Fig. 4
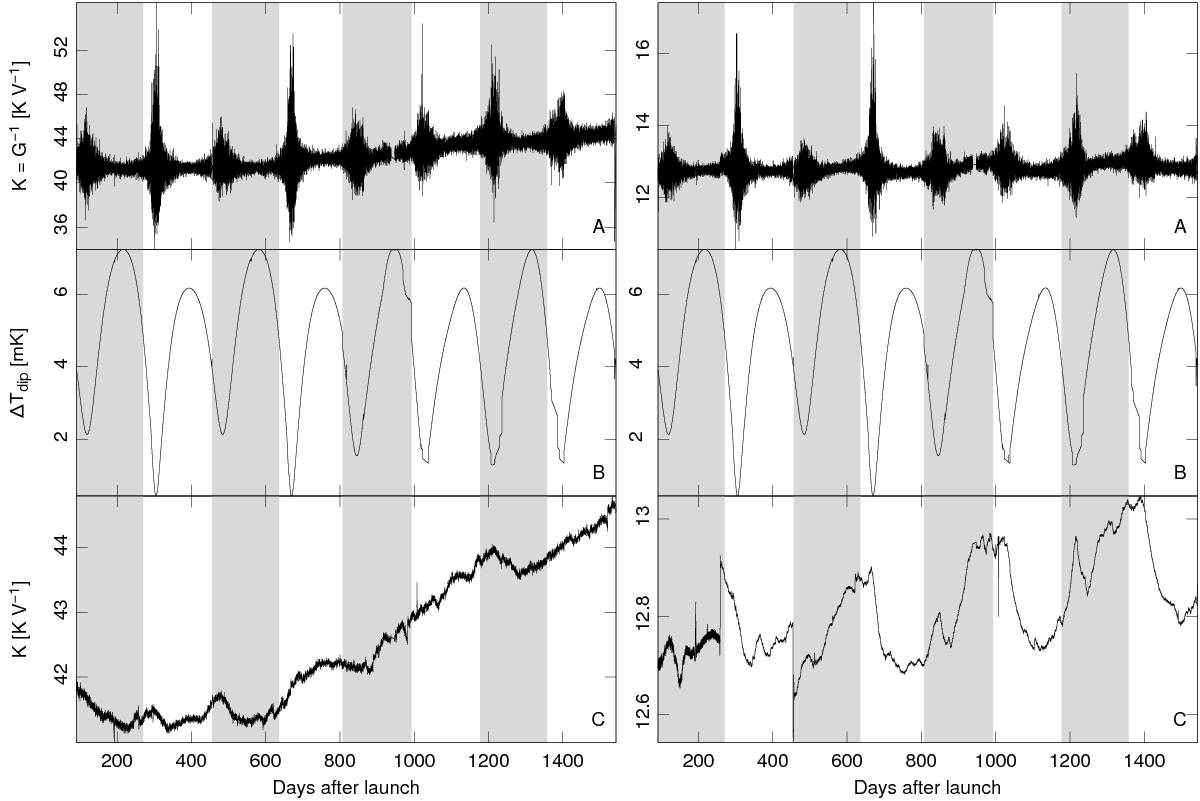
Variation in time of a few quantities relevant for calibration for radiometers LFI-21M (70 GHz, left) and LFI-27M (30 GHz, right). Grey/white bands indicatecomplete sky surveys. All temperatures are thermodynamic. Panel A): calibration constant K estimated using the expected amplitude of the CMB dipole. The uncertainty associated with the estimate changes with time, according to the amplitude of the dipole as seen in each ring. Panel B): expected peak-to-peak difference in the dipole signal (solar + orbital). The shape of the curve depends on the scanning strategy of Planck, and it is strongly correlated with the uncertainty in the gain constant (see panel A)). The deepest minima happen during Surveys 2 and 4; because of the higher uncertainties in the calibration (and the consequent bias in the maps), these surveys have been neglected in some of the analyses in this Planck data release (see, e.g., Planck Collaboration XIII 2016). Panel C): the calibration constants K used to actually calibrate the data for this Planck data release are derived by applying a smoothing filter to the raw gains in panel A). Details regarding the smoothing filter are presented in Appendix A.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


