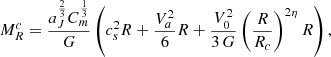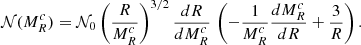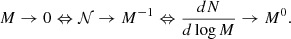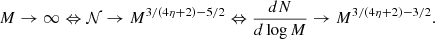| Issue |
A&A
Volume 668, December 2022
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A147 | |
| Number of page(s) | 18 | |
| Section | Astrophysical processes | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202243803 | |
| Published online | 15 December 2022 | |
Influence of magnetic field and stellar radiative feedback on the collapse and the stellar mass spectrum of a massive star-forming clump
1
AIM, CEA, CNRS, Université Paris-Saclay, Université Paris-Diderot, Sorbonne Paris-Cité, 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette, France
e-mail: patrick.hennebelle@cea.fr
2
INAF-IAPS, Via del Fosso del Cavaliere 100, 00133 Roma, Italy
3
Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics, Department of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Manchester, Manchester M13 9PL, UK
4
Physikalisches Institut, University of Cologne, Zülpicher Str. 77, 50937 Köln, Germany
5
INAF – Osservatorio Astronomico di Cagliari, Via della Scienza 5, 09047 Selargius, CA, Italy
6
Instituto de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Apdo. Postal 3-72, 58089 Morelia, Michoacán, México
7
Universität Heidelberg, Zentrum für Astronomie, Institut für theoretische Astrophysik, Albert-Ueberle-Str. 2, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany
Received:
17
April
2022
Accepted:
22
October
2022
Context. In spite of decades of theoretical efforts, the physical origin of the stellar initial mass function (IMF) is still a subject of debate.
Aims. We aim to gain an understanding of the influence of various physical processes such as radiative stellar feedback, magnetic field, and non-ideal magneto-hydrodynamics on the IMF.
Methods. We present a series of numerical simulations of collapsing 1000 M⊙ clumps, taking into account the radiative feedback and magnetic field with spatial resolution down to 1 AU. We performed both ideal and non-ideal MHD runs, and various radiative feedback efficiencies are considered. We also developed analytical models that we confront with the numerical results.
Results. We computed the sum of the luminosities produced by the stars in the calculations and it shows a good comparison with the bolometric luminosities reported in observations of massive star-forming clumps. The temperatures, velocities, and densities are also found to be in good agreement with recent observations. The stellar mass spectrum inferred for the simulations is, generally speaking, not strictly universal and it varies, in particular, with magnetic intensity. It is also influenced by the choice of the radiative feedback efficiency. In all simulations, a sharp drop in the stellar distribution is found at about Mmin ≃ 0.1 M⊙, which is likely a consequence of the adiabatic behaviour induced by dust opacities at high densities. As a consequence, when the combination of magnetic and thermal support is not too high, the mass distribution presents a peak located at 0.3–0.5 M⊙. When the magnetic and thermal support are high, the mass distribution is better described by a plateau, that is, dN/dlog M ∝ M−Γ, Γ ≃ 0. At higher masses, the mass distributions drop following power-law behaviours until a maximum mass, Mmax, whose value increases with field intensity and radiative feedback efficiency. Between Mmin and Mmax, the distributions inferred from the simulations are in good agreement with an analytical model inferred from gravo-turbulent theory. Due to the density PDF ∝ρ−3/2 relevant for collapsing clouds, values on the order of Γ ≃ 3/4 are inferred both analytically and numerically. More precisely, after 150 M⊙ of gas have been accreted, the most massive star has a mass of about 8 M⊙ when magnetic field is significant, and 3 M⊙ only when both the radiative feedback efficiency and magnetic field are low, respectively.
Conclusions. When both the magnetic field and radiative feedback are taken into account, they are found to have a significant influence on the stellar mass spectrum. In particular, both of these effects effectively reduce fragmentation and lead to the formation of more massive stars.
Key words: gravitation / turbulence / ISM: clouds / ISM: structure / stars: formation
© The Authors 2022
 Open Access article, published by EDP Sciences, under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Open Access article, published by EDP Sciences, under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article is published in open access under the Subscribe-to-Open model. Subscribe to A&A to support open access publication.
1. Introduction
Star formation is a topic of fundamental importance in astrophysics, particularly with regard to the mass distribution of stars, described by the initial mass function (IMF, Salpeter 1955; Kroupa 2001; Chabrier 2003; Bastian et al. 2010; Offner et al. 2014; Lee et al. 2020), which plays a crucial role in setting the abundances of heavy elements and regulating stellar feedback. These, in turn, play major roles in the formation and evolution of galaxies and the interstellar medium. In the efforts to find a complete description of the IMF, it is sometimes overlooked that observed stellar masses span more than three orders of magnitudes: from 0.1 M⊙ to more than 100 M⊙. This fact likely implies the existence of several regimes of dominant physical processes and star formation conditions. It is clear that this problem requires a long standing community effort and over the past few decades, several teams have conducted systematic investigations with the help of numerical simulations, introducing progressively more and more physical processes with an increasingly higher numerical resolution.
The first attempts to obtain stellar mass spectra from numerical simulations in isothermal, self-gravitating, supersonic turbulent flows were made by Klessen (2001) and Bate et al. (2003). Together with several high-resolution studies performed by various authors (e.g. Girichidis et al. 2011; Bonnell et al. 2011; Ballesteros-Paredes et al. 2015; Lee & Hennebelle 2018a), they find stellar mass spectra that present similarities with the observationally inferred mass spectra. In particular, at high masses the distributions are compatible with power laws, namely, dN/dlog M ∝ M−Γ, although in many runs, values of Γ = 3/4 to 1 have been obtained, which are seemingly shallower than the canonical Γ ≃ 1.3 value inferred by Salpeter (1955) as discussed in Lee & Hennebelle (2018a). The inferred distributions also present a peak, which (when the simulations are strictly isothermal) is due to limited spatial resolution, however. A robust, numerically converged peak is obtained when an effective equation of state with an adiabatic index larger than 4/3 is taken into account (Lee & Hennebelle 2018b).
The influence of the magnetic field on the stellar mass spectrum was investigated by Haugbølle et al. (2018), Lee & Hennebelle (2019), and Guszejnov et al. (2020) perfoming high spatial resolution simulations with various magnetisations. The resulting mass spectra have been found to be similar to those inferred from simulations without magnetic field. In particular, Guszejnov et al. (2020) stress that magnetic field cannot provide a characteristic mass that may explain the peak of the IMF and that thermal processes have to be considered.
Several attempts have been made to study the IMF using radiative transfer calculations. Urban et al. (2010) considered radiative feedback, that is, stellar and accretion luminosity, by adding them onto the sink particles. They concluded that isothermal and radiative transfer calculations are significantly different, in particular the stars are much more massive in simulations with radiative feedback. Bate (2009) performed high resolution calculations, introducing the sink particles at a very high density, namely n > 1019 cm−3. However, stellar feedback onto the sink particles is not explicitly added. This means that the accretion luminosity onto the star is not accounted for and this makes stellar feedback much weaker than it should be. Krumholz et al. (2012) performed adaptive mesh refinement calculations with a resolution of 20–40 AU. Both stellar and accretion luminosity are added to the sinks. A relatively flat mass spectrum, that is to say, such that Γ ≃ 0 is inferred when winds are not considered while in the presence of stellar winds the mass spectra present a peak around 0.3 M⊙ and a power-law with Γ ≃ 0.5 − 1. Likely enough when winds are present, the radiation escape along the cavities and the heating is reduced. Mathew & Federrath (2020) presented simulations with a spatial resolution of 200 AU and performed calculations that use either a polytropic equation of state or heating from stars. They found that when heating is included, more massive stars would form. Hennebelle et al. (2020a) conducted adaptive mesh simulations with a spatial resolution of 4 AU and down to 1 AU. Both stellar and accretion luminosity are treated, with various efficiencies, facc, ranging from 0 to 50%, as well as two sets of initial conditions, namely, very compact and more standard clumps have been considered. For the most compact clumps and when facc is high, a flat mass spectrum develops. Otherwise all runs present mass spectra with a peak around 0.3–0.5 M⊙ and a power law at higher masses, even when radiative feedback is not considered, that is, facc = 0, and when a barotropic equation of state is used instead. High efficiency radiative feedback runs however tend to present a broader distribution, both at the low mass and high mass end, with high-mass stars up to two to three times more massive than in the barotropic and low-feedback efficiency runs.
In the present paper, we pursue the investigation of the origin of the stellar mass spectrum within a massive star-forming clump. In particular, we focus on the role that magnetic field may have, in conjunction with radiative feedback. A number of studies performed calculations with both magnetic field and radiative feedback although most of the time, without predicting the mass spectrum. As revealed in previous works (Peters et al. 2010, 2011; Commerçon et al. 2011; Myers et al. 2013), both these physical processes significantly influence the collapse and star formation, particularly by reducing the fragmentation. Moreover, their joint effect is not a mere superposition. These studies, however, have not presented sufficient statistics to allow any conclusions to be drawn regarding the stellar mass spectrum. A stellar mass spectrum was obtained by Li et al. (2018), where a magnetised and radiative calculation was performed at a spatial resolution of about 30 AU. These statistics need to be expanded and various initial conditions must be systematically explored. To do so, we performed high-resolution simulations of massive star-forming clumps where both magnetic field and radiative feedback are accounted for. To get a good description of the small scales which are mandatory to describe the formation of low-mass stars, we employed an adaptive mesh refinement with a spatial resolution down to 1 AU. As the magnetic intensity is likely to be varying from clump to clump, and not many constraints from observations are available yet, we explored three magnetisations. In addition, the radiative feedback efficiency is subject to large uncertainties, so we considered two different values. Importantly, we also perform a simulation in which non-ideal MHD effects, namely, ambipolar diffusion (Mestel & Spitzer 1956), are explicitly taken into account. We stress that these runs are the first for which both magnetic field and radiative feedback are taken into account, while considering a configuration which leads to sufficient statistics and spatial resolution to provide a reliable stellar distribution in the range from 0.1 to 10 M⊙.
The paper is structured as follows. Section 2 presents the equations that we solved for the purposes of this work, along with the relevant physical processes as well as the numerical methods used to solve these equations. It also presents the initial conditions and describes the various runs presented in the paper. In Sect. 3, we look at the evolution of the clump during its collapse and investigate the effect of the magnetisation and radiative feedback. We study the global properties, such as the total accreted mass and radiated energy, the temperature, magnetic field, and mass distribution. An analytical model is presented in the appendix, developed with the aim to understand the temperature distribution in the simulations. We make comparisons with observational results. In Sect. 4, we present the stellar mass spectrum obtained in the simulations. They are quantitatively compared with an analytical model which gives more insight into the effect of the different physical processes and is also presented in an appendix. In Sect. 5, we provide a discussion and our conclusions are given in Sect. 6.
2. Numerical simulations
2.1. Equations, numerical methods, and setup
In this paper, we solve the equations of the radiative magneto-hydrodynamics. All the radiative quantities are estimated in the co-moving frame and assuming the grey approximation; that is to say that the radiative energies are integrated over the entire frequency spectrum (e.g. Commerçon et al. 2011). The equations are:
where ρ is the material density, u is the velocity, P the thermal pressure, λ is the radiative flux limiter (Minerbo 1978), Er is the radiative energy, FL = 1/(4π)(∇×B) × B is the Lorentz force, ϕ is the gravitational potential, ET the total energy ET = ρϵ + 1/2ρu2 + B2/(8π)+Er (ϵ is the gas specific internal energy), B is the magnetic field, EAD is the ambipolar electromotor field (EMF), κP is the Planck mean opacity, κR is the Rosseland mean opacity, ℙr is the radiation pressure, S⋆ the luminosity source, and T is the gas temperature. The ambipolar EMF is given by
where ηAD is the ambipolar diffusion resistivity, calculated as a function of the density, temperature, and magnetic field amplitude.
The numerical method is overall very similar to the one used in Hennebelle et al. (2020b). The simulations were performed with the adaptive mesh refinement (AMR) magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) code RAMSES (Teyssier 2002; Fromang et al. 2006). When non-ideal MHD, namely, ambipolar diffusion, is included the scheme, as described in Masson et al. (2012) and used in previous studies (Masson et al. 2016; Hennebelle et al. 2020a; Mignon-Risse et al. 2021; Commerçon et al. 2022; Lebreuilly et al. 2021). The resistivities are the ones calculated in Marchand et al. (2016).
In all simulations presented here, radiative transfer is accounted for using the flux limited diffusion method assuming grey approximation (see Commerçon et al. 2011, 2014). The flux limited diffusion method is known to present some restrictions for instance it does not treat shadows well due to its isotropic nature. More accurate methods such as the M1 method (González et al. 2007), the hybrid method (Kuiper et al. 2010; Mignon-Risse et al. 2020) or the Variable Eddington Tensor method (Menon et al. 2022) have been developed and deal significantly better with anisotropic radiative transfer (see also Jaura et al. 2018; Peter et al. 2022). However, they tend to be more costly than the flux limited diffusion method employed in this work, and are often limited in their current implementations. This certainly represents a line for future improvements.
At high density, the equation of state is taken from Saumon & Chabrier (1992) and Saumon et al. (1995) which takes into account H2, H, H+, He, He+, and He2+ (the He mass concentration is 0.27). The opacities are as described in Vaytet et al. (2013). For the range of temperatures and densities covered in this work, the opacities are the ones calculated in Semenov et al. (2003).
The boundary conditions are periodic. The cloud is initially spherical and has a radius four times lower than the computational domain size. All simulations were run on a regular grid of 2563 computing cells and ten have been further added during the course of the calculation leading to a total number of 18 AMR levels. The resolution criterion is the Jeans length and it is resolved with at least ten points. In the present paper, the issue of numerical resolution is not further discussed and we refer to the appendix of Hennebelle et al. (2020b) for an investigation of the impact of numerical resolution.
2.2. Sink particles and stellar feedback
The sink particle algorithm is described in Bleuler & Teyssier (2014). Sink particles are formed at the highest refinement level at the peak of clumps whose maximum density is larger than nacc. The sink particles are created if the parent clump has a density n > nacc and if it is sufficiently gravitationally bound (see Bleuler & Teyssier 2014). The value of nacc is equal to 1013 cm−3. With this value of nacc, the computational cells having a density equal to nacc possess a mass of roughly 1–2% of the mass of the first hydrostatic core, ML = 0.03 M⊙. At each time step, 10% of the gas mass inside the sink’s accretion radius and with a density above nacc is retrieved from the grid and accreted by the sink. The sinks are not allowed to merge. The impact of changing the value of nacc has been discussed in Hennebelle et al. (2020b). It has been found that both the spatial resolution and the value of nacc may influence the peak of the stellar distribution. However, once the first hydrostatic core is sufficiently resolved, this should not be the case.
Sink particles are also a source of radiation due to the stellar luminosity and gas accretion. The accretion luminosity is given by:
where M* and R* are, respectively, the star’s mass and radius, while Ṁ is the accretion rate. If all the kinetic energy of the infalling gas was radiated away, we would have facc ≃ 1. The accretion luminosity has been shown to be the dominant source of gas heating at early time and has important effects on the surrounding gas (e.g. Krumholz et al. 2007; Offner et al. 2009). The stellar luminosity of the protostars L* and R* are taken from Kuiper & Yorke (2013; see also Hosokawa & Omukai 2009). As discussed in Hennebelle et al. (2020b), the value of facc that should be used is not clearly established. In particular, the radiation is emitted on a very small scale, namely, of a few stellar radii, and is not expected to propagate uniformly because of the highly anisotropic density distribution (e.g. Krumholz et al. 2012). As in Hennebelle et al. (2020b), we performed simulations in which we used an ‘effective’ accretion luminosity and explore the values facc = 0.1 and 0.5. By considering an effective luminosity smaller than the estimated total luminosity, we envisage that the rest of the energy either escape preferentially along the cavities open by winds and jets or is converted into jet or a wind kinetic energy. This is obviously an important source of uncertainties which requires further investigation.
We started by considering accretion and stellar luminosities when the sink has a mass of about 2 ML, that is, 0.07 M⊙. The reason is that due to the limited spatial resolution, when the sink is introduced the protostar is not truly formed yet. Since the size of the sink particles is not very different from the radius of the first hydrostatic core, it seems reasonable to assume that the protostar is formed only when the sink reaches a mass equal to a few ML. We note that although this assumption is reasonable, it clearly requires further investigation. For instance, Bhandare et al. (2020) who performed two-dimensional simulations of the second Larson cores, namely, the young protostar, found that they grow with time far beyond the solar radii. This clearly suggests that at least some of the accretion energy is not fully radiated away but somehow stored in the star for some time. Indeed, the accretion shock at the edge of the second Larson core is subcritical (Vaytet et al. 2013), meaning that most of the accretion energy is advected inside the protostar and not immediately radiated away. This constitutes an important source of uncertainty for calculations such as those performed in this work.
2.3. Initial conditions and performed runs
Our initial conditions consist of spherical clouds in which a turbulent velocity field has been added. The velocity field has a classical Kolmogorov power-spectrum equal to 11/3 with random phases. A fully self-consistent approach would require to also set up the density and magnetic field fluctuations, however, this is not a straightforward task. In practice, it requires running a large-scale series of simulations and zooming in or at least performing a preliminary run without self-gravity (see for instance Lane et al. 2022). We note that Lee & Hennebelle (2018a) have compared various approaches, such as starting from a previous phase in which the simulation is run without self-gravity and starting directly from a prescribed turbulent field, as done here. They found very similar results. This suggests that, at least in the context of collapsing clumps, the choice of the initial turbulent field may not be so important, probably because as the collapse proceeds, the fluctuations evolve and the initial perturbations are largely forgotten.
The clump we consider in this study has a mass of 103 M⊙ and an initial radius of 0.4 pc corresponding to a uniform density of about 8 × 104 cm−3 initially. Observationally, this corresponds to relatively standard massive star-forming clumps (e.g. Urquhart et al. 2014; Elia et al. 2017, 2021; Lin et al. 2022). With an initial temperature of 10 K, the ratio of the thermal over gravitational energy is about 0.008. The clump density leads to a freefall time of about 110 kyr. The initial value of the Mach number is equal to 7 leading to a turbulent over gravitational energy ratio of about 0.4, that is to say, the clumps are close to being initially virialised.
We set up the simulations with a uniform initial magnetic field through the cloud and intercloud medium. We considered two initial mean-field strengths, with mass-to-flux ratios, μ, of 10 and 100, respectively (corresponding to about 100 μG and 10 μG, respectively). These values are motivated by the observations of μ on the order of a few in dense cores (e.g. Crutcher 2012; Myers & Basu 2021). This selection also aims to account for the broad dispersions in the μ values of the massive clumps identified in the 1-kpc scale simulation presented in Hennebelle (2018). In these MHD simulations, which have a spatial resolution down to 400 AU, it has been found that the mass-to-flux ratio, which presents a broad dispersion, is indeed on the order of a few for Solar mass cores but is lower for the more massive ones. More precisely, Fig. 5 of Hennebelle (2018) shows the distribution of self-gravitating objects with density larger than 104 cm−3. It shows a clear trend that the mass-to-flux ratio, μ, is increasing with mass in spite of a broad distribution. The most massive clumps displayed has a mass of about 100 M⊙ and, thus, it is necessary to extrapolate to get a hint on 1000 M⊙ clumps. Based on this figure, we would expect that the typical μ of a 1000 M⊙ clumps is certainly larger than 10. This may at first sight be surprising because low mass cores have been observed to present values of μ on the order of a few (Pattle et al. 2022). It should, however, be remembered that the mass-to-flux ratio is the ratio of a volume over a surface weighted quantity; thus, considering objects with similar mean density, the mass-to-flux is expected to increase with the object size.
Another fundamental aspect is the physics of the magnetic field evolution. Whereas many studies have assumed ideal MHD, it is however clear that this is a poor approximation at high density in star-forming regions (e.g. Zhao et al. 2020). We performed one run with ambipolar diffusion and a magnetisation corresponding to μ = 10. Due to the small time steps induced by the second order derivative in the ambipolar diffusion operator, this numerical simulation is quite challenging and has required about 500 000 cpu h. Table 1 summarises the various runs performed.
Summary of the runs performed.
Two ideal MHD runs (MHD10f05 and MHD100f05) and one purely hydrodynamical runs (HYDROf05) allow us to investigate the role of the magnetic field during the collapse notably on the initial mass function; whereas the non-ideal MHD run (NMHD10f05) is the most realistic simulation and to our knowledge is the first simulation of a massive star-forming clump which includes both radiative feedback and non-ideal MHD. These four runs are complemented by two runs with a lower accretion luminosity parameter, facc = 0.1, namely MHD10f01 and HYDROf01 which allow to assess and discuss the influence of radiative feedback on our results. All simulations are carried out until at least 150 M⊙ of gas have been accreted onto the sink particles, except run NMHD10f05 for which the final mass accreted by the sinks is 100 M⊙. This is because, as explained above, this simulation is more computationally demanding.
3. General clump description
In this section, we look at the global evolution and final properties of the collapsing clump as a whole. We start by describing the general morphology, before proceeding to discuss the star formation and luminosity. We then study the gas density and temperature distribution inside the clump.
3.1. Total accreted mass
Figure 1 displays the total mass accreted (top-left panel) by sink particles, Mtot, * as a function of time for the six simulations. The total accretion rate is also plotted (top-right panel). Since it is a heavily fluctuating quantity, the latter is calculated by averaging its instantaneous value over 100 uniformly spaced time intervals. As indicated above, all simulations are run until about 150 M⊙ have been accreted, corresponding to a star-formation efficiency of 15%. There are two exceptions, NMHDf05 for which at the end of the simulation 100 M⊙ have been turned into the sinks, and MHD10f05 for which the final total mass of sinks is equal to 200 M⊙. Two groups of simulations are easily distinguished. On one hand, the hydrodynamical simulations and the low magnetised one, MHD100f05 and, on the other hand, the more magnetised ones, namely, MHD10f01, MHD10f05, and NMHDf05. As expected, due to magnetic support, the latter group of simulations collapses a bit more slowly. Two points are worth mentioning, first the simulations with facc = 0.1 and with facc = 0.5 behave very similarly showing that in spite of strong heating, radiation does not significantly alter the large scale dynamics. A similar conclusion is also reached for the ambipolar diffusion. This is because i) thermal support is rather weak and an increase of temperature even by a factor of several does not make thermal support sufficiently strong to provide a significant support at the clump scale and also because ii) magnetic field is only significantly modified by non-ideal MHD processes, at high density (say n > 107 cm−3). Interestingly, we see that after a fast increase the accretion rate, Ṁtot,∗, reaches values, which are nearly identical for all simulations and equal to about 10−2 M⊙ yr−1. This is because the accretion rate is controlled by the largest scale – here, the clump which is globally collapsing. The magnetic intensity considered here is too weak to significantly modify this global dynamics.
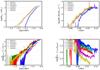 |
Fig. 1. Total mass, accretion rate and luminosity as a function of time. Top row shows the total accreted mass (top-left panel) and the total accretion rate (top-right panel) as a function of time for the various runs. Bottom-left panel portrays the total luminosity while bottom-right panel shows the same quantity divided by Lglob = 0.5 × GM∗,tot Ṁ∗,tot/(2 R⊙). |
3.2. Total luminosity
The bottom-left panel of Fig. 1 portrays the total luminosities, ∑(L* + Lacc) of the sink particles (see also Fig. C.1). As for the accretion rate, after an increase which takes about 0.02 Myr, it reaches, in the case with facc = 0.5, a plateau at about 1 − 2 × 105 L⊙. In the case of f = 0.1, the total luminosity is 10–20 times lower for run HYDROf01 and 3 times lower for run MHD10f01. We note that Fig. 1 shows that the clumps spend about 0.02 Myr in the protostellar phase with a luminosity several times lower than the peak values.
It is interesting to compare these values with the observations. Although what is observationally available is the bolometric luminosities rather than the total source luminosities, they are obviously related and can be compared. In particular, it is expected that the radiation emitted by the star in the visible domain is quickly absorbed and reemitted in the infrared by the dust. For instance, Fig. 12 in Elia et al. (2017) displays the bolometric luminosities as a function of mass for a sample of clumps. As can be seen our values agree well with the luminosity distribution of the protostellar 1000 M⊙ clumps, which range from 102 to few 105 L⊙ although these values correspond to their upper values when facc = 0.5. We note, however, that the bolometric luminosities calculated in Elia et al. (2017) correspond to wavelengths longer than 20 μm. Therefore these values represent themselves lower limits of the real luminosities.
Lin et al. (2022) present detailed observations for several massive star-forming clumps with comparable mass and radii (see their Table 6). Luminosities of a few 105 L⊙ are also reported. Since the mass of the clump is 1000 M⊙, this means that once the luminosity is about 105 L⊙, the luminosity per solar mass is about 10 − 100 L⊙/M⊙. Again, this is in good agreement with the values seen in Fig. 13 of Elia et al. (2017).
In order to define a reference the luminosities can be compared to, we defined a quantity Lglob = 0.5 × GM∗,tot Ṁ∗,tot/(2 R⊙), which would correspond to the accretion luminosity of an object of mass, M*, tot, and radius, 2 R⊙, accreting at a rate, Ṁ∗,tot, with an efficiency of facc = 0.5. The ratio ∑L*/Lglob is expected to be smaller than 1 because the luminosity is a non-linear quantity, which decreases with the number of stars. It gives a sense of how fragmented is the clump and how efficiently is the gravitational energy converted into radiation. The bottom-right panel shows ∑L*/Lglob for the six runs as a function of time. As expected, this quantity decreases with time and, at a later time, it reaches values as small as 10−3 and as high as 2 × 10−2, depending on the run. Interestingly, there is a clear trend for the magnetised runs to have values that are 1.5–2 times larger than their hydrodynamical counterpart. As we show later in this work, this is because magnetic field tends to reduce fragmentation, therefore building more massive stars that present higher luminosities.
3.3. General morphology
Figure 2 portrays the column density of the whole clump at time t = 0.11 Myr, which (as seen from Fig. 1) corresponds to a time where approximately 100–120 M⊙ have been accreted. The dark circles show the sink particles, which represent individual stars. The six simulations present a similar pattern. A complex network of intervowen and interconnected filaments have formed and three of them appear to be a little more prominent. Their length is approximately ≃0.3 pc and is comparable to the whole clump size. The three main filaments intersect, forming a hub located approximately at y = 0.75 pc and z = 0.65 pc. The stars are represented by the dark circles, which are mainly (though not exclusively) located in the hub and in the filaments. We recall that density filaments are naturally produced both by MHD turbulence (Hennebelle 2013; Federrath 2016; Xu et al. 2019), shocks (Abe et al. 2021), and by gravity (e.g. Smith et al. 2014; Abe et al. 2021), which for different reasons tend both to amplify anisotropies.
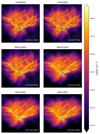 |
Fig. 2. Column density at t = 0.11 Myr for the six runs. The dark circles represent the sink particles aiming at describing the stars. |
Beyond these general similarities, significant differences between the six simulations are clearly visible. First of all, we see that radiative feedback has a clear influence on the cloud evolution and its fragmentation (Krumholz et al. 2007; Hennebelle et al. 2020b). For instance, there are more sinks in run HYDROf01 than in run HYDROf05 and in run MHD10f01 than in MHD10f05 (this will be further quantified in Sect. 5.1). This is a clear consequence of less heating when f = 0.1 than when f = 0.5. The impact on the gas structure appears to remain more limited. Second, clearly the magnetic field significantly reduces the numbers of sinks. This is particularly obvious by comparing run HYDROf05 with run MHD10f05 as well as run HYDROf01 with run MHD10f01. It is also clear that sink particles tend to form in higher column density regions in the magnetised runs. This clearly is a consequence of the support provided by the magnetic field which efficiently stabilises the gas particularly when its column density is not too high. This obviously happens only if the magnetic field is strong enough. Indeed, in run MHD100f05 which has an initial magnetic field that is ten times lower than run MHD10f05, the sink distribution is very similar to run HYDROf05. Interestingly, the sink distribution in run NMHDf05 is comparable to run MHD10f05 except near the high column densities areas, where a small excess of sinks is sometimes visible. This stems from the fact that ambipolar diffusion is efficient only at small scales and at high density.
4. Gas and magnetic field distribution
4.1. Density, velocity, and temperature profiles
Figure 3 displays radial profiles of various density-weighted quantities for runs MHD10f05 (left) and HYDROf05 (right) and at several timesteps. For the sake of concision, only two simulations are being displayed and discussed here. The adopted centre is the position of the most massive sink particle, which is located in the hub at y = 0.75 pc and z = 0.65 pc.
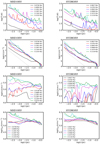 |
Fig. 3. Radial profiles at several timesteps in HYDROf05 and MHD10f05, respectively. The black dashed line in the density panel shows the singular isothermal sphere density. |
The first row displays the gas temperature, which we recall is initially uniform and equal to 10 K. As time goes on, temperature increases by two to three orders of magnitude in the centre and about one order of magnitude in the clump’s outer part. The temperature profile in the clump inner part broadly behaves as r−1, while it is almost flat in the clump outer part. We further note the presence of many temperature peaks associated to sink particles distributed through the clouds. We also stress that the temperature is clearly larger by a factor ≃1.5 in run MHD10f05 than in run HYDROf05. We come back to this particular point later in this work, however, we note here that this effect is similar to what was reported by Commerçon et al. (2011), on the basis of radiative MHD calculations and with higher temperatures reported in the MHD case. This is a consequence of the non-linearity of the accretion luminosity proportional to ṀM. By reducing fragmentation and extracting angular momentum, magnetic field increases both M and Ṁ leading to higher accretion luminosity. These temperatures appear to be in good agreement with the ones presented in Fig. 10 of Lin et al. (2022). For instance, the temperature at few 0.01 pc is about 100–200 K while at 0.1 pc it is typically 50–70 K.
The second row shows the density profiles. The straight line represents the density of the singular isothermal sphere (SIS), that is, 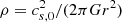 , where cs, 0 is the sound speed taken here equal to 0.2 km s−1. As the process of collapse proceeds, the density increases from outside-in and after roughly 0.1 Myr, it presents a power law-like shape close to, but slightly shallower than, r−2. As we see the values evolve with times and also slightly depend on the radius. We see however than it is nearly two orders of magnitude denser than the SIS, which is an expected consequence of the low initial thermal energy and the compactness of the cloud. The density in run HYDROf05 is slightly lower than in run MHD10f05, which is a consequence of the magnetic support. We recall that the r−2 density profile is the expected density structure of a spherical collapsing cloud (e.g. Larson 1969; Shu 1977) since, together with a uniform radial velocity, it leads to a roughly constant accretion rate through the cloud (Li 2018; Gómez et al. 2021). When turbulence is included, it is however common to find profiles slightly shallower, for instance ρ ∝ r−1.5 is often reported (e.g. Murray & Chang 2015; Li et al. 2018); however, in the present case this value seems a little too shallow.
, where cs, 0 is the sound speed taken here equal to 0.2 km s−1. As the process of collapse proceeds, the density increases from outside-in and after roughly 0.1 Myr, it presents a power law-like shape close to, but slightly shallower than, r−2. As we see the values evolve with times and also slightly depend on the radius. We see however than it is nearly two orders of magnitude denser than the SIS, which is an expected consequence of the low initial thermal energy and the compactness of the cloud. The density in run HYDROf05 is slightly lower than in run MHD10f05, which is a consequence of the magnetic support. We recall that the r−2 density profile is the expected density structure of a spherical collapsing cloud (e.g. Larson 1969; Shu 1977) since, together with a uniform radial velocity, it leads to a roughly constant accretion rate through the cloud (Li 2018; Gómez et al. 2021). When turbulence is included, it is however common to find profiles slightly shallower, for instance ρ ∝ r−1.5 is often reported (e.g. Murray & Chang 2015; Li et al. 2018); however, in the present case this value seems a little too shallow.
The radial velocity through the cloud is presented in the third row. At 0.1 Myr, a constant radial velocity of ≃1.5 − 2 km s−1 appears to reasonably represent the cloud radial velocity for radius between 0.03 and 0.3 pc. The radial velocity increases towards the cloud inner part where it reaches ≃10 km s−1. The parallel velocity, which represent both turbulent and rotation (i.e. the non-radial component) is displayed in the fourth row. Due to the chosen initial conditions, it is of the order of ≃2 km s−1 in the cloud outer part. As the collapse proceeds and due to the increase of vr, turbulence is further amplified toward the cloud centre (Hennebelle 2021) and this behaviour explains the density profile being shallower than r−2. These velocity values are in good agreement with the values presented in Fig. 22 of Lin et al. (2022). For instance at 0.1 pc, values of about 3 km s−1 are reported.
4.2. Mass distribution
The mass distribution, which we recall is equivalent to the mass weighted density PDF, is displayed in Fig. 4 for the six simulations at several time steps. The distribution contains several features and going from low to high densities four domains can be identified: the interclump medium, the clump outer part, the collapsing envelopes, and the high density material. We stress that the last two do not correspond to a single physical region but, rather, they develop around each individual collapse centre.
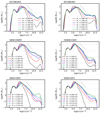 |
Fig. 4. Mass distribution as a function of density at several timesteps for the six runs. Section 4.2 describes the corresponding physical regimes. The dotted line shows a powerlaw behaviour M ∝ n−1/2 as expected for a density PDF ∝n−3/2 (see Sect. 4.2.3). |
4.2.1. The interclump medium
At low density, the mass distribution presents a roughly lognormal shape which peaks at about 500 cm−3 (e.g. Vázquez-Semadeni 1994; Federrath et al. 2008; Kritsuk et al. 2011) and remains stationary through time. It is due to the development of turbulence in the cloud outerpart. The latter has formed by the turbulent-driven expansion of the cloud external layer and, clearly, it contains a small amount of mass.
4.2.2. The clump’s outer part
At higher density, that is, ρ ≃ 105 − 106 cm−3, a second peak of the mass distribution located at the cloud initial mean density, is visible. It contains most of the mass of the cloud and shifts toward higher densities as collapse proceeds. Meanwhile (as expected), the mass it contains declines over time. Overall the mass distribution of this density range is similar for the six simulations. We can nevertheless note that the peak is a bit broader for the two hydro runs, than for the more magnetised runs MHD10f01, MHD10f05, and NMHDf05. This is likely a consequence of the magnetic field which is known to reduce the turbulent dispersion of the density distribution (e.g. Molina et al. 2012).
4.2.3. The collapsing envelopes
At densities higher than its peak value, the mass distribution is better described by a power law behaviour up to densities of 109 and even 1010 cm−3. This part of the mass distribution corresponds to the n ∝ r−α, α ≃ 2 envelope discussed in Fig. 3.
We recall that there is a simple correspondence between α and the index of the mass distribution. Let 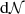 be the number of fluid particles located between radius r and r + dr. We have dṄ∝r2dr. But since n ∝ r−α, we have dṄ/dlog n ∝ n−3/α and the mass weighted density PDF is:
be the number of fluid particles located between radius r and r + dr. We have dṄ∝r2dr. But since n ∝ r−α, we have dṄ/dlog n ∝ n−3/α and the mass weighted density PDF is:
For α ≃ 2, we thus find that ndṄ/dlog n ∝ n−1/2, which indeed is close to the observed bevaviour of the mass distribution between 107 and 109 − 1010 cm−3 as shown by a comparison with the dotted lines.
Several aspects are worth noting. First at early stages (black and red curves), the mass distributions evolve with time. More mass is gradually accumulated at high densities as collapse proceeds. Once the n ∝ r−2 envelope is fully developed, the mass distribution is stationary. This is all consistent with the stationarity observed in Fig. 3, illustrating that the accretion rate remains broadly constant with time.
4.2.4. The high-density material
At density larger than 109 − 1010 cm−3, the mass distribution becomes flatter, meaning that mass is pilling up. This is a consequence of rotational and thermal supports. Indeed protoplanetary disks form (see Lebreuilly et al. 2021, for a description of disks in similar simulations). Clearly the amount of mass significantly varies with magnetisation and it is several times higher in the hydro runs than in the significantly magnetised ones (MHD10). This is a clear consequence of magnetic braking, which, via the extraction of angular momentum, leads to smaller and less massive disks.
4.3. Temperature versus density distributions
Figure 5 shows the mean temperature as a function of density in the six simulations. In each density bin, the mean temperature is simply the mass weighted temperature. The overall behaviour is as suggested by the temperature profiles shown in Sect. 4.1.
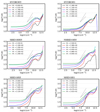 |
Fig. 5. Mass-weighted temperature in density intervals as a function of density at six time steps for the six runs. The dotted lines show a powerlaw behaviour of T ∝ n1/2 and T ∝ n0.3, respectively. |
The temperature associated to the high density material is typically larger than ≃300 K and reaches values of few thousands K. As expected, the temperature increases with f.
For the lower density material (i.e. n < 109 cm−3), we see first that the temperature decreases roughly as T ∝ n−0.3 − 0.5 (as indicated by the dotted line) and then at density of about ≃107 cm−3, it reaches a plateau and remains constant, T = Text, at lower densities. Depending on the runs and the time, the temperatures vary between 10 and up to ≃30 K.
To interpret these temperatures, we developed a simple spherical model which is presented in Sect. A. Although we see from Fig. 2 that the clouds are not spherical and that the sources are not clustered in the centre as assumed in our model, this nevertheless allows us to get a deeper understanding of these temperatures. The inferred power-law behaviours are as described by Eqs. (A.4) and (A.8). More precisely, Eq. (A.4) combined with Eq. (A.1) predicts that for T > 100 K, T ∝ n0.5 while for T < 100 K, T ∝ n0.3.
To quantitatively estimate the values of Text, we use Eq. (A.9):
where we recall that δ is as defined by Eq. (A.1) and τ0 is the optical depth at which the radiation is free streaming.
From Figs. 1 and 5, we see that when Ltot ≃ 105 L⊙, Text ≃ 30 K, whereas when Ltot ≃ 104 L⊙Text ≃ 20 K, which is close to what Eq. (5) predicts. Looking at Fig. 5 of Elia et al. (2017), we see that 20–30 K corresponds to the temperature of the warmest star-forming clumps, which agrees well with the relatively high luminosities that we inferred. The HiGAL-based temperature is the average termperature of the cold dust in a clump. They are derived from 160-to-500 (and 870, 1100, when available) μm grey-body fit, so that probed temperatures cannot be higher than this value. Since the mass in the outer part of the clump dominates, this cold component corresponds to that of the outer layers and of most of the volume of the clump. This should therefore broadly correspond to Text.
4.4. Magnetic field distributions
Figure 6 portrays the volume weighted magnetic intensity as a function of gas density for the four magnetised simulations. Overall, we see that, at least for n between 107 and 109 cm−3, the magnetic field scales with density broadly as B ∝ n1/2, a result observed in previous works (see for instance Hennebelle & Inutsuka 2019, for a review). This is a consequence of the field amplification induced by field lines dragging by collapsing motion. Even more simply, this is likely a consequence of energy equipartition. As seen in Fig. 3, v2 depends weakly on r while n ∝ r−2, therefore the kinetic energy scales as r−2 and thus B ∝ r−1 ∝ n1/2. Interestingly, this implies that the Alfvén velocity, Va, remains roughly constant in this range of density. We see, however, that its value is not identical for the four runs. We estimate that for runs MHD10f05 and MHD10f01, Va ≃ 1 − 1.2 km s−1, while for run MHD100f05, Va is less than half this value. When non-ideal MHD is treated, the Alfvén velocity is reduced by tens of percents at n ≃ 109 cm−3.
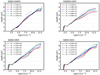 |
Fig. 6. Magnetic field as a function of density at several timesteps for the four magnetised runs. The dotted line shows a powerlaw behaviour B ∝ n1/2. |
At lower densities, the behaviour depends on the field intensity. For run MHD100f05, the dependence of B on n, is a bit stiffer. This is expected as when the field is weak, the clump contraction tends to be spherical in which case B ∝ n2/3 (Li et al. 2015). This explains why the magnetic field at high density in run MHD100f05 is larger than a tens of the B values in run MHD10f05. Magnetic intensity is more vigorously amplified when it is weaker.
At high densities, that is, n > 109 cm−3, the magnetic field is further amplified up to density values on the order of 1011 cm−3. The highest magnetic intensities vary from one run to the other. In the most magnetised runs, MHD10f05 and MHD10f01, it reaches ≃100 G and about one third of this in run MHD100f05. Run NMHDf05 presents different behaviour. For n > 1010 cm−3, the intensity is nearly independent of n and the largest intensities is about ≃30 G. This behaviour, which has been discussed previously (e.g. Masson et al. 2016; Wurster & Li 2018) is a consequence of ambipolar diffusion that tends to diffuse the field. This implies that the influence of magnetic field on the high density gas is significantly reduced compared to ideal MHD runs.
5. Stellar mass spectrum
5.1. Fragmentation and massive stars
Figure 7 portrays the number of sink particles as a function of accreted mass (left panel) as well as the mass of the most massive star (right panel). The number of sinks at the end of the simulations is typically between 100 and 300 depending of the runs. As anticipated from the clump images, both magnetic field and radiative feedback reduce fragmentation. Here, we see that the differences between runs HYDROf05 and MHD10f05 or between HYDROf01 and MHD10f01 is about a factor of 2, the difference being more pronounced for the two runs with facc = 0.5. On the other hand, the differences between runs MHD10f05 and MHD10f01 is on the order of 50%, showing that whereas radiative feedback contributes to reduce fragmentation, its effect is comparatively lower than magnetic field. Indeed, although the initial magnetisation of run MHD100f05 is quite weak, it nevertheless reduces the fragmentation by tens of percents compared to run HYDROf05. Interestingly, run NMHDf05, which treats ambipolar diffusion and has the same magnetisation than run MHD10f05, presents a number of sinks similar to run MHD100f05.
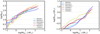 |
Fig. 7. The number of sinks (left panel), Ntot and the largest sink mass (right panel) as a function of the total accreted mass, Mtot, in several runs. |
In all runs but HYDROf01, two phases can be distinguished. When Mtot, * is smaller than ≃3 M⊙ (≃10 for run HYDROf05), the number of sinks increases fast and is nearly proportional to 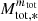 with mtot ≃ 0.7 − 1. Beyond this value, the number of sinks increases much less rapidly and typically mtot ≃ 0.2 − 0.3. For instance for run MHD10f05, the number of sinks has roughly doubled between the time when Mtot, * = 10 M⊙ and Mtot, * = 100 M⊙. This is most certainly related to radiative feedback and to the global increase of temperature within the clumps. The consequence is obvioulsy that the sink particles, build their masses in this second phase after fast fragmentation has occurred.
with mtot ≃ 0.7 − 1. Beyond this value, the number of sinks increases much less rapidly and typically mtot ≃ 0.2 − 0.3. For instance for run MHD10f05, the number of sinks has roughly doubled between the time when Mtot, * = 10 M⊙ and Mtot, * = 100 M⊙. This is most certainly related to radiative feedback and to the global increase of temperature within the clumps. The consequence is obvioulsy that the sink particles, build their masses in this second phase after fast fragmentation has occurred.
At the end of the runs, the mass of the most massive star is between 3 and 10 M⊙. The observed trends are in good agreement with the sink numbers. The mass of the most massive star is higher when magnetic field and radiative feedback are larger and magnetisation is comparatively slightly more efficient than radiative feedback in producing massive stars. Two phases of growth can also be distinguished, typically below and above Mtot, * ≃ 10 M⊙, where Mmax grows respectively slowly and fastly. We observe that 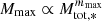 with mmax ≃ 0.5 when Mtot, * < 10 M⊙, while mmax ≃ 1 otherwise.
with mmax ≃ 0.5 when Mtot, * < 10 M⊙, while mmax ≃ 1 otherwise.
We note an important feature of the stellar mass distribution is that in a group of stars which in total contains about 100–120 M⊙, a star more massive than 8 M⊙ is expected. We see that in our simulations only runs MHD10f05 and MHD10f01 have reached this value. Runs HYDROf05 and MHD100f05 are slightly below while run HYDROf01 is almost a factor of 3 below. This may constitute a hint that magnetic field is playing a role regarding the building of the massive stars, essentially by reducing the cloud fragmentation.
5.2. The sink mass function
Figure 8 displays the sink mass function, ought to represent the initial mass function, for the six runs and three values of Mtot, *.
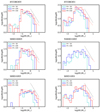 |
Fig. 8. Mass spectra at various times characterised by the total accreted mass, for the six runs and for three values of the accreted mass. The red dotted lines represent the analytical model presented in the paper for comparison. The black dotted one shows for reference a M−1 power laws. |
5.2.1. Analytical model
Before presenting the stellar mass spectra induced from the simulations, we discuss an analytical model that will be useful to interpret the results. It is in essence the model proposed in Hennebelle & Chabrier (2008), in which the density PDF is the one appropriated to the gravitational collapse and stated by Eq. (4) as proposed in Lee & Hennebelle (2018a). For the sake of completeness, it is described in Appendix B. Equations (B.6) and (B.7) are the final equations to be used. Let us remember that the model predicts two asymptotic behaviours. At small mass, when thermal or magnetic support dominates, Γ → 0, while at larger mass, when turbulent support dominates, Γ → 3/4. The transition between these two regimes occurs at scales or equivalently masses (see Eq. (B.6)) for which thermal and magnetic and turbulent supports are comparables.
In order to be compared with the numerical simulations, one needs to specify the values of the sound speed, cs, of the Alfvén speed, Va, and of the turbulent velocity dispersion, V0. All these values can be inferred from the results presented in Sect. 4. Another important point when comparing simulations with the analytical model is the normalisation. For this purpose, we write:
Thus, 𝒩0 as defined by Eq. (B.7), is determined once Mtot, *, Mmin, and Mmax are specified. The various parameters are reported in Table 2. Since cs, Va, and V0 are all evolving with time and positions, the reported values are global estimates.
We recall that the model is isothermal in nature. The sound speed may vary for instance over time but remains uniform within the whole cloud. This has an important consequence, which is that the model does not predict a minimum stellar mass. We should, however, remember that the isothermal assumption becomes invalid when the density reaches density on the order of 1010 cm−3 when the gas becomes progressively adiabatic. As discussed in Hennebelle et al. (2019), the change of thermal behaviour, which leads to the formation of the first hydrostatic core (Larson 1969), results in a peak or cut-off for the IMF at typically several times the mass of the first hydrostatic cores, ML (that we recall is about ML ≃ 0.03 M⊙). This implies that the analytical model is valid for masses larger than a few times ML and this is why we choose Mmin = 0.1 M⊙. The values of Mmax are taken from Fig. 7.
5.2.2. The hydrodynamical runs
The two top panels of Fig. 8 show results for run HYDROf05 and HYDROf01. The mass spectra are similar to those obtained in Hennebelle et al. (2020b) with slightly different initial conditions and less spatial resolution. Essentially, most of the sinks have their mass between few 10−2 and few M⊙. The distributions present a plateau that ranges between ≃0.1 and ≃0.5 M⊙. A relatively sharp drop occurs around 0.1 M⊙ and we get a small number of objects at lower mass, particularly in run HYDROf05. At mass larger than ≃0.5 M⊙, the distribution drops following a powerlaw-like behaviour, whose index cannot be reliably determined due to the lack of statistics. A tentative M−1 distribution (dotted line) is represented for comparison. This value is similar to what previous authors have inferred from simulations (Bonnell et al. 2011; Girichidis et al. 2011; Ballesteros-Paredes et al. 2015; Lee & Hennebelle 2018a,b; Padoan et al. 2020). Overall, we see that there is a good agreement between the analytical model (red dotted line), and the sink mass distribution, or M > 0.1 M⊙. We stress that the main effect of increasing radiative feedback is to broaden the distribution toward larger masses. From the analytical model, we see that this is compatible with this being a consequence of the mean cloud temperature increasing due to the radiative heating.
The peak of the distribution however is barely affected. This confirms, as claimed in Hennebelle et al. (2020b), that radiative feedback is not responsible of setting the peak of the IMF. In fact, at early time (total accreted mass of 50 M⊙), the distribution is clearly peaked toward 0.1–0.2 M⊙ which is several times the mass of the first hydrostatic core. As time goes on, the mass of the most massive stars increases while the number of low mass objects remains constant or increases moderately. This is entirely compatible with the idea that the stars inherite a minimum mass reservoir equal to a few times the mass of the first hydrostatic core (Hennebelle et al. 2019; Colman & Teyssier 2020), which is swiftly accreted. After this, the stars keep accreting from their mass reservoir which likely is set by gravo-turbulence (Padoan et al. 1997; Hennebelle & Chabrier 2008; Hopkins 2012). While this process should largely be deterministic in nature, it is also likely the case that stochastic processes modulate this accretion as well (Bonnell et al. 2001; Basu & Jones 2004; Basu et al. 2015).
5.2.3. The influence of magnetic field on the stellar mass spectrum
The influence of magnetic field can be seen by comparing, on one hand, runs HYDROf05, MHD100f05 and MHD10f05 and, on the other hand, run HYDROf01 with run MHD10f01. Clearly, magnetic field has a significant impact on the mass spectrum that it tends to broaden towards larger masses. In fact, the low mass distribution is almost unchanged. Again this provides further confirmation that radiative feedback has no significant impact on the low mass end of the stellar initial mass function since as discussed above magnetic field leads to stronger radiative feedback. This also obviously shows that magnetic field does not influence the low mass end of mass spectrum in good agreement with the idea that it is mainly linked to the mass of the hydrostatic core.
Run MHD10f05 presents a plateau that extends from about 0.1 M⊙ to ≃2 M⊙. It is reminiscent of run A presented in Fig. 6 of Lee & Hennebelle (2018a) and the run presented in Fig. 2 bottom panel of Jones & Bate (2018). These runs have in common to have a high thermal energy initially or equivalently a low Mach number. The analytical model suggests that when thermal support is high, a collapsing clump would indeed develop a stellar mass spectrum, dN/dlog M ∝ M0, while when turbulent support dominates the support of the mass reservoir, dN/dlog M ∝ M−3/4 is expected. Likely enough run MHD10f05 falls in the regime where thermal and magnetic field dominates over turbulence at the scale of the mass reservoirs and this explains the flat mass spectrum. This is indeed what the good agreement with the MHD models and the simulations suggests since the broad plateau (where dN/dlog M ∝ M0) displayed by the analytical models is due to combination of a high Alfvén velocity and a high sound speed.
Compared to run MHD10f05, the mass spectum of run MHD10f01 presents a plateau that is less broad. This is the case both for the numerical and the analytical models, which are again in good agreement. This clearly is due to the lower temperatures in run MHD10f01, which compared to run MHD10f05, leads to weaker thermal support.
5.2.4. The impact of ambipolar diffusion
The mass spectrum of run NMHDf05 presents similarities with the one of run MHD10f05 but also significant differences. Overall it is more similar to the mass spectrum of run MHD10f01. First of all, unlike run MHD10f05, it does not present a plateau that extends up to ≃3 M⊙ but rather stops at 1 M⊙ and the most massive stars are also less massive. This is in good agreement with the slightly lower magnetic field which is found for run NMHDf05 (see Fig. 6) than for run MHD10f05. The similarity with run MHD10f01 likely comes from the total support due to both thermal and magnetic supports are closer because run MHD10f01 has stronger field but lower temperatures than run NMHDf05.
A more surprising difference comes from the low-mass objects. As can be seen, there are more sink particles of masses lower than 0.1 M⊙ in run NMHDf05 than in the ideal MHD runs but also more than in the hydrodynamical runs. The reason for this remains to be clarified. The most likely explanation is the relatively weak magnetic field intensity at density above 1010 cm−3 in run NMHDf05 compared for instance to run MHD10f05. As seen from Fig. 6, the change of behaviour is relatively sharp, with B being very comparable in runs NMHDf05 and MHD10f05 below 1010 cm−3. Thus while in both runs, high densities may develop due to field support, the field support drops at density above 1010 cm−3 for run NMHDf05 and this may favor fragmentation. This may also be due to the difference in the disk populations that form in the various runs and presented in Lebreuilly et al. (2021). The disks formed in non-ideal MHD runs are intermediate in mass and size between the hydrodynamical disks and the ones which form in ideal MHD runs. While the latter are usually very stable due to the fast growth of a toroidal magnetic component, but since more mass is available in bigger disks, the former fragments tend to form bigger objects than in non-ideal MHD disks.
6. Discussions
6.1. Dependence of the high-mass slope of the stellar mass spectrum
As discussed in the previous section, our numerical results suggest that from a few solar mass to at least 7–8 M⊙, the stellar distribution presents a power law behaviour dN/dlog M ∝ M−Γ, with Γ ≃ 3/4. Analytically, this behaviour is found when at the scale of the individual mass reservoir, (i) the dominant support against gravity is turbulence and (ii) when the density PDF is ∝ρ−3/2, which is a consequence of gravitational collapse. On the other-hand, when the density PDF is close to a lognormal distribution, we do expect Γ ≃ 1.3, as discussed in Lee & Hennebelle (2018a). In essence, the density PDF is a direct estimate of how the gas mass is distributed amongst densities and therefore controls the number of density fluctuations at a given density. Typically a log-normal distribution has less dense gas than a PDF ∝ρ−3/2 and therefore less small mass objects are produced with the former than with the latter. The transition between the two exponents, Γ = 3/4 and Γ = 1.3, is expected to occur at the density, ntrans, which typically connects the turbulent log-normal PDF to the power law ∝ρ−3/2 gravitational PDF. In the present simulations this occurs around ≃106 cm−3. Combining Eqs. (B.3) and (B.6), we can estimate the mass, Mtrans it corresponds to
where for simplicity, we have assumed η = 0.5 and 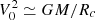 . Because of the sixth power which appears for V0 or Rc, the clump radius, the value of Mtrans is clearly not accurate and likely can abruptly change from one environment to another. Typically, we expect a fast transition around Rc ≃ 0.3 pc. It is however illustrative and shows that for our simulations, at high mass, the mass spectra are expected to be mostly if not exclusively described by the Γ = 3/4 exponent since our stellar masses are smaller than 15 M⊙. It also shows that in a less dense and compact clump, the transition should occur at smaller masses since the value of V0, or equivalently the value of Rc, should be smaller. While most of the studies which have started from massive clumps, comparable to the ones studied here, tend to present Γ lower than the canonical Salpeter exponent (see the discussion in Lee & Hennebelle 2018a), those works that have the IMF obtained from larger scale clouds studies – obtaining the IMF in larger scale simulations with initial conditions that correspond to more standard giant molecular clouds – generally report Γ values that are closer to 1.3. This is the case, for instance, for the run XL-F presented in Fig. 4 of He et al. (2019) and the run presented in Fig. 3 of Padoan et al. (2020) for masses between 10 and 50 M⊙, respectively. This is also the case for the runs presented in Ntormousi & Hennebelle (2019) and the core mass function extracted from these simulations (Louvet et al. 2021).
. Because of the sixth power which appears for V0 or Rc, the clump radius, the value of Mtrans is clearly not accurate and likely can abruptly change from one environment to another. Typically, we expect a fast transition around Rc ≃ 0.3 pc. It is however illustrative and shows that for our simulations, at high mass, the mass spectra are expected to be mostly if not exclusively described by the Γ = 3/4 exponent since our stellar masses are smaller than 15 M⊙. It also shows that in a less dense and compact clump, the transition should occur at smaller masses since the value of V0, or equivalently the value of Rc, should be smaller. While most of the studies which have started from massive clumps, comparable to the ones studied here, tend to present Γ lower than the canonical Salpeter exponent (see the discussion in Lee & Hennebelle 2018a), those works that have the IMF obtained from larger scale clouds studies – obtaining the IMF in larger scale simulations with initial conditions that correspond to more standard giant molecular clouds – generally report Γ values that are closer to 1.3. This is the case, for instance, for the run XL-F presented in Fig. 4 of He et al. (2019) and the run presented in Fig. 3 of Padoan et al. (2020) for masses between 10 and 50 M⊙, respectively. This is also the case for the runs presented in Ntormousi & Hennebelle (2019) and the core mass function extracted from these simulations (Louvet et al. 2021).
6.2. Observationally inferred mass distribution in actively star-forming regions
While it may sound surprising at first not to find Γ ≃ 1.3, which is the slope inferred by Salpeter (1955), it should be stressed that recent observations have been inferring that in some actively star-forming regions, the IMF may indeed be top-heavy (Zhang et al. 2018; Lee et al. 2020). More precisely, in the Arches cluster Hosek (2019) inferred Γ ≃ 0.8. On the other hand, recent studies of the core mass function also obtained within massive star-forming regions have also inferred power law behaviours with indices of Γ ≃ 0.95 (Motte et al. 2018; Pouteau et al. 2022). As cores are widely assumed to be the progenitors of stars out of which they build their mass, the inferred Γ values are compatible with the idea that the shape of the IMF in massive star-forming regions is inherited from the shape of the CMF, at least at high masses, although eventually it should be compared with the IMF of the very same region.
While more detailed investigations, including careful comparisons between simulations and observations must be carried out before firm conclusions can be drawn, there is a clear suggestion coming from both observations and theories that systematic variations of the IMF may occur, particularly in very compact star-forming regions.
6.3. Limits of the present work and the ‘universality’ of the IMF
Our work presents several important limits that need to be discussed. Indeed, one of the conclusion is that the combination of magnetic field and radiative transfer possibly leads to more variability that what observational inferences of the IMF may have led us to conclude. Admittedly, this question even for our own Galaxy remains difficult to address, particularly because of the relatively limited samples that are often available but it seems nevertheless unavoidable that at least some level of fluctuations should be present (see for instance the comprehensive discussion provided in Dib 2022).
Determining whether the variations observed in the present work are compatible with the galactic fluctuations of the IMF, is beyond the scope of the present paper, but it is worth to noting that an important source of variations is due to the efficiency of the accretion luminosity expressed by the parameter facc. Whereas there may be some variability of facc, it is not likely that it is a factor of 5, as we have been exploring here. The other possibly extreme variations we have considered is magnetic intensity since we have explored a factor of 10 (and even go to pure hydrodynamical cases). This is not well constrained yet, but a 1000 M⊙ clump is a relatively large ensemble and it is unclear what the variations of the magnetisation are in the galactic populations.
Finally, we stress that a potentially important process has been omitted in this work, namely, that of the protostellar jets. Recently, Guszejnov et al. (2021) have explored their impact in simulations comparable to the ones presented here (with a resolution of few tens of AU). They concluded that protostellar jets may be playing a significant role in setting the IMF in particular for the formation of low-mass objects in the presence of a significant initial magnetic field. Whether this process may help explaining the universality of the IMF is not, however, clear at present.
7. Conclusions
With the goal of understanding how magnetic field and radiative feedback influence the collapse and the fragmentation of a massive star-forming clump, we performed high-resolution adaptive mesh calculations with a spatial resolution down to about 1 AU. Six runs featuring two radiative feedback efficiencies, three magnetic intensities as well as the impact of non-ideal MHD are explored here. We show that the physical characteristics of the simulated star-forming clumps show a good comparison with various observations. This is, for instance, the case for the observational bolometric luminosities that we compared with the total luminosities of the sink particles produced in the simulations as well as for the gas temperatures. For the latter, we develop an analytical model which agrees well with the temperatures inferred from the simulations.
The stellar mass spectra of the six runs are analysed in detail and compared with an analytical model in which thermal, magnetic, and turbulent supports are playing a major role. Overall the analytical model reproduces well the numerical mass spectra for masses above ≃0.1 M⊙. At this mass, which corresponds to a few times the mass of the first hydrostatic core, the underlying gas thermodynamics is nearly adiabatic and specific models should be considered (e.g. Hennebelle et al. 2019). The combination between simulations and analytical results allows us to clearly assess the role and influence of each physical process which are as follows:
-
In the density range at which the gas is not adiabatic, the density PDF which is ∝ρ−3/2 is deeply shaping the stellar mass spectrum and leads to two physical distinct regimes for the mass spectra.
-
At masses larger than ≃ 0.1 M⊙, thermal pressure and magnetic field may lead to a flat mass spectrum, namely, dN/dlog M ∝ M−Γ with Γ ≃ 0 if they are strong enough compared to turbulence.
-
At larger scales, turbulence dominates and may lead to a mass spectrum with Γ ≃ 3/4. At even larger scales and lower density, the PDF is expected to be log-normal in shape and stiffer mass spectra, with larger Γ are expected.
-
the transition between the regime with Γ ≃ 0 and Γ ≃ 3/4 is not universal and depends on the local physical processes such as thermal support, magnetic field, and Mach number.
Generally speaking, we find that the main effect of magnetic field and radiative transfer is to reduce the total number of fragments and to increase the mass of the most massive stars. These latter have been found to increase with the magnetic intensity and the radiation feedback efficiency. For instance, in the present work, we found that for the hydrodynamical simulation with the lowest efficiency, the most massive star produced after 150 M⊙ have been accreted, is about 3 M⊙. With a higher radiative feedback efficiency or a sufficiently strong initial field, stars of masses 7–8 M⊙ are produced. We therefore conclude that whereas magnetic field and radiative feedback may not be essential to explain the peak or the various slope values of the IMF, they may be essential to reproduce the exact shape (such as the transition between the various regimes), the level of fragmentation, that is, the number of stars formed and the mass of the most massive stars.
Acknowledgments
We thank the anonymous referee for a useful report. This work was granted access to HPC resources of CINES and CCRT under the allocation x2014047023 made by GENCI (Grand Équipement National de Calcul Intensif). This research has received funding from the European Research Council synergy grant ECOGAL (Grant : 855130). G.A.F also acknowledges support from the Collaborative Research Centre 956, funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) project ID 184018867. T.N. acknowledges support from CONACyT Ciencia de Frontera project ID 86372. R.S.K. also acknowledges funding from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) via the Collaborative Research Center “The Milky Way System” (SFB 881 – funding ID 138713538 – subprojects A1, B1, B2 and B8), from the Heidelberg Cluster of Excellence (EXC 2181 - 390900948) “STRUCTURES”, funded by the German Excellence Strategy, and from the German Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action for funding in the project “MAINN” (funding ID 50OO2206).
References
- Abe, D., Inoue, T., Inutsuka, S.-I., & Matsumoto, T. 2021, ApJ, 916, 83 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Ballesteros-Paredes, J., Hartmann, L. W., Pérez-Goytia, N., & Kuznetsova, A. 2015, MNRAS, 452, 566 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Bastian, N., Covey, K. R., & Meyer, M. R. 2010, ARA&A, 48, 339 [Google Scholar]
- Basu, S., & Jones, C. E. 2004, MNRAS, 347, L47 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Basu, S., Gil, M., & Auddy, S. 2015, MNRAS, 449, 2413 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Bate, M. R. 2009, MNRAS, 392, 1363 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Bate, M. R., Bonnell, I. A., & Bromm, V. 2003, MNRAS, 339, 577 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Bhandare, A., Kuiper, R., Henning, T., et al. 2020, A&A, 638, A86 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Bleuler, A., & Teyssier, R. 2014, MNRAS, 445, 4015 [Google Scholar]
- Bonnell, I. A., Bate, M. R., Clarke, C. J., & Pringle, J. E. 2001, MNRAS, 323, 785 [Google Scholar]
- Bonnell, I. A., Smith, R. J., Clark, P. C., & Bate, M. R. 2011, MNRAS, 410, 2339 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Chabrier, G. 2003, PASP, 115, 763 [Google Scholar]
- Colman, T., & Teyssier, R. 2020, MNRAS, 492, 4727 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Commerçon, B., Teyssier, R., Audit, E., Hennebelle, P., & Chabrier, G. 2011, A&A, 529, A35 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Commerçon, B., Debout, V., & Teyssier, R. 2014, A&A, 563, A11 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Commerçon, B., González, M., Mignon-Risse, R., Hennebelle, P., & Vaytet, N. 2022, A&A, 658, A52 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Crutcher, R. M. 2012, ARA&A, 50, 29 [Google Scholar]
- Dib, S. 2022, A&A, 666, A113 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Elia, D., Molinari, S., Schisano, E., et al. 2017, MNRAS, 471, 100 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Elia, D., Merello, M., Molinari, S., et al. 2021, MNRAS, 504, 2742 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Federrath, C. 2016, MNRAS, 457, 375 [Google Scholar]
- Federrath, C., Klessen, R. S., & Schmidt, W. 2008, ApJ, 688, L79 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Fromang, S., Hennebelle, P., & Teyssier, R. 2006, A&A, 457, 371 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Girichidis, P., Federrath, C., Banerjee, R., & Klessen, R. S. 2011, MNRAS, 413, 2741 [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, G. C., Vázquez-Semadeni, E., & Palau, A. 2021, MNRAS, 502, 4963 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- González, M., Audit, E., & Huynh, P. 2007, A&A, 464, 429 [Google Scholar]
- Guszejnov, D., Grudić, M. Y., Hopkins, P. F., Offner, S. S. R., & Faucher-Giguère, C.-A. 2020, MNRAS, 496, 5072 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Guszejnov, D., Grudić, M. Y., Hopkins, P. F., Offner, S. S. R., & Faucher-Giguère, C.-A. 2021, MNRAS, 502, 3646 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Haugbølle, T., Padoan, P., & Nordlund, Å. 2018, ApJ, 854, 35 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- He, C.-C., Ricotti, M., & Geen, S. 2019, MNRAS, 489, 1880 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Hennebelle, P. 2013, A&A, 556, A153 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Hennebelle, P. 2018, A&A, 611, A24 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Hennebelle, P. 2021, A&A, 655, A3 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Hennebelle, P., & Chabrier, G. 2008, ApJ, 684, 395 [Google Scholar]
- Hennebelle, P., & Inutsuka, S.-I. 2019, Front. Astron. Space Sci., 6, 5 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Hennebelle, P., Lee, Y.-N., & Chabrier, G. 2019, ApJ, 883, 140 [Google Scholar]
- Hennebelle, P., Commerçon, B., Lee, Y.-N., & Charnoz, S. 2020a, A&A, 635, A67 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Hennebelle, P., Commerçon, B., Lee, Y.-N., & Chabrier, G. 2020b, ApJ, 904, 194 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, P. F. 2012, MNRAS, 423, 2037 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Hosek, M. W., Jr., Lu, J. R., Anderson, J., et al. 2019, ApJ, 870, 44 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Hosokawa, T., & Omukai, K. 2009, ApJ, 691, 823 [Google Scholar]
- Jaura, O., Glover, S. C. O., Klessen, R. S., & Paardekooper, J. P. 2018, MNRAS, 475, 2822 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Jones, M. O., & Bate, M. R. 2018, MNRAS, 478, 2650 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Klessen, R. S. 2001, ApJ, 556, 837 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kritsuk, A. G., Norman, M. L., & Wagner, R. 2011, ApJ, 727, L20 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kroupa, P. 2001, MNRAS, 322, 231 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Krumholz, M. R., Klein, R. I., & McKee, C. F. 2007, ApJ, 656, 959 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Krumholz, M. R., Klein, R. I., & McKee, C. F. 2012, ApJ, 754, 71 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper, R., & Yorke, H. W. 2013, ApJ, 772, 61 [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper, R., Klahr, H., Dullemond, C., Kley, W., & Henning, T. 2010, A&A, 511, A81 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Lane, H. B., Grudić, M. Y., Guszejnov, D., et al. 2022, MNRAS, 510, 4767 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Larson, R. B. 1969, MNRAS, 145, 271 [Google Scholar]
- Lebreuilly, U., Hennebelle, P., Colman, T., et al. 2021, ApJ, 917, L10 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-N., & Hennebelle, P. 2018a, A&A, 611, A88 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-N., & Hennebelle, P. 2018b, A&A, 611, A89 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-N., & Hennebelle, P. 2019, A&A, 622, A125 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-N., Offner, S. S. R., Hennebelle, P., et al. 2020, Space Sci. Rev., 216, 70 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.-X. 2018, MNRAS, 477, 4951 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Li, P. S., McKee, C. F., & Klein, R. I. 2015, MNRAS, 452, 2500 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Li, P. S., Klein, R. I., & McKee, C. F. 2018, MNRAS, 473, 4220 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y., Wyrowski, F., Liu, H. B., et al. 2022, A&A, 658, A128 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Louvet, F., Hennebelle, P., Men’shchikov, A., et al. 2021, A&A, 653, A157 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Marchand, P., Masson, J., Chabrier, G., et al. 2016, A&A, 592, A18 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Masson, J., Teyssier, R., Mulet-Marquis, C., Hennebelle, P., & Chabrier, G. 2012, ApJS, 201, 24 [Google Scholar]
- Masson, J., Chabrier, G., Hennebelle, P., Vaytet, N., & Commerçon, B. 2016, A&A, 587, A32 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, S. S., & Federrath, C. 2020, MNRAS, 496, 5201 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Menon, S. H., Federrath, C., Krumholz, M. R., et al. 2022, MNRAS, 512, 401 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Mestel, L., & Spitzer, L., Jr. 1956, MNRAS, 116, 503 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Mignon-Risse, R., González, M., Commerçon, B., & Rosdahl, J. 2020, A&A, 635, A42 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Mignon-Risse, R., González, M., Commerçon, B., & Rosdahl, J. 2021, A&A, 652, A69 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Minerbo, G. N. 1978, J. Quant. Spectr. Rad. Transf., 20, 541 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Molina, F. Z., Glover, S. C. O., Federrath, C., & Klessen, R. S. 2012, MNRAS, 423, 2680 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Motte, F., Nony, T., Louvet, F., et al. 2018, Nat. Astron., 2, 478 [Google Scholar]
- Murray, N., & Chang, P. 2015, ApJ, 804, 44 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Myers, A. T., McKee, C. F., Cunningham, A. J., Klein, R. I., & Krumholz, M. R. 2013, ApJ, 766, 97 [Google Scholar]
- Myers, P. C., & Basu, S. 2021, ApJ, 917, 35 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Ntormousi, E., & Hennebelle, P. 2019, A&A, 625, A82 [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Offner, S. S. R., Klein, R. I., McKee, C. F., & Krumholz, M. R. 2009, ApJ, 703, 131 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Offner, S. S. R., Clark, P. C., Hennebelle, P., et al. 2014, in Protostars and Planets VI, eds. H. Beuther, R. S. Klessen, C. P. Dullemond, & T. Henning (Tucson: University of Arizona Press), 53 [Google Scholar]
- Padoan, P., Nordlund, A., & Jones, B. J. T. 1997, MNRAS, 288, 145 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Padoan, P., Pan, L., Juvela, M., Haugbølle, T., & Nordlund, Å. 2020, ApJ, 900, 82 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Pattle, K., Fissel, L., Tahani, M., Liu, T., & Ntormousi, E. 2022, arXiv e-prints [arXiv:2203.11179] [Google Scholar]
- Peters, T., Klessen, R. S., Mac Low, M.-M., & Banerjee, R. 2010, ApJ, 725, 134 [Google Scholar]
- Peters, T., Banerjee, R., Klessen, R. S., & Mac Low, M.-M. 2011, ApJ, 729, 72 [Google Scholar]
- Peter, T., Klessen, R. S., Kanschat, G., Glover, S. C. O., & Bastian, P. 2022, arXiv e-prints [arXiv:2207.12848] [Google Scholar]
- Pouteau, Y., Motte, F., Nony, T., et al. 2022, A&A, 664, A26 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Salpeter, E. E. 1955, ApJ, 121, 161 [Google Scholar]
- Saumon, D., & Chabrier, G. 1992, Phys. Rev. A, 46, 2084 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Saumon, D., Chabrier, G., & van Horn, H. M. 1995, ApJS, 99, 713 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Semenov, D., Henning, T., Helling, C., Ilgner, M., & Sedlmayr, E. 2003, A&A, 410, 611 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Shu, F. H. 1977, ApJ, 214, 488 [Google Scholar]
- Smith, R. J., Glover, S. C. O., & Klessen, R. S. 2014, MNRAS, 445, 2900 [Google Scholar]
- Teyssier, R. 2002, A&A, 385, 337 [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Urban, A., Martel, H., & Evans, N. J. I. 2010, ApJ, 710, 1343 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Urquhart, J. S., Moore, T. J. T., Csengeri, T., et al. 2014, MNRAS, 443, 1555 [Google Scholar]
- Vaytet, N., Chabrier, G., Audit, E., et al. 2013, A&A, 557, A90 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Semadeni, E. 1994, ApJ, 423, 681 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster, J., & Li, Z.-Y. 2018, Front. Astron. Space Sci., 5, 39 [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S., Ji, S., & Lazarian, A. 2019, ApJ, 878, 157 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.-Y., Romano, D., Ivison, R. J., Papadopoulos, P. P., & Matteucci, F. 2018, Nature, 558, 260 [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B., Tomida, K., Hennebelle, P., et al. 2020, Space Sci. Rev., 216, 43 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
Appendix A: A simple analytical model for the temperature
To better understand the temperature profils through the clump, we make use of the simple model discussed in Hennebelle et al. (2020b), improving on various aspects. The model assumes that the cloud is spherically symmetric and that all sources are located in the clump centre. As seen in § 4.1, the radial profil of the density field in collapsing envelopes is given by:
where δρ is a dimensionless factor which typically is equal to ≃30-100. We assume that gas and dust have the same temperature and are stationary. The grey body approximation that is being used, leads when the medium is optically thick to
where a is the radiation density constant. In this expression we assume that all the emitting sources are located in the clump centre. The opacity temperature dependences (e.g. Semenov et al. 2003), suggest that we can distinguish two regimes of temperature:
where α is typically between 1 and 2. In this work, we adopted α = 1.5. Combining Eqs. (A.1), (A.2), and (A.3), we get:
where rcrit is the radius at which T = Tcrit and is given by
Finally, Text is the temperature where the optical depth is about 1 and rext the corresponding radii. We therefore have κ(Text)ρ(rext)rext ≃ τ0 where τ0 should be on the order of 1. Combining Eqs. (A.1), (A.3), and (A.4), we obtain for rext
At this point, the radiative flux becomes simply equal to the term cER and Eq. (A.2) becomes invalid. Under the assumption that the temperature remains the one of a blackbody, it then remains constant at larger radii and thus:
The expression for Text is obtained by continuity at rext. By combining Eq. (A.8) and Eq. (A.7), we find that
Appendix B: Analytical model of the mass spectrum
For completeness, we describe here the analytical model developed in Hennebelle & Chabrier (2008) and Lee & Hennebelle (2018a) that we use in the paper to interpret the numerical results.
It is based on the equality of mass of the density fluctuation which are unstable at a scale, R, (left-hand term) and the mass that ends up into the structures, namely, the stars:
where 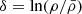 , ṖR is the density PDF, P(R, M) is the probability of finding a self-gravitating clump of mass M′ embedded into a self-gravitating clump of mass MR unstable at scale R. It is assumed to be 1.
, ṖR is the density PDF, P(R, M) is the probability of finding a self-gravitating clump of mass M′ embedded into a self-gravitating clump of mass MR unstable at scale R. It is assumed to be 1.
Taking the derivative with respect to R, we get:
The mass of the density fluctuations is given by
Here we assume that the density PDF is given by
The gravitational instability criterion for a clump of mass M at scale R is
where cs is the sound speed, Va the Alfvén speed, V0 the rms velocity dispersion at the cloud scale, Rc is the cloud radius and η an exponent to describe the turbulent scale dependence. Typically η = 0.3 − 0.5 and in this work the value η = 0.5 is assumed for simplicity. Equation (B.5) is the standard Jeans mass expression in which the support is assumed to be as suggested by the virial theorem. We note that the surface terms are not taken into account, they would typically modify this expression by a factor of 2. Taking the standard definition of the Jeans mass, the mass enclosed in a sphere of diameter equal to the Jeans length, we get aJ = π5/2/6. With Eq. (B.3), this implies:
where 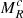 is the critical mass at scale R.
is the critical mass at scale R.
 |
Fig. B.1. This figure complements Fig. 1. Left panel displays the total stellar luminosities and right one the total accretion luminosity. |
With Eq. (B.4) and Eq. (B.2) leads to:
Knowing the cloud physical conditions, cs, Va, V0, together with Eq. (B.6), Eq. (B.7) allow to predict the stellar mass spectrum. The normalisation coefficient Ṅ0 is determined by specifying the total mass within stars.
It is useful to see that
In this limit, the mass reservoir is thermally supported and the mass spectra present a plateau, namely, 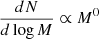 .
.
On the other hand, in the limit:
As revealed by Eq. (B.6), in this limit the mass reservoir is dominated by the turbulent dispersion. For η = 0.5, the mass spectrum is 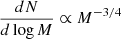 .
.
We recall that at small masses, the asymptotic behaviour will eventually break down when the gas becomes adiabatic due to the dust opacity and the formation of the first hydrostatic core, while at large masses, the assumption of the density PDF being ∝ρ−3/2, is eventually invalid (typically it eventually turns into a log-normal distribution). Therefore while useful, these asymptotic behaviours must be handled with care.
Appendix C: Accretion and stellar luminosities
To get a better understanding of the origins of the luminosities, we investigate the stellar and accretion luminosities separately. The two panels of Fig. C.1 show the sum of the stellar luminosities (left panel) and the sum of the accretion luminosities (right panel). In a first phase, up to time ≃0.1 Myr, the accretion luminosity largely dominates. Then, as stars of few solar masses have formed, the stellar luminosities increase steeply and then reach values comparable to the accretion luminosities.
All Tables
All Figures
 |
Fig. 1. Total mass, accretion rate and luminosity as a function of time. Top row shows the total accreted mass (top-left panel) and the total accretion rate (top-right panel) as a function of time for the various runs. Bottom-left panel portrays the total luminosity while bottom-right panel shows the same quantity divided by Lglob = 0.5 × GM∗,tot Ṁ∗,tot/(2 R⊙). |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 2. Column density at t = 0.11 Myr for the six runs. The dark circles represent the sink particles aiming at describing the stars. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 3. Radial profiles at several timesteps in HYDROf05 and MHD10f05, respectively. The black dashed line in the density panel shows the singular isothermal sphere density. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 4. Mass distribution as a function of density at several timesteps for the six runs. Section 4.2 describes the corresponding physical regimes. The dotted line shows a powerlaw behaviour M ∝ n−1/2 as expected for a density PDF ∝n−3/2 (see Sect. 4.2.3). |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 5. Mass-weighted temperature in density intervals as a function of density at six time steps for the six runs. The dotted lines show a powerlaw behaviour of T ∝ n1/2 and T ∝ n0.3, respectively. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 6. Magnetic field as a function of density at several timesteps for the four magnetised runs. The dotted line shows a powerlaw behaviour B ∝ n1/2. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 7. The number of sinks (left panel), Ntot and the largest sink mass (right panel) as a function of the total accreted mass, Mtot, in several runs. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 8. Mass spectra at various times characterised by the total accreted mass, for the six runs and for three values of the accreted mass. The red dotted lines represent the analytical model presented in the paper for comparison. The black dotted one shows for reference a M−1 power laws. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. B.1. This figure complements Fig. 1. Left panel displays the total stellar luminosities and right one the total accretion luminosity. |
| In the text | |
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.



![$$ \begin{aligned} \begin{array}{llll} \partial _t \rho + \nabla \cdot \left[\rho \boldsymbol{u} \right]&= 0, \\ \partial _t \rho \boldsymbol{u} + \nabla \cdot \left[\rho \boldsymbol{u}\otimes \boldsymbol{u} + P \mathbb{I} \right]&= - \lambda \nabla E_{\rm r} +\boldsymbol{F}_{\rm L} -\rho \nabla \phi ,\\ \partial _t E_{\rm T} + \nabla \cdot \left[\boldsymbol{u}\left( E_{\rm T} + P_{\rm } + \frac{B^2}{8 \pi } \right) \right.&\\ \left.- {1 \over 4 \pi }\left(\boldsymbol{u}\cdot \boldsymbol{B}\right)\boldsymbol{B}-\boldsymbol{E}_{\rm AD}\times \boldsymbol{B}\right]&= - \mathbb{P} _{\rm r}\nabla :\boldsymbol{u} - \lambda \boldsymbol{u} \nabla E_{\rm r} \\& + \nabla \cdot \left(\frac{c\lambda }{\rho \kappa _{\rm R}} \nabla E_{\rm r}\right)+ S_\star \\ & -\rho \boldsymbol{u}\cdot \nabla \phi , \\ \partial _t E_{\rm r} + \nabla \cdot \left[\boldsymbol{u}E_{\rm r}\right]&= - \mathbb{P} _{\rm r}\nabla :\boldsymbol{u} + \nabla \cdot \left(\frac{c\lambda }{\rho \kappa _{\rm R}} \nabla E_{\rm r}\right) \\& + \kappa _{\rm P}\rho c(a_{\rm R}T^4 - E_{\rm r})\\& + S_\star ,\\ \partial _t \boldsymbol{B} - \nabla \times \left[\boldsymbol{u}\times \boldsymbol{B} +\boldsymbol{E}_{\rm AD}\right]&=0,\\ \nabla \cdot \boldsymbol{B}&=0,\\ \Delta \phi&= 4\pi G \rho , \end{array} \end{aligned} $$](/articles/aa/full_html/2022/12/aa43803-22/aa43803-22-eq1.gif)
![$$ \begin{aligned} \boldsymbol{E}_{\rm AD} = \frac{\eta _{\rm AD}}{B^2}\left[\left(\nabla \times \boldsymbol{B}\right) \times \boldsymbol{B} \right] \times \boldsymbol{B}, \end{aligned} $$](/articles/aa/full_html/2022/12/aa43803-22/aa43803-22-eq2.gif)
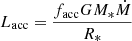
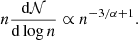
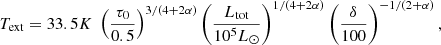
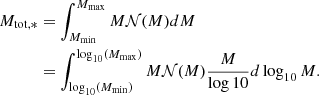
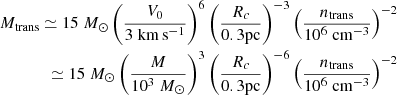
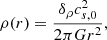
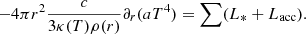
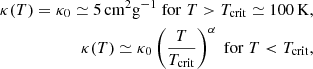
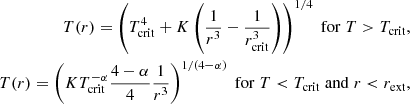
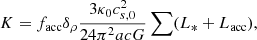
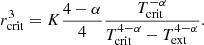
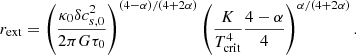
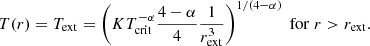
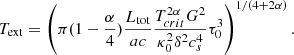
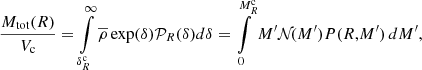
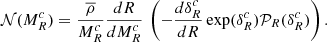
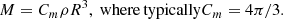
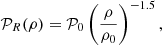
![$$ \begin{aligned} M > M_J = a_J { \Bigl [ c_s^2 + {V_a^2 \over 6} + {V_0^2 \over 3} \left({R \over R_c } \right)^{2 \eta } \Bigr ]^{3 \over 2} \over \sqrt{G^3 \overline{\rho } \exp (\delta ) } }, \end{aligned} $$](/articles/aa/full_html/2022/12/aa43803-22/aa43803-22-eq27.gif)