- Details
- Published on 04 August 2021
Vol. 652
4. Extragalactic astronomy
COALAS. I. ATCA CO(1–0) survey and luminosity function in the Spiderweb protocluster at z = 2.16
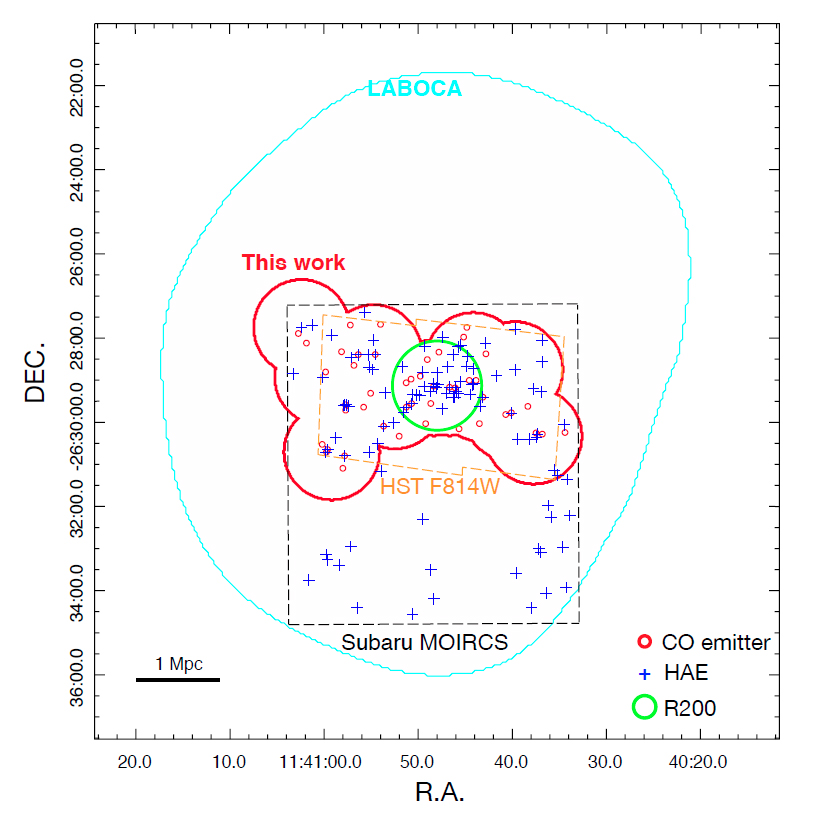
Galaxy clusters assemble and collapse around z=2 in the first half of the life of the Universe, but the process is still not completely understood. The COALAS project obtained molecular gas observations of the Spiderweb protocluster field at z = 2.16. A total of 475 hours of Australia Telescope Compact Array (ATCA) observations cover a large ~5 Mpc region and over 13 000 km/s in velocity. The authors detect CO(1-0) emission in 46 galaxies, which is the largest sample of molecular gas measurements in a protocluster to date.
Half of the CO emitters are gravitationally unbound to the cluster core, suggesting that the cluster core is collapsed while its outer regions are still assembling. One main result is the high proportion of CO-rich galaxies, which are at least ten times more numerous than in the field at the same redshift. This environmental effect reverses what is seen at z=0, where cluster galaxies are gas deficient with respect to the field.


