Fig. 10
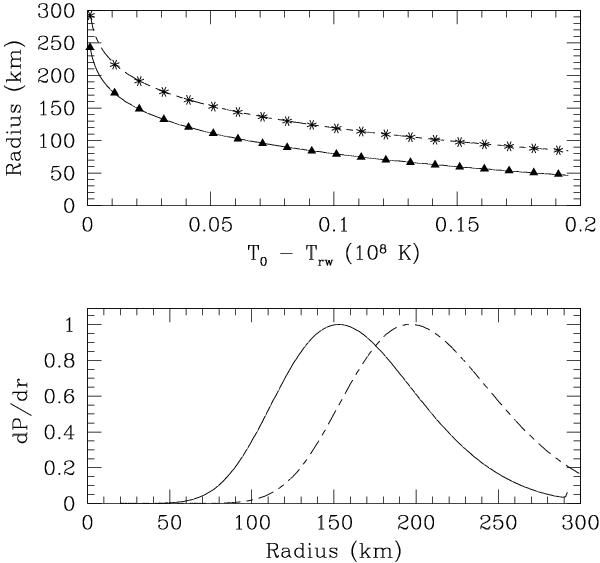
Distribution of runaway radii. Top: runaway radius as a function of the temperature above the runaway temperature (Trw, see Table 5): stars belong to model CF88, and triangles to model LER-1.5-0.1-1.0. The lines are quadratic fits to the dependence of runaway radii on temperature: r = ax2 + bx + c, where r is in km and 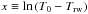 , with both temperatures in 108 K. The parameters of the polinomial are a = − 2.87, b = − 64.08, and c = − 13.09 for the CF88 rate, and a = − 2.72, b = − 60.59, and c = − 45.21 for the LER-1.5-0.1-1.0 rate. Bottom: probability distribution function of runaway radii, in arbitrary units. The probability distribution function has been obtained as the product of the exponential probability distribution function (EPDF) of temperatures proposed by WWK04 (Eq. (38)), dP/dT, and the inverse of the derivative dr/dT computed from the polinomial fit to r(T). The curves belong to the CF88 rate (short-long dash) and the LER-1.5-0.1-1.0 rate (solid).
, with both temperatures in 108 K. The parameters of the polinomial are a = − 2.87, b = − 64.08, and c = − 13.09 for the CF88 rate, and a = − 2.72, b = − 60.59, and c = − 45.21 for the LER-1.5-0.1-1.0 rate. Bottom: probability distribution function of runaway radii, in arbitrary units. The probability distribution function has been obtained as the product of the exponential probability distribution function (EPDF) of temperatures proposed by WWK04 (Eq. (38)), dP/dT, and the inverse of the derivative dr/dT computed from the polinomial fit to r(T). The curves belong to the CF88 rate (short-long dash) and the LER-1.5-0.1-1.0 rate (solid).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


