Fig. 3.
Download original image
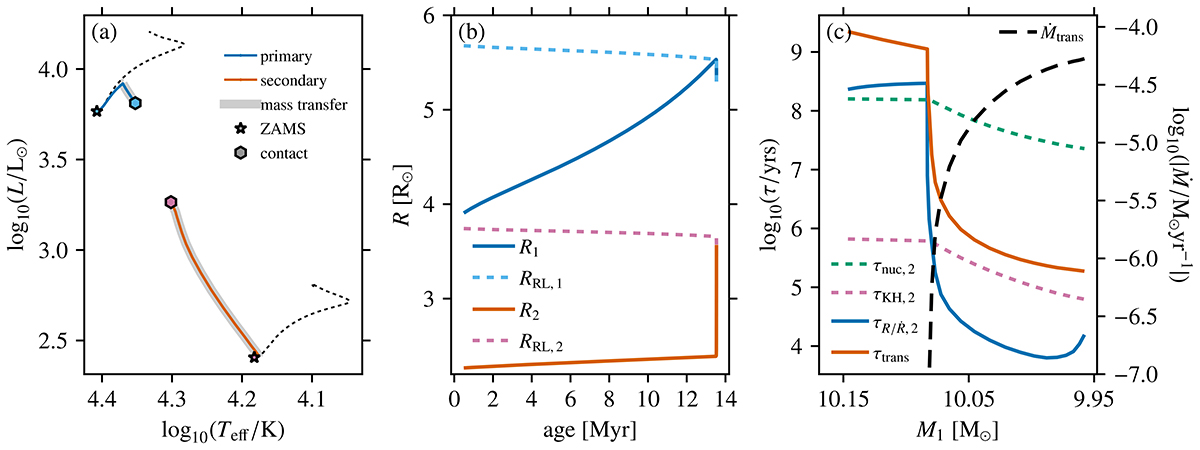
Example of a M1, i = 10.2 M⊙, qi = 0.4, and ai = 12.4 R⊙ binary system forming a contact binary during the MS of the primary (Case A) because of the thermal expansion of the secondary (accretor) star. Panel a shows an HRD with the evolutionary tracks of the primary and secondary stars (solid lines). The dashed black lines show the evolutionary tracks of single stars with the same initial masses as the binary components and initial rotation rates of Ω/Ωc = 0.25. Panel b shows the evolution of the radius R (solid lines) and Roche lobe radius RRL (dashed lines) of both components. The timescales governing the evolution of the binary and the mass-transfer rate (black dashed line) are shown in panel c as a function of the decreasing primary star mass. The secondary’s nuclear (τnuc, 2) and thermal (τKH, 2) timescales are shown with a dashed green and pink line, respectively. The expansion (τR/Ṙ,2) and mass-transfer (τtrans) timescales are shown with a solid blue and orange line, respectively.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


