Fig. 1.
Download original image
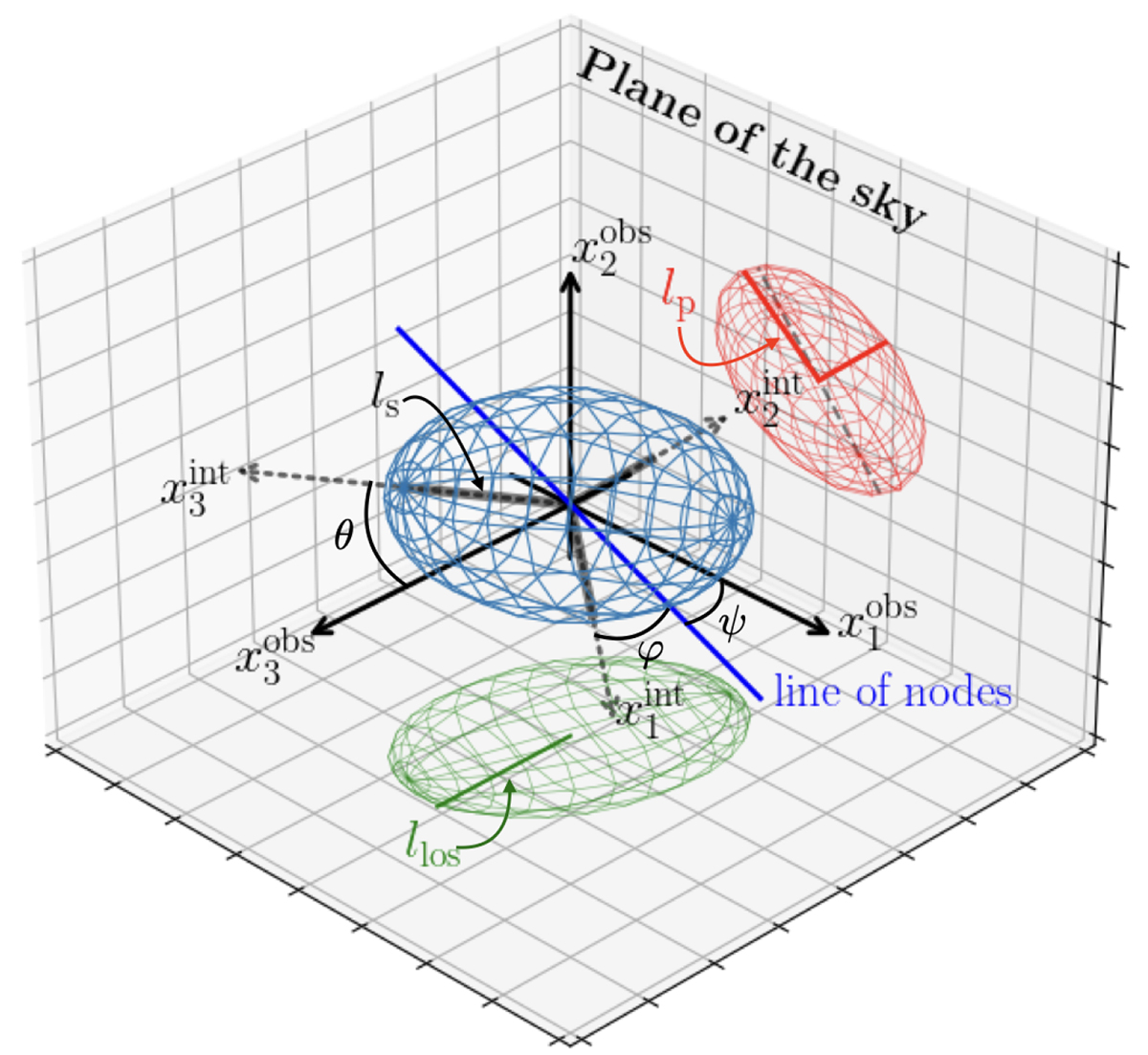
Triaxial ellipsoid model and coordinate systems used in the triaxial analysis. The intrinsic coordinate system of the ellipsoid is denoted by dotted gray arrows (![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() ), where
), where ![]() represents the major axis. The black arrows (
represents the major axis. The black arrows (![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() ) correspond to the observer’s coordinate system, where
) correspond to the observer’s coordinate system, where ![]() is aligned with the observer’s line of sight. In other words, an observer views the ellipsoid in the
is aligned with the observer’s line of sight. In other words, an observer views the ellipsoid in the ![]() direction. The three Euler angles (θ, φ, ψ) characterize the intrinsic coordinate system of the ellipsoid in relation to the observer’s coordinate system. The blue line represents the line of nodes, which is the intersection of the
direction. The three Euler angles (θ, φ, ψ) characterize the intrinsic coordinate system of the ellipsoid in relation to the observer’s coordinate system. The blue line represents the line of nodes, which is the intersection of the ![]() plane and the
plane and the ![]() plane, and it is aligned with the vector
plane, and it is aligned with the vector ![]() . The red ellipse denotes the projection of the ellipsoid on the sky plane, with lp representing its semimajor axis. The dashed black line on the ellipse shows the projected major axis of the ellipsoid on the sky plane. The green ellipse is the projection of the ellipsoid onto the plane that is perpendicular to the sky plane, and llos is the half size of the ellipse along the observer line of sight. See also Figs. 2 and 3 in Sereno et al. (2012).
. The red ellipse denotes the projection of the ellipsoid on the sky plane, with lp representing its semimajor axis. The dashed black line on the ellipse shows the projected major axis of the ellipsoid on the sky plane. The green ellipse is the projection of the ellipsoid onto the plane that is perpendicular to the sky plane, and llos is the half size of the ellipse along the observer line of sight. See also Figs. 2 and 3 in Sereno et al. (2012).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


