| Issue |
A&A
Volume 581, September 2015
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A15 | |
| Number of page(s) | 35 | |
| Section | Stellar structure and evolution | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201526617 | |
| Published online | 25 August 2015 | |
Online material
Appendix A: Key quantities of our model sequences
Important characteristics of our models.
Appendix B: Photoionising flux
Time averaged ionising fluxes (L), and time averaged (Q) and peak photon emission rates (Qmax) of the ionising photons for hydrogen (H), neutral helium (He) and singly ionised helium (He+) during the main-sequence evolution for each stellar sequence.
Appendix C: Isochrones
Figure C.1 shows isochrones of our stellar evolutionary calculations for several ages and rotational rates.
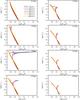 |
Fig. C.1
Isochrones of different ages of rotating stellar evolutionary models are shown in the HR diagram. The initial surface rotational velocity is chosen in steps of 100 km s-1 from non-rotating to 600 km s-1. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
© ESO, 2015
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


