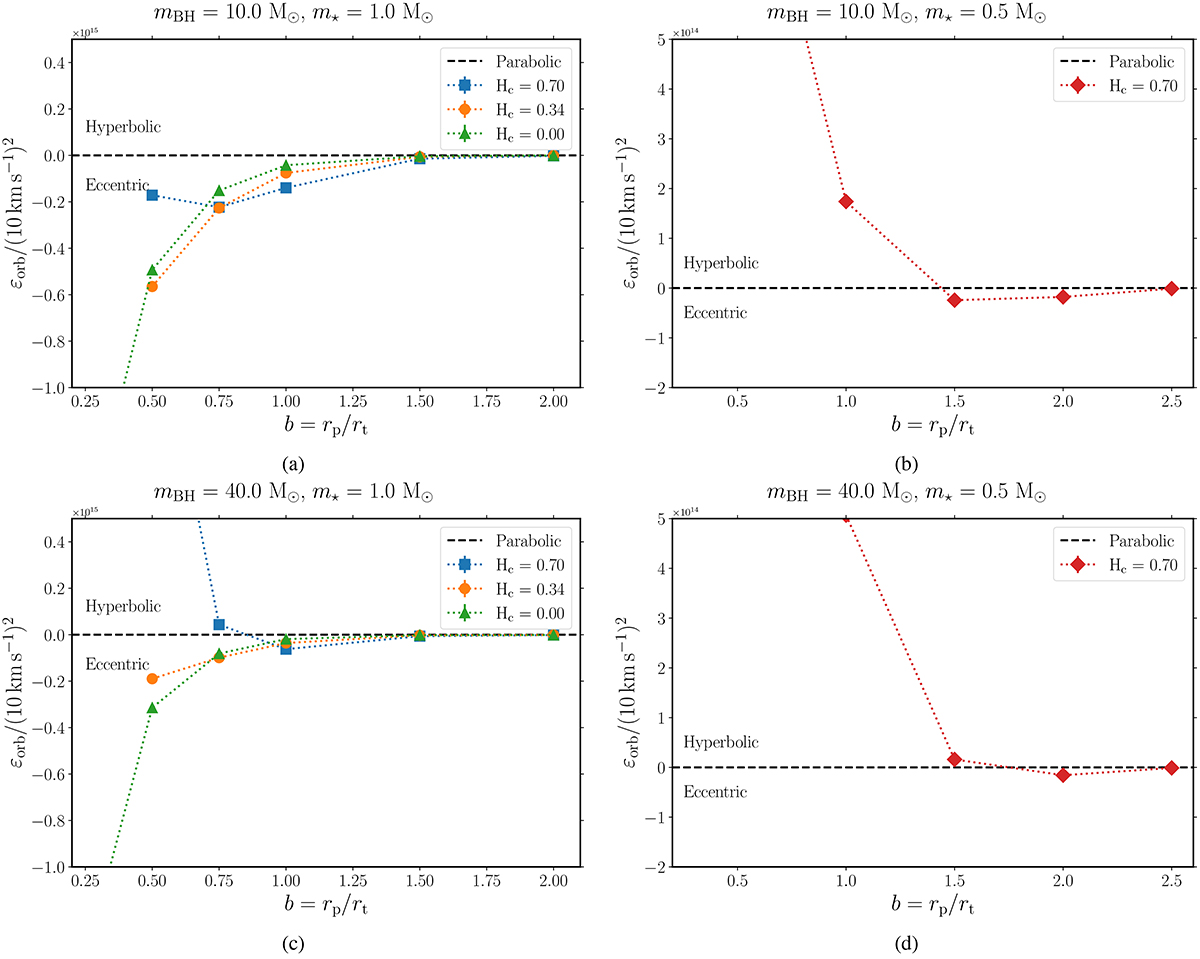
Post-disruption normalized specific orbital energies of the star-BH system, εorb, for a star of mass 1 M⊙ (left) and 0.5 M⊙ (right) initially in a parabolic orbit, due to a BH of mass 10 M⊙ (top) and 40 M⊙ (bottom), as a function of impact parameter b and MS age (Hc abundance). The dashed line represents parabolic orbits and separates the parameter space into bound (eccentric) and unbound (hyperbolic) orbits. When mass loss is relatively low, a lower value of b generally results in more negative εorb in the case of 1 M⊙ star. This trend continues for the TAMS star. However, for the ZAMS and MAMS stars, significant mass losses can reverse this trend, with hyperbolic orbits also being a possibility (e.g., 1 M⊙ ZAMS star and 40 M⊙ BH mass with b < 1.00) 0.5 M⊙ stars, on the other hand, can become unbound for larger b, with boundedness also depending on the mass of the BH.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


