| Issue |
A&A
Volume 676, August 2023
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | C5 | |
| Number of page(s) | 2 | |
| Section | Letters to the Editor | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202347174e | |
| Published online | 21 August 2023 | |
Letter to the Editor
Discovery of H2CCCH+ in TMC-1 (Corrigendum)
1
I. Physikalisches Institut, Universität zu Köln, Zülpicher Str. 77, 50937 Köln, Germany
e-mail: asvany@ph1.uni-koeln.de
2
Dept. de Astrofísica Molecular, Instituto de Física Fundamental (IFF-CSIC), Serrano 121, 28006 Madrid, Spain
3
Centro de Desarrollos Tecnológicos, Observatorio de Yebes (IGN), 19141 Yebes, Guadalajara, Spain
4
Observatorio Astronómico Nacional (OAN, IGN), Madrid, Spain
5
Institut des Sciences Moléculaires (ISM), CNRS, Univ. Bordeaux, 351 cours de la Libération, 33400 Talence, France
6
Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Bordeaux, Univ. Bordeaux, CNRS, B18N, allée Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 33615 Pessac, France
7
, Serrano 123, 28006 Madrid, Spain
Key words: astrochemistry / ISM: molecules / ISM: individual objects: TMC-1 / methods: laboratory: molecular / molecular data / errata / addenda
Several errors were inadvertently introduced in two tables during the production process. In Table 1, the left arrows were changed to right arrows, and in Table A.1, spaces were inserted before the decimal points of the values. The corrected tables are presented here.
Ground state rotational transition frequencies of H2CCCH+, determined by laboratory and astronomical detections.
Calculated and experimental spectroscopic parameters of H2CCC and H2CCCH+ (in MHz). Equilibrium rotational constants calculated at the ae-CCSD(T)/cc-pwCVQZ level of theory; zero-point vibrational corrections ΔA0, ΔB0, ΔC0; and centrifugal distortion constants calculated at the fc-CCSD(T)/ANO1 level. Best theoretical estimates for the rotational and centrifugal distortion constants X of H2CCCH+ are estimated as 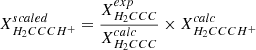 (i.e., using isoelectronic H2CCC as a calibrator).
(i.e., using isoelectronic H2CCC as a calibrator).
References
- Cernicharo, J., Marcelino, N., Agúndez, M., et al. 2020, A&A, 642, L8 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Vrtilek, J. M., Gottlieb, C. A., Gottlieb, E. W., Killian, T. C., & Thaddeus, P. 1990, ApJ, 364, L53 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
© The Authors 2023
 Open Access article, published by EDP Sciences, under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Open Access article, published by EDP Sciences, under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article is published in open access under the Subscribe to Open model. Subscribe to A&A to support open access publication.
All Tables
Ground state rotational transition frequencies of H2CCCH+, determined by laboratory and astronomical detections.
Calculated and experimental spectroscopic parameters of H2CCC and H2CCCH+ (in MHz). Equilibrium rotational constants calculated at the ae-CCSD(T)/cc-pwCVQZ level of theory; zero-point vibrational corrections ΔA0, ΔB0, ΔC0; and centrifugal distortion constants calculated at the fc-CCSD(T)/ANO1 level. Best theoretical estimates for the rotational and centrifugal distortion constants X of H2CCCH+ are estimated as 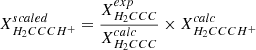 (i.e., using isoelectronic H2CCC as a calibrator).
(i.e., using isoelectronic H2CCC as a calibrator).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


