Fig. 3
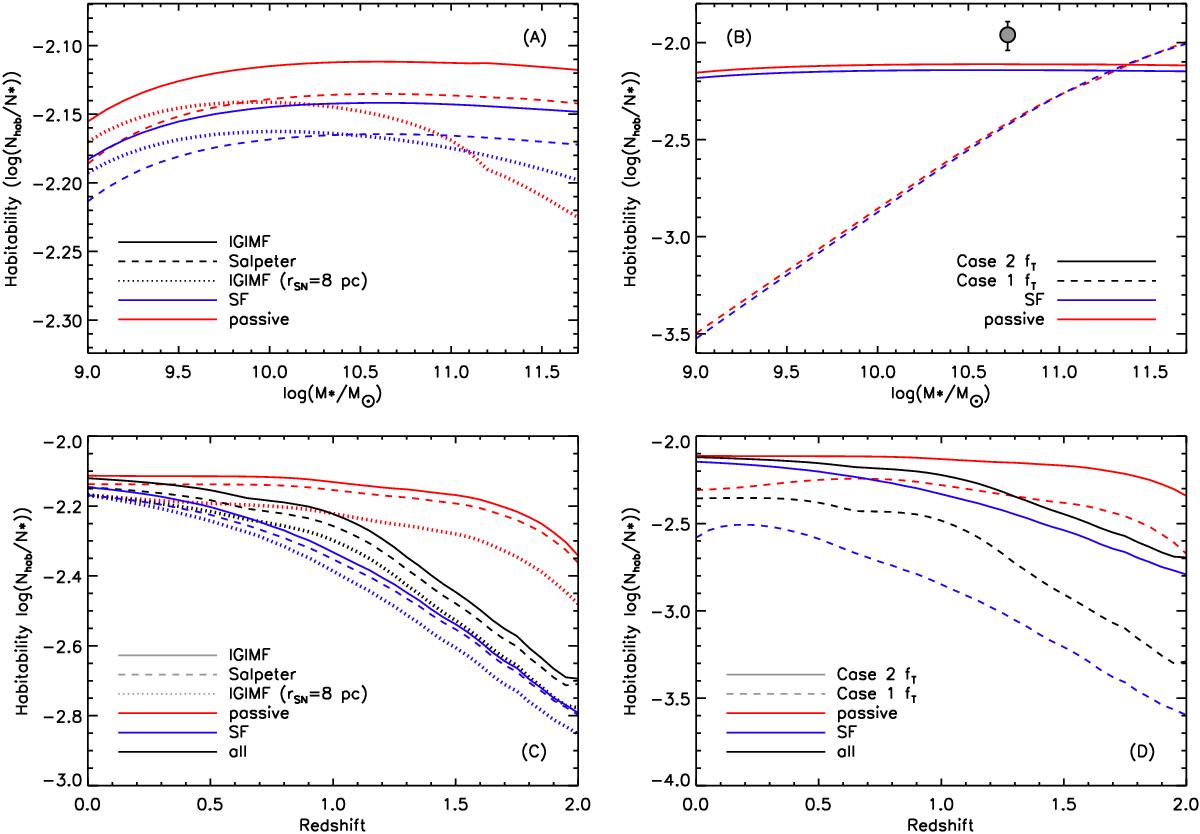
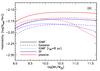
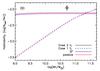
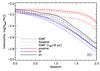
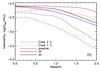
A) Galaxy habitability at z = 0 as a function of mass and IMF (IGIMF and Salpeter; solid and dashed lines, respectively), for SF (blue) and passive (red) galaxies and a metallicity-anticorrelated (Case 2) fT. To illustrate the effect of SN on the mass-dependency of hG, the dotted lines show the IGIMF case with the lethal radius of Gehrels et al. (2003)rII = rIa = 8 pc and trec>tH. B) Galaxy habitability at z = 0 of SF (blue) and passive (red) galaxies, using the IGIMF and for the two different cases of terrestrial planet incidence (Cases 1 and 2; dashed and solid lines, respectively). The filled gray circle shows the ratio of stars with terrestrial planet candidates in the habitable zone to the total number of stars with at least one planet candidate, taken from the NASA Exoplanet Archive using the same criteria (star mass, illuminance, planetary radius) as described in Sect. 2.2. The error bar assumes Poisson uncertainties. C) Galaxy habitability integrated over the range of galaxy masses, as a function of redshift and IMF (IGIMF and Salpeter; solid and dashed lines, respectively), for SF (blue) and passive (red) galaxies. As in A), this panel assumes a Case 2 fT. The dotted lines show the evolution of habitability in the IGIMF case if we use the larger (8 pc) SN lethal radius of Gehrels et al. (2003). D) As in C), evolution of galaxy habitability with redshift as a function of the metallicity dependence of fT. In both panels, the black lines show the evolution of habitability averaged over the whole galaxy population (SF and passives).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.