Table 3
CO, H2O, and OH rotational excitation.
| Source | Warm CO | H2O (em.) | H2O (abs.) | Ra | OH 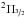 b b |
OHc | ||||||||
| Trot(K) |
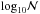
|
Trot(K) |
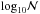
|
Trot(K) | lnNlow | (arc sec) | Trot(K) | Trot(K) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
| G327-0.6 | 295(60) | 51.9(0.3) | ... | ... | 210(80) | 34.5(0.5) | ... | 105(12) | 77(29) | |||||
| W51N-e1 | 330(15) | 52.9(0.1) | 320(120) | 50.1(0.5) | 200(90) | 34.0(0.5) | 3.4 | 66(-) | 54(29) | |||||
| DR21(OH) | 290(15) | 51.7(0.1) | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | 98(27) | 79(30) | |||||
| W33A | 245(40) | 51.6(0.2) | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | |||||
| G34.26+0.15 | 365(15) | 52.3(0.1) | ... | ... | 270(210) | 34.0(0.6) | ... | 89(5) | 71(15) | |||||
| NGC6334-I | 370(20) | 51.9(0.1) | ... | ... | 180(40) | 34.6(0.3) | ... | 93(-) | 71(50) | |||||
| NGC7538-IRS1 | 220(20) | 51.7(0.2) | 400(90) | 48.2(0.2) | 170(70) | 33.1(0.5) | 1.1 | 52(-) | 54(37) | |||||
| AFGL2591 | 220(20) | 51.7(0.2) | 460(110) | 49.1(0.2) | 160(130) | 33.9(1.1) | 1.6 | 105(29) | 89(21) | |||||
| W3-IRS5 | 375(10) | 52.4(0.1) | 260(40) | 49.3(0.2) | 220(160) | 34.1(0.6) | 3.2 | 109(3) | 83(22) | |||||
| G5.89-0.39 | 295(10) | 52.2(0.1) | 250(40) | 49.1(0.2) | 250(190) | 34.6(0.6) | 3.0 | 96(1) | 77(16) | |||||
Notes. Rotational temperatures of H2O and OH within the 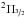 ladder are calculated using at least 10 and 3 lines / doublets, respectively, and are shown in boldface. Non-detections are marked with dots. For OH temperatures determined using only 2 transitions, the associated error is not given and marked with “-”.
ladder are calculated using at least 10 and 3 lines / doublets, respectively, and are shown in boldface. Non-detections are marked with dots. For OH temperatures determined using only 2 transitions, the associated error is not given and marked with “-”.
Size of the H2O emitting region assuming that all H2O lines trace the same physical component (see Sect. 4.2.2.).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


