| Issue |
A&A
Volume 533, September 2011
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A74 | |
| Number of page(s) | 8 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201117379 | |
| Published online | 30 August 2011 | |
IGR J11014-6103: a newly discovered pulsar wind nebula?
1
ISDC data center for astrophysics, University of Geneva,
chemin d’Écogia,
16 1290
Versoix,
Switzerland
e-mail: lucia.pavan@unige.ch
2
Institut für Astronomie und Astrophysik, Kepler Center for Astro
and Particle Physics, Eberhard-Karls-Universität, Sand 1, 72076
Tübingen,
Germany
Received: 31 May 2011
Accepted: 9 July 2011
Context. IGR J11014-6103 is one of the still unidentified hard X-ray INTEGRAL sources, reported for the first time in the 4th IBIS/ISGRI catalog.
Aims. We investigated the nature of IGR J11014-6103 by carrying out a multiwavelength analysis of the available archival observations performed in the direction of the source.
Methods. We present the results of the timing and spectral analysis of all the X-ray observations of IGR J11014-6103 carried out with ROSAT, ASCA, Einstein, Swift, and XMM-Newton. We used them to search for possible counterparts to the source in the optical, infrared, radio and γ-ray domain.
Results. Our analysis reveals that IGR J11014-6103 is comprised of three different X-ray emitting regions: a point-like source, an extended object, and a cometary-like “tail” (~4 arcmin). A possible radio counterpart positionally coincident with the source was also identified.
Conclusions. Based on these results, we suggest that the emission from IGR J11014-6103 is generated by a pulsar wind nebula produced by a high-velocity pulsar. IGR J11014-6103 might be the first of these systems detected with INTEGRAL IBIS/ISGRI.
Key words: stars: individual: IGR J11014-6103 / stars: mass-loss / stars: neutron
© ESO, 2011
1. Introduction
The IBIS/ISGRI telescope (Ubertini et al. 2003) onboard INTEGRAL (Winkler et al. 2003) has been operating for seven years now, and the latest available catalog of sources detected with this telescope contains more that 700 objects (Bird et al. 2010). A large number of them belong to the class of X-ray binaries (26%) and active galactic nuclei (35%); a relatively small fraction is represented by cataclysmic variables (5%), and another 4% comprises supernova remnants, globular clusters, and soft γ-ray repeaters. About 30% of the IBIS/ISGRI sources are still unclassified (see e.g. Chaty et al. 2010, for a recent review).
In this paper, we investigate the nature of the still unidentified INTEGRAL source IGR J11014-6103. This source was reported for the first time in the fourth IBIS/ISGRI catalog (Bird et al. 2010), and was detected in the IBIS/ISGRI mosaic at a significance level of 5.4σ (20–100 keV). The position of IGR J11014-6103 obtained with INTEGRAL is RA = 165.341 deg, Dec = −61.056 deg (J2000), with an associated uncertainty of 4.3 arcmin (90% c.l.). The averaged source fluxes in the 20–40 keV and 40–100 keV energy bands are 0.4 ± 0.1 mCrab and 0.6 ± 0.2 mCrab, respectively1. The light curve of the source, obtained from the online tool Heavens2 (Walter et al. 2010), does not show any evidence of variability. A possible counterpart to IGR J11014-6103 in the soft X-ray (0.3–10 keV) domain was identified by Malizia et al. (2011). In the Swift /XRT field of view (FoV) around IGR J11014-6103, they detected a source located at RA = 165.44 deg, Dec = −61.022 deg (associated uncertainty ~6″). By using the refined X-ray position, these authors also suggest that IGR J11014-6103 could be associated to the ROSAT source 1RXH J110146.1-610121 and the serendipitous XMM-Newton source 2XMM J110147.1-61012.
In Sect. 2 we report on the analysis of all the available X-ray observations performed with Swift, XMM-Newton, ROSAT, and ASCA, in the direction of IGR J11014-6103. We use the results of this analysis in Sect. 3 to search for possible counterparts to the source in the optical, infrared and radio domains. A discussion of the nature of IGR J11014-6103 is presented in Sect. 4.
2. X-ray observations of IGR J11014-6103
A summary of all X-ray observations analyzed in this section is provided in Table 1, and we discuss each in turn in this section.
X-ray observation log of IGR J11014-6103.
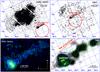 |
Fig. 1 Upper left: FoV around IGR J11014-6103 as observed by EPIC-MOS1 onboard XMM-Newton (0.5–12 keV). Upper right: Swift /XRT FoV around IGR J11014-6103 (1–9 keV). Bottom left: zoom of the EPIC-MOS1 FoV. In this case we kept the colors and removed the coordinate grid and the error circles around the detected sources for clarity. Bottom right: zoom of the XRT FoV. In this figure we marked the source detected with Swift (uncertainty of 4.4″ at 90% c.l.), and sources N and S detected with XMM-Newton (uncertainty of 2″ at 90% c.l.). The contours determined from the XMM-Newton observations are also overplotted (in green), together with the error circle representing the INTEGRAL position of IGR J11014-6103 (in red) and the error circle of the Einstein source 2E 2383 (in blue, uncertainty of 39″ at 90% c.l., see Sect. 2.5). The intensity scale, here and in the following images, is logarithmic and the grid is in galactic coordinates. |
2.1. Swift
The FoV around IGR J11014-6103 was observed twice with Swift /XRT on 2011 March 10 and 12 for total exposure times of 3.1 ks and 2.1 ks, respectively (observations ID. 00045395001 and 00045395002). We analyzed the Swift /XRT (Gehrels et al. 2004) data collected in photon-counting mode (PC) by using standard procedures (Burrows et al. 2005) and the latest calibration files available. Filtering and screening criteria were applied by using ftools, and only event grades of 0–12 were considered. Exposure maps were created through the xrtexpomap task. No obvious sources were detected in the two observations separately. We maximized the S/N by summing up all the available data (effective exposure time 5.1 ks) and extracted a single image of the XRT FoV around IGR J11014-6103. In this image, we detected a faint source (S/N = 5.5 in the 1–9 keV energy band, see Fig. 1) at RA = 165.444 deg, Dec = −61.023 deg (associated uncertainty 4.4″ at 90% c.l.; we used the xrtcentroid tool). This is compatible with being the same source as the one already identified by Malizia et al. (2011), and it is the only source detected inside the INTEGRAL error box. It is thus the most likely counterpart to IGR J11014-6103 in soft X-rays. Given the relatively short exposure time and the low count rate of the source, we could not extract a meaningful spectrum. Instead, we estimated the source count rate (0.011 ± 0.002 counts/s, 1–9 keV) with sosta (available within the ftool ximage), and used this result within webpimms in order to derive the corresponding X-ray flux (see also Bozzo et al. 2009). In the conversion between count rate and flux, we adopted an absorbed (NH = 0.7 × 1022 cm-2) power-law (Γ = 1.6) model (see Sect. 2.2). The inferred X-ray flux in the 2–10 keV energy band was (6.3 ± 1.2) × 10-13 erg cm-2 s-1 (not corrected for absorption). Even though a single point source is detected with the xrtcentroid tool, Fig. 1 reveals marginal evidence of diffuse emission around the source and the presence of an elongated structure (~4 arcmin) extending in the northwest direction from the point source. We discuss this evidence further in Sect. 2.2.
2.2. XMM-Newton
XMM-Newton observed the region around IGR J11014-6103 on 2000 July 28 (obs. ID 0111210201, total exposure time ~11 ks) and on 2003 July 21 (obs. ID 0152570101, total exposure time ~60 ks). In both cases, the observations were centered on the nearby supernova remnant (SNR) MSH 11-61A, and thus IGR J11014-6103 was offset with respect to the instrument aimpoint by about 15 arcmin. During obs. ID 0152570101, the EPIC-pn and EPIC-MOS cameras were operated in small-window and full-frame modes, respectively. IGR J11014-6103 was only within the EPIC-MOS FoV. During obs. ID 0111210201 all the EPIC cameras were operated in full frame mode, and IGR J11014-6103 was observed with both the EPIC-pn and EPIC-MOS. In all cases, only part of the INTEGRAL error circle around IGR J11014-6103 was included in the FoV of the EPIC cameras (see Fig. 1).
We processed the XMM-Newton observation data files with the two pipelines epproc and emproc in order to produce EPIC-pn and EPIC-MOS cleaned event files, respectively (SAS v.10.0.1). To identify the high-background time intervals, we followed the SAS online analysis thread3 and extracted the lightcurves from the full FoV of the EPIC cameras in the 10–12 keV energy band. We discarded the time intervals in which the 10–12 keV FoV count rate was larger than 0.4 cts/s from further analysis. The resulting effective exposure times were 47.3 ks and 8.0 ks for the EPIC-MOS1 cameras in observations ID 0152570101 and 0111210201 respectively, and 5.7 ks for EPIC-pn camera in observation ID 0111210201. All cleaned event files were barycentered with the barycen tool.
 |
Fig. 2 Left: close view of the EPIC-MOS1 FoV around sources N and S (see Sect. 2.2); Right: simulated PSF of the EPIC-MOS1 camera at energies in the (0.2–12) keV energy range by assuming the same offset position as that of sources N and S. The two panels have the same angular scale. |
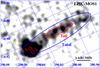 |
Fig. 3 Zoom of the EPIC-MOS1 FoV around IGR J11014-6103 during observation ID. 0152570101 (0.2–12 keV). The regions used for the extraction of the spectra of sources N and S are indicated with red small circles; the region used for the spectral analysis of the tail with a red ellipse. We also show the extraction region used to perform the spectral analysis of the entire emitting region (dashed ellipse; see Sect. 2.2). |
A visual inspection of the EPIC-MOS image extracted from the XMM-Newton observation with the longer exposure time (ID 0152570101, see Fig. 1) reveals that the source detected with Swift /XRT is indeed composed of three different emitting regions: two sources separated by ~22 arcsec (hereafter sources N and S) and a dimmer elongated structure (~4 arcmin, hereafter, the “tail”). In the EPIC images extracted from obs. ID 0111210201 only the two brighter sources are clearly visible. In this observation, the tail is only marginally detectable owing to the shorter exposure time. To check that sources N and S are not just produced by the distortion of the EPIC-MOS point spread function (PSF) at large offset angles, we used the psfgen task to simulate the 2D-PSF of the instrument at the location of these two sources. We used a circular region for the simulation ~180″ wide centered on source N and set the level parameter to “ELLBETA”. The comparison between the simulated PSF profiles and the measured intensity profiles obtained from the data is shown in Fig. 2. The simulated PSF did not present a double peak in the intensity profile in a direction comparable with that observed from the XMM-Newton data. In particular, we note that the distortion of the PSF caused by the off-axis position of the source on the EPIC-MOS detectors occurs primarily along the azimuthal direction, whereas sources N and S are separated in the opposite direction.
Sources N and S have also already been identified in the second XMM-Newton catalog of serendipitous X-ray sources (Watson et al. 2009) as 2XMM J110147.1-610124 and 2XMM J110145.0-610140, respectively. The catalogued positions are (RA = 165.4465 deg, Dec = −61.0234 deg) for the first, and (RA = 165.4377 deg, Dec = −61.0279 deg) for the latter (the nominal positional accuracy of the EPIC cameras is ~2″, see e.g. Pavan et al. 2011, and references therein). 2XMM J110147.1-610124 is reported as extended, and is characterized by a radial elongation of 8.1″.
In Fig. 1 the image extracted from Swift /XRT is compared with the one obtained from the deeper XMM-Newton observation. The contours around the extended emission from XMM-Newton are almost coincident with the emission in XRT. This confirms the marginal detection of the extended emission noticed before in the Swift /XRT data (see Sect. 2.1), and suggests that the single point source detected with this telescope is indeed a blend of the two brighter objects revealed by XMM-Newton.
We also performed a spectral analysis of the X-ray emission from the two brighter sources and the tail by extracting the corresponding spectra from the EPIC-MOS1 data in obs. ID 0152570101 (EPIC-MOS2 data could not be used for the spectral analysis because in this camera the sources were located close to the gap between two different CCDs). The extraction regions (shown in Fig. 3) were chosen in order to maximize the S/N and to minimize the reciprocal contamination. To take the background contribution into account, we selected a circular source-free region of radius 2 arcmin located in the same CCD as IGR J11014-6103 and at approximately the same distance from the central SNR. We also checked that the results presented in this paper would not be affected by different (reasonable) choices of the background region. Given the relatively low number of counts, all the spectra were grouped to have at least 5 photons for each energy bin and fit with an absorbed power-law model using C-statistics (Cash 1979 we used Xspec v.12). We checked that similar results (to within the uncertainties) would be obtained by grouping the spectra with 25 photons per energy bin and using χ2 statistics. The results of the fits, and the best-fit parameters obtained from the spectral analysis of the entire region (Fig. 3), are summarized in Table 2. In the same table we also report the estimate of the X-ray flux in the 0.2–2.4 keV energy band (F0.2−2.4 keV), to more easily compare it with the results obtained from ROSAT /HRI observations (see Sect. 2.3). We found marginal evidence for a difference between the power-law photon index of sources N and S, and show the most relevant contour plots derived from the spectral fits in Fig. 4. The spectrum extracted from the tail provided only poor constraints on the properties of its X-ray emission. A similar analysis carried out on the EPIC-MOS and EPIC-pn data of the observation ID. 0111210201 did not reveal any significant variation in the estimated spectral parameters and fluxes from the three regions.
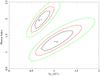 |
Fig. 4 Contour plot of the absorption column density (NH) and power-law photon index (Γ) derived from the EPIC-MOS1 data for sources N and S in observation ID. 0152570101. The contours correspond to 68%, 90%, and 99% confidence levels. |
Results of the spectral fit parameters obtained from XMM-Newton observation ID. 0152570101.
To compare the fluxes estimated with XMM-Newton and those reported for IGR J11014-6103 in the fourth IBIS/ISGRI catalog (see Sect. 1), we performed a simultaneous fit of the MOS 1 (ID. 0152570101) spectrum from the entire source (Fig. 3) and the IBIS/ISGRI spectrum of IGR J11014-6103 obtained from the Heavens web-tool. The two spectra could be reasonably well fit using an absorbed power-law model, with spectral parameters compatible with those determined previously using only the XMM-Newton data (best-fit values reported in the last line of Table 2). We obtained NH = 0.6 ± 0.2, Γ = 1.5 ± 0.2 (χ2/d.o.f. = 0.8/74) and 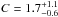 . Here, C is the normalization constant introduced to take into account both the intercalibration between the EPIC-MOS1 and IBIS/ISGRI, and any possible flux change of compact emission regions between the different observations. We considered EPIC-MOS1 as reference detector, therefore the constant is applied to the ISGRI spectrum. We noticed that fixing C = 1 would not significantly change the results of the fit. The estimated 2–10 keV, 20–40 keV, and 40–80 keV X-ray fluxes of the sources were (1.9 ± 0.2) × 10-12 erg cm-2 s-1,
. Here, C is the normalization constant introduced to take into account both the intercalibration between the EPIC-MOS1 and IBIS/ISGRI, and any possible flux change of compact emission regions between the different observations. We considered EPIC-MOS1 as reference detector, therefore the constant is applied to the ISGRI spectrum. We noticed that fixing C = 1 would not significantly change the results of the fit. The estimated 2–10 keV, 20–40 keV, and 40–80 keV X-ray fluxes of the sources were (1.9 ± 0.2) × 10-12 erg cm-2 s-1, 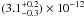 erg cm-2 s-1, and
erg cm-2 s-1, and 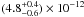 erg cm-2 s-1, respectively. These are fully compatible with those reported by Bird et al. (2010), i.e. (3.0 ± 0.8) × 10-12 erg cm-2 s-1 in the 20–40 keV and (5.6 ± 2) × 10-12 erg cm-2 s-1 in the 40–100 keV band. The unfolded MOS1+ISGRI spectrum of IGR J11014-6103 is shown in Fig. 5. A simultaneous MOS1+ISGRI spectral analysis was carried out also using the EPIC spectra of source S alone (without including the tail and source N). This source indeed seems to have a harder spectrum and higher estimated flux in the 2–10 keV band than do source N and the tail. No significant differences in the three spectral parameters have been measured, except for a marginal hint of an increase in the intercalibration constant needed in the fit.
erg cm-2 s-1, respectively. These are fully compatible with those reported by Bird et al. (2010), i.e. (3.0 ± 0.8) × 10-12 erg cm-2 s-1 in the 20–40 keV and (5.6 ± 2) × 10-12 erg cm-2 s-1 in the 40–100 keV band. The unfolded MOS1+ISGRI spectrum of IGR J11014-6103 is shown in Fig. 5. A simultaneous MOS1+ISGRI spectral analysis was carried out also using the EPIC spectra of source S alone (without including the tail and source N). This source indeed seems to have a harder spectrum and higher estimated flux in the 2–10 keV band than do source N and the tail. No significant differences in the three spectral parameters have been measured, except for a marginal hint of an increase in the intercalibration constant needed in the fit.
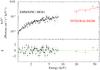 |
Fig. 5 Unfolded XMM-Newton and IBIS/ISGRI spectrum of IGR J11014-6103. We fitted both spectra with a single absorbed power-law model (solid line). In the bottom panel we show the residuals from this fit. |
We also searched in the EPIC data for indications of variability for sources N and S on time scales of seconds to hours, but did not spot any relevant feature. We carefully searched for coherent pulsations. We used the PN data for the short observation (ID. 0111210201) and decided to analyze sources N and S jointly to maximize the number of source photons. Cutting out source S for an analysis of source N (and vice versa) would result in too high a loss of source photons for a detailed timing analysis. The total number of photons obtained for both sources together was 693. By adopting an epoch-folding technique with 16 phase bins, we determined an upper limit on the pulsed fraction for a sinusoidal signal of 56% (at 90% c.l.) in the 0.002 to 6.8 Hz frequency range (we followed the approach of Leahy et al. 1983). In the long observation (ID. 0152570101) we could use only the data of MOS1 (1275 photons) and MOS2 (2087 photons), so we explored the frequency range 0.001–0.2 Hz: the upper limits on the pulsed fraction are 44% and 33% (at 90% c.l.).
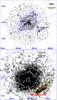 |
Fig. 6 Top: ROSAT /HRI FoV around IGR J11014-6103 (observation ID. RH500445A01). The image is in the 0.2–2.4 keV energy band with a resolution of 5″ (see Sect. 2.3). We overplot on this image the XMM-Newton contour levels (in blue) determined from the EPIC-MOS1 data in observation ID. 0152570101 (see also Fig. 1). The black circle represents the INTEGRAL position of IGR J11014-6103. The bright extended emission in the center of the FoV is SNR MSH 11-61A. Bottom: ASCA /GIS2 FoV around IGR J11014-6103 (observation ID. 51021000). The image is in the 0.5–10 keV energy band. Extended emission is clearly visible on the bottom right side of the detector, below SNR MSH 11-61A. We overplot on this image the XMM-Newton contours (in white), the INTEGRAL error circle of IGR J11014-6103 (red circle), and the extraction region adopted for the GIS spectral analysis (yellow ellipse). |
2.3. Rosat
We retrieved all available ROSAT (Truemper 1982) data in the direction of IGR J11014-6103 from the Heasarc archive. The FoV around IGR J11014-6103 was observed with the HRI (Pfeffermann et al. 1987) onboard ROSAT on several occasions (observations ID. RH500445A01, RH500340N00, RH500445N00, RH900619A01, and RH900619N00). Among these, observation ID. RH500445A01 was characterized by the longest available exposure time (46 ks) and was performed on 1997 June 28. We show in Fig. 6 the HRI image (5″ resolution, 0.2–2.4 keV). Within the INTEGRAL error circle of IGR J11014-6103 a single point-like source is detected. This source has already been classified in the HRI catalog as 1RXH J110146.1-610121 (Voges et al. 1999), located at RA = 165.442 deg and Dec = −61.022 deg. The nominal positional accuracy of the HRI is approximately 10″ (Predehl & Prieto 2001), and thus the ROSAT position is consistent with that of the source revealed with Swift and with source N detected with XMM-Newton. Given the limited spatial resolution, sensitivity, and energy coverage of the HRI with respect to the EPIC cameras, it is not surprising that the closeby source S and the tail are not detected in this case (source S is also fainter than source N in the ROSAT energy band, see Table 2). We suggest that, as for the case of Swift /XRT, the ROSAT source is indeed a blend of sources N and S. The estimated count rate of 1RXH J110146.1-610121 in the HRI energy band (0.2–2.4 keV) is 0.0038 ± 0.0004 cts/s. This would convert into an X-ray flux of (9 ± 1) × 10-13 erg cm-2 s-1 (2–10 keV) if an absorbed power-law spectral model with NH = 0.7 × 1022 cm-2 and Γ = 1.6 is used (see Sect. 2.2). The flux of the ROSAT source thus qualitatively agrees with that of sources N and S estimated from XMM-Newton data.
We noted that the FoV around IGR J11014-6103 was observed also with the PSPC onboard ROSAT on two occasions on 1993 July 23 (observation ID. RP500307N00) and on 1994 July 5 (observation ID. RP500307A01). However, in these two cases the relatively low exposure time (~2 ks) and the offset position of the source with respect to the instrument aimpoint did not result in a clear detection of the source. We thus do not discuss these data in more detail.
2.4. ASCA
In the Heasarc archive we found two observations carried out with the GIS telescope (Ohashi et al. 1996) onboard ASCA (Tanaka et al. 1994) which included the region around IGR J11014-6103 in their FoV. The first of these observations, ID. 51021000, was performed on 1994 March 1 with a total exposure time of 43.4 ks. The second observation, ID. 51021010, lasted for 40.5 ks and was carried out about 10 months later, on 1995 January 16. Both these observations were aimed at the SNR MSH 11-61A and did not cover entirely the INTEGRAL error circle around the position of IGR J11014-6103. However, the extended emitting region already identified with XMM-Newton is clearly detected in the GIS images (see Fig. 6). In comparison with the HRI camera onboard ROSAT, the GIS has a broader energy coverage (0.5–10 keV) and a higher sensitivity, but a significantly lower spatial resolution (the GIS PSF is ~1 arcmin and strongly dependent on energy, Tanaka et al. 1994). It is thus not surprising that the GIS is not able to distinguish the two sources (N and S) detected with XMM-Newton and ROSAT, but can reveal the diffuse emission around them.
We analyzed GIS2 and GIS3 data following standard procedures and the latest available calibration files (see e.g. Pavan et al. 2011, and references therein). Source spectra in the two observations were extracted using the elliptical region shown in Fig. 6. Given the presence of the nearby SNR MSH 11-61A, we extracted the background spectra from different regions located at the same radial distances of IGR J11014-6103 from MSH 11-61A. Even though the S/N of the data was relatively poor, the GIS spectra could be reasonably well fit using an absorbed power-law model. From the GIS2 data in observation 51021000, we measured Γ = 1.6 ± 0.3 and estimated a 2–10 keV X-ray flux of 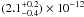 erg cm-2 s-1 (
erg cm-2 s-1 (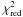 /d.o.f. = 0.7/21). These values are compatible (to within the errors) with those inferred from the XMM-Newton data. From observation 51021010, we obtained Γ = 1.2 ± 0.5 and
/d.o.f. = 0.7/21). These values are compatible (to within the errors) with those inferred from the XMM-Newton data. From observation 51021010, we obtained Γ = 1.2 ± 0.5 and 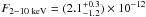 erg cm-2 s-1 (
erg cm-2 s-1 (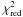 /d.o.f. = 0.9/16). In both cases we fixed the absorption column density to the best value measured from XMM-Newton. Compatible results (to within the uncertainties) were obtained from the GIS3 data.
/d.o.f. = 0.9/16). In both cases we fixed the absorption column density to the best value measured from XMM-Newton. Compatible results (to within the uncertainties) were obtained from the GIS3 data.
2.5. Einstein
The region around IGR J11014-6103 was also observed with the Einstein/IPC detector (0.2–4.5 keV, Giacconi et al. 1979) on 1980 August 12 with an exposure time ~11 ks. A visual inspection of the Einstein/IPC image revealed a source (2E 2383) that is spatially coincident with sources N and S and marginal evidence of an extended tail similar to that observed in XMM-Newton. 2E 2383 is reported in the 2E catalog at RA = 11h:01m:47.5s, Dec = −61°:01′:22″(related uncertainty 39″, see Fig. 1; Harris et al. 1994). The source count rate was 0.011 ± 0.002 cts/s, which correspond to F2−10 keV = (9 ± 2) × 10-13 erg cm-2 s-1 (assuming a column density NH = 0.7 × 1022 cm-2 and a power-law spectrum with slope Γ = 1.6, see Sect. 2.2). This flux is compatible with the one measured with XMM-Newton.
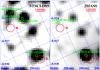 |
Fig. 7 Search for optical and infrared counterparts to the sources N and S. Left: STCI-DSS image. We overplot the position of sources N and S (radius equal to the position accuracy, 2″) as determined from the EPIC-MOS1 observation, and the most likely optical counterpart from the USNO-A2.0 and USNO-B1.0 catalogs (green circles, with radius 0.6″). Right: 2MASS image. The position of sources N and S is indicated as above. We marked the location of the potential infrared counterparts retrieved from the 2MASS catalog (green circles, with radius 0.6″). |
3. Counterparts to IGR J11014-6103
In this section we take advantage of the improved positions for the three emitting regions included in the INTEGRAL error circle around IGR J11014-6103 to search for the corresponding counterparts in the optical, infrared, and radio domain. In Sect. 3.3, we also report on a possible γ-ray detection.
3.1. Optical/IR data
We used publicly available optical and near infrared images from STSCI-DSS and 2MASS surveys. Potential counterparts to sources N and S are shown in Fig. 7. For source N, we did not find any obvious counterpart in the optical domain. The closest cataloged USNO-A2.0 sources are located more than ~7″ away from the EPIC-MOS1 position of the source. The nearest classified object in the USNO-B1.0 catalog is 0289-0254424 (R1 = 12.21, B2 = 15.97), located at RA = 165.4471 deg, Dec = −61.0221 deg. In the infrared domain, the closest cataloged source is the 2MASS object J11014730-6101213 located at RA = 165.447122 deg, Dec = −61.022602 deg. This object is reported in the catalog with J = 15.95, H = 15.54, and K ≤ 15.46. For source S, the closest cataloged source in the optical domain (USNO-A2.0 catalog) is 0225-10220547. This is located at RA = 165.438870 deg, Dec = −61.027375 deg and is characterized by B = 16.5 and R = 13.0. In the infrared domain, the closest object from the 2MASS catalog to the position of source S is J11014532-6101383, located at RA = 165.438860 deg, Dec = −61.027306 deg and characterized by J = 11.16, H = 10.19, and K = 9.89.
3.2. Radio data
To search for radio counterparts to IGR J11014-6103, we used data from the MGPS-2 archive. The MGPS-2 is a high-resolution and large-scale survey of the galactic plane carried out with the Molonglo Observatory Synthesis Telescope (MOST) at a frequency of 843 MHz (Murphy et al. 2007). The MGPS-2 image covering the field around IGR J11014-6103 is shown in Fig. 8. We noticed a relatively bright radio source from this figure, J110149-610104, positionally consistent with sources N and S. The radio source is reported in the MGPS catalog as “compact”, because its dimensions are comparable to the convoluted beam of the survey, and located at RA = (165.4559 ± 0.0017) deg, Dec = (−61.0178 ± 0.0017) deg. The associated flux at 843 MHz is 24.2 ± 4.8 mJy (corresponding to (2.04 ± 0.40) × 10-16 erg cm-2 s-1).
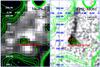 |
Fig. 8 Left: radio image (and contours) at 843 MHz around the position of IGR J11014-6103 retrieved from the MGPS-2 archive. We mark in red the position of the source MGPS2 J110149-610104. Right: EPIC-MOS1 image from observation ID. 0152570101. We overplot on the image the radio contours derived from the MGPS-2 data in green and mark in red the position of the radio source J110149-610104 and the two XMM-Newton sources N and S. |
3.3. γ-ray data
We also noticed the presence of an EGRET source, 3EG J1102-6103, which might be related with IGR J11014-6103. In the latest available EGRET catalog, 3EG J1102-6103 is located at RA = 165.60 deg, Dec = −61.05 deg, with an associated uncertainty of 0.6 deg. The error circle around 3EG J1102-6103 would thus be compatible with the position of IGR J11014-6103, as determined before. At present, however, we are unable to confirm this association because of other possible counterparts located within the EGRET error circle of 3EG J1102-6103. Among these, there are the SNR MSH 11-61A and the young energetic pulsar PSR J1105-6107 (Kaspi et al. 1997).
In the Fermi/LAT catalog we did not find any source positionally coincident with IGR J11014-6103. We did not attempt any estimate of an upper limit on the source flux from the Fermi data. This calculation would indeed depend crucially on the properties of the still relatively poorly known high-energy Galactic background in such a highly crowded region.
4. Discussion and conclusions
In this paper we analyzed all publicly available X-ray observations carried out in the direction of the unidentified source IGR J11014-6103 with Swift, XMM-Newton, ROSAT, ASCA, and Einstein. The entire INTEGRAL error circle around IGR J11014-6103 has been covered in the soft (1–10 keV) X-ray energy band with Swift and ROSAT. The analysis of these data led to detecting a single X-ray source inside the error circle given by INTEGRAL (see also Malizia et al. 2011). However, the deepest observations of the region around IGR J11014-6103, performed with the EPIC cameras onboard XMM-Newton, revealed that the source detected with Swift/XRT and ROSAT is very likely a blend of two distinct objects: a point-like source and an 8.1 arcsec extended object. The same observations also revealed a cometary-like tail (~4 arcmin) extending from the two sources and included within the INTEGRAL error circle around IGR J11014-6103. The X-ray spectra of the three objects displayed only marginally significant differences (see Table 2 and Fig. 4).
The ROSAT /HRI and ASCA /GIS observations of the same region were unable to disentangle the three emitting components. This can be ascribed to the narrower energy range coverage of the former instrument and the lower spatial resolution of the telescopes onboard ASCA and ROSAT than with the EPIC cameras (see fluxes in the 0.2–2.4 keV band in Table 2 and Sects. 2.3, 2.4). In all cases, we showed that the X-ray emitting properties of the entire region in the INTEGRAL error circle of IGR J11014-6103 agreed among all the available instruments. In Sect. 2.2, we also showed that the joint XMM-Newton+INTEGRAL spectrum could be reasonably well described using a single absorbed power-law model, with a normalization constant between the two instruments ≃1. All these results suggest that IGR J11014-6103 is a persistent X-ray emitter that has in the past ~31 years displayed only marginal variations (if any) in the 0.3–100 keV energy band.
The improved X-ray positions of sources N and S also permitted searching for their possible optical and infrared counterparts. The closest cataloged 2MASS, USNO-A2.0, and USNO B1.0 objects to sources N and S lie just outside the 90% c.l. error circle determined with XMM-Newton, so further observations with the ACIS telescope onboard Chandra are needed to reduce the likelihood of a chance coincidence. We found a possible radio counterpart close to sources N and S. The radio contours derived from the publicly available MGPS-2 data match reasonably well those of the X-ray emission detected with XMM-Newton around sources N and S. The presence of an EGRET source, 3EG J1102-6103, positionally coincident with IGR J11014-6103 was also reported.
Because IGR J11014-6103 is located only 11 arcmin away from the nearby SNR MSH 11-61A, we first considered the possibility that the X-ray emission coming from the unidentified INTEGRAL source was related to the SNR. However in none of the investigated wavelengths (X-ray, radio, optical, NIR) could we clearly identify any emitting structures located between MSH 11-61A and IGR J11014-6103 that could have favored such an association (see also Rosado et al. 1996).
As an alternative and perhaps more viable hypothesis, we considered that the morphology and emission properties of the 4 arcmin extended X-ray tail in IGR J11014-6103 might resemble the elongated features observed in the case of PSR B2224+65 (“the Guitar” nebula, Hui & Becker 2007) and PSR J0357+3205 (De Luca et al. 2011). In both cases a pulsar (PSR) has been firmly detected at one end of the elongated structures, and the cometary-like tails have been tentatively explained in the “bow-shock pulsar wind nebulae” (bsPWN) scenario. These elongated cometary-like objects form when a pulsar escapes from the associated supernova remnant and moves with a very high velocity through the interstellar medium (typically hundreds of km/s, i.e. orders of magnitude higher than the velocities of the cold and warm components of the interstellar medium, see e.g. Roberts et al. 2005, and references therein). Close to the pulsar, the relativistic wind of the compact object usually gives rise to a subluminous cavity in X-rays surrounded by a termination shock. In this region, particles are thermalized and accelerated, thus producing a conspicuous X-ray and radio emission (through synchrotron processes from the interaction with the local magnetic field). As the pulsar is moving, a bow shock is formed in front of it and the flow of material advects the emitting particles back along the direction of motion, leading to the formation of an elongated cometary structure (see e.g. Gaensler & Slane 2006, for a detailed discussion). In a few cases, deep X-ray observations with the ACIS telescope onboard Chandra permitted to clearly disentangle the different contributions to the total X-ray and radio emission produced by the structures around a bsPWN (see e.g. the case of the PWN G359.23-0.82; Gaensler et al. 2004).
If the structures detected in IGR J11014-6103 are indeed originating in the pulsar wind, the X-ray tail can be interpreted as coming from relic electrons spread along the direction of motion of the PSR. Source N, extended in X-rays and closer to the peak of the radio emission, would represent, according to this interpretation, the compact PWN (with possible contribution also coming from the bow-shock). The detection of a radio source located close to source N would support this scenario, since radio synchrotron emission is expected from particles accelerated at the termination shock; see the cases of, e.g. PSRs B1853+01 (Frail et al. 1996; Petre et al. 2002), B1957+20 (Stappers et al. 2003), B1757-24 (Frail & Kulkarni 1991; Kaspi et al. 2001).
While the association between the extended source N and the “tail” seems morphologically plausible, the association of source S to this region is less straightforward. In case source S is not physically related to the X-ray tail, it might just by chance be located along the line of sight to the extended structure. The pulsar responsible for the formation of the compact and relic PWNe, might, in this case, be unresolved and comprised in the emission detected from source N.
When, instead, the point-like source S is physically connected to the PWN, it would be reasonable to associate it to the PSR generating the X-ray structures. Under this scenario the misalignment between the direction of the 4 arcmin tail and the axis between sources N and S would imply a significant tilt between the proper motion of the PSR and the position of the compact PWN. A similar misalignment, however, has already been observed in, e.g., PSR B2224+65, and ascribed to the strong interaction between the fast-moving pulsar and its dense surrounding environment (Hui & Becker 2007). Indeed, as for the case of PSR B2224+65, the environment around MSH 11-61A and IGR J11014-6103 has been found to be a complex and dense region, characterized by the presence of several background and foreground molecular clouds (Filipovic et al. 2005, and references therein).
Following the joint XMM+ISGRI spectral analysis (see Sect. 2.2), we conservatively assume that sources N and S both contribute to the ISGRI emission (the tail component indeed has a much lower flux). Spectral properties (hardness and flux stability) similar to those observed in the present case (see Fig. 5) have already been measured in AX J1838.0-0655 among others. This source is a young (τc ≡ P/2Ṗ = 23 kyr) pulsar, surrounded by a PWN (Gotthelf & Halpern 2008). The best-fit power-law slope in the 2–100 keV was measured at Γ = 1.5 +/−0.2 (Malizia et al. 2005). We note, however, that the highly-magnetized neutron stars (“magnetars”, for a review see, e.g., Mereghetti 2008) also share similar spectral properties. SGR 1806-20, for example, showed a power-law slope Γ = 1.6−2.0 in the range 1–100 keV (Esposito et al. 2007). Because the 1–10 keV spectra of magnetars are usually (phenomenologically) modeled with a combined black body+power-law (BB+PL) model (Mereghetti 2008), the lack of the BB component in the XMM-Newton spectrum might be an issue for this interpretation. We therefore estimated for source S (i.e. the component showing the higher 2–10 keV flux) the contribution of an eventual black body spectral component. We used a temperature kT = 0.5, in agreement with the one measured for SGR 1806-20 (Esposito et al. 2007) and for magnetars in general. The relatively low S/N meant we could only obtain a poorly constrained upper limit on the ratio between the fluxes of the BB and PL components FBB/FPL < 0.1. This would be compatible with the value measured in the case of SGR 1806-20 (FBB/FPL = 0.03, Esposito et al. 2007). The present data therefore do not argue against a magnetar hypothesis. We note also that a possible association between a magnetar and a PWN has already been suggested by Vink & Bamba (2009).
Further observations with an X-ray telescope characterized by a finer spatial resolution (i.e. the ACIS onboard Chandra) and increased spectral and timing statistics are required to solve the issues above and firmly establish the real nature of IGR J11014-6103. In case these observations confirm that IGR J11014-6103 is a newly discovered PWN generated by a high-velocity PSR, this will be the first detection with INTEGRAL of one of these systems (to the best of our knowledge).
Acknowledgments
This work made use of data obtained from the High Energy Astrophysics Science Archive Research Center (Heasarc), provided by NASAs Goddard Space Flight Center. We thank an anonymous referee for useful comments.
References
- Bird, A. J., Bazzano, A., Bassani, L., et al. 2010, ApJS, 186, 1 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzo, E., Giunta, A., Stella, L., et al. 2009, A&A, 502, 21 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows, D. N., Hill, J. E., Nousek, J. A., et al. 2005, Space Sci. Rev., 120, 165 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Cash, W. 1979, ApJ, 228, 939 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Chaty, S., Zurita Heras, J. A., & Bodaghee, A. 2010, PoS(INTEGRAL 2010), 047 [Google Scholar]
- De Luca, A., Marelli, M., Mignani, R., et al. 2011, ApJ, 733, 104 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, P., Mereghetti, S., Tiengo, A., et al. 2007, A&A, 476, 321 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Filipovic, M., Payne, J., & Jones, P. 2005, Serbian Astron. J., 170, 47 [Google Scholar]
- Frail, D. A., & Kulkarni, S. R. 1991, Nature, 352, 785 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Frail, D. A., Giacani, E. B., Goss, W. M., & Dubner, G. 1996, ApJ, 464, L165 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Gaensler, B., & Slane, P. 2006, ARA&A, 44, 17 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Gaensler, B., Swaluw, E., Camilo, F., et al. 2004, ApJ, 616, 383 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Gehrels, N., Chincarini, G., Giommi, P., et al. 2004, ApJ, 611, 1005 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Giacconi, R., Branduardi, G., Briel, U., et al. 1979, ApJ, 230, 540 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Gotthelf, E. V., & Halpern, J. P. 2008, ApJ, 681, 515 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Harris, D., Forman, W., Gioa, I., et al. 1994, EINSTEIN Observatory catalog of IPC X-ray sources, SAO HEAD CD-ROM Series I (Einstein) [Google Scholar]
- Hui, C., & Becker, W. 2007, A&A, 467, 1209 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspi, V. M., Bailes, M., Manchester, R. N., et al. 1997, ApJ, 485, 820 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspi, V. M., Gotthelf, E. V., Gaensler, B. M., & Lyutikov, M. 2001, ApJ, 562, L163 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy, D. A., Darbro, W., Elsner, R. F., et al. 1983, ApJ, 266, 160 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Malizia, A., Bassani, L., Stephen, J. B., et al. 2005, ApJ, 630, L157 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Malizia, A., Landi, R., Bassani, L., et al. 2011, The Astronomer’s Telegram, 3290, 1 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Mereghetti, S. 2008, A&ARv, 15, 225 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, T., Mauch, T., Green, A., et al. 2007, MNRAS, 382, 382 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi, T., Ebisawa, K., Fukazawa, Y., et al. 1996, PASJ, 48, 157 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Pavan, L., Bozzo, E., Ferrigno, C., et al. 2011, A&A, 526, A122 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Petre, R., Kuntz, K. D., & Shelton, R. L. 2002, ApJ, 579, 404 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffermann, E., Briel, U. G., Hippmann, H., et al. 1987, in SPIE Conf. Ser. 733, ed. E.-E. Koch, & G. Schmahl, 519 [Google Scholar]
- Predehl, P., & Prieto, A. 2001 [arXiv:astro-ph/0109542] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, M., Brogan, C., Gaensler, B., et al. 2005, Astrophys. Space Sci., 297, 93 [Google Scholar]
- Rosado, M., Ambrocio-Cruz, P., Le Coarer, E., & Marcelin, M. 1996, A&A, 315, 243 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Stappers, B. W., Gaensler, B. M., Kaspi, V. M., van der Klis, M., & Lewin, W. H. G. 2003, Science, 299, 1372 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, Y., Inoue, H., & Holt, S. S. 1994, PASJ, 46, L37 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Truemper, J. 1982, Adv. Space Res., 2, 241 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Ubertini, P., Lebrun, F., Di Cocco, G., et al. 2003, A&A, 411, L131 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Vink, J., & Bamba, A. 2009, ApJ, 707, L148 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Voges, W., Aschenbach, B., Boller, T., et al. 1999, A&A, 349, 389 [NASA ADS] [Google Scholar]
- Walter, R., Rohlfs, R., Meharga, M., et al. 2010, PoS(INTEGRAL 2010), 162 [Google Scholar]
- Watson, M. G., Schröder, A. C., Fyfe, D., et al. 2009, A&A, 493, 339 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler, C., Courvoisier, T., Di Cocco, G., et al. 2003, A&A, 411, L1 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
All Tables
Results of the spectral fit parameters obtained from XMM-Newton observation ID. 0152570101.
All Figures
 |
Fig. 1 Upper left: FoV around IGR J11014-6103 as observed by EPIC-MOS1 onboard XMM-Newton (0.5–12 keV). Upper right: Swift /XRT FoV around IGR J11014-6103 (1–9 keV). Bottom left: zoom of the EPIC-MOS1 FoV. In this case we kept the colors and removed the coordinate grid and the error circles around the detected sources for clarity. Bottom right: zoom of the XRT FoV. In this figure we marked the source detected with Swift (uncertainty of 4.4″ at 90% c.l.), and sources N and S detected with XMM-Newton (uncertainty of 2″ at 90% c.l.). The contours determined from the XMM-Newton observations are also overplotted (in green), together with the error circle representing the INTEGRAL position of IGR J11014-6103 (in red) and the error circle of the Einstein source 2E 2383 (in blue, uncertainty of 39″ at 90% c.l., see Sect. 2.5). The intensity scale, here and in the following images, is logarithmic and the grid is in galactic coordinates. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 2 Left: close view of the EPIC-MOS1 FoV around sources N and S (see Sect. 2.2); Right: simulated PSF of the EPIC-MOS1 camera at energies in the (0.2–12) keV energy range by assuming the same offset position as that of sources N and S. The two panels have the same angular scale. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 3 Zoom of the EPIC-MOS1 FoV around IGR J11014-6103 during observation ID. 0152570101 (0.2–12 keV). The regions used for the extraction of the spectra of sources N and S are indicated with red small circles; the region used for the spectral analysis of the tail with a red ellipse. We also show the extraction region used to perform the spectral analysis of the entire emitting region (dashed ellipse; see Sect. 2.2). |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 4 Contour plot of the absorption column density (NH) and power-law photon index (Γ) derived from the EPIC-MOS1 data for sources N and S in observation ID. 0152570101. The contours correspond to 68%, 90%, and 99% confidence levels. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 5 Unfolded XMM-Newton and IBIS/ISGRI spectrum of IGR J11014-6103. We fitted both spectra with a single absorbed power-law model (solid line). In the bottom panel we show the residuals from this fit. |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 6 Top: ROSAT /HRI FoV around IGR J11014-6103 (observation ID. RH500445A01). The image is in the 0.2–2.4 keV energy band with a resolution of 5″ (see Sect. 2.3). We overplot on this image the XMM-Newton contour levels (in blue) determined from the EPIC-MOS1 data in observation ID. 0152570101 (see also Fig. 1). The black circle represents the INTEGRAL position of IGR J11014-6103. The bright extended emission in the center of the FoV is SNR MSH 11-61A. Bottom: ASCA /GIS2 FoV around IGR J11014-6103 (observation ID. 51021000). The image is in the 0.5–10 keV energy band. Extended emission is clearly visible on the bottom right side of the detector, below SNR MSH 11-61A. We overplot on this image the XMM-Newton contours (in white), the INTEGRAL error circle of IGR J11014-6103 (red circle), and the extraction region adopted for the GIS spectral analysis (yellow ellipse). |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 7 Search for optical and infrared counterparts to the sources N and S. Left: STCI-DSS image. We overplot the position of sources N and S (radius equal to the position accuracy, 2″) as determined from the EPIC-MOS1 observation, and the most likely optical counterpart from the USNO-A2.0 and USNO-B1.0 catalogs (green circles, with radius 0.6″). Right: 2MASS image. The position of sources N and S is indicated as above. We marked the location of the potential infrared counterparts retrieved from the 2MASS catalog (green circles, with radius 0.6″). |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 8 Left: radio image (and contours) at 843 MHz around the position of IGR J11014-6103 retrieved from the MGPS-2 archive. We mark in red the position of the source MGPS2 J110149-610104. Right: EPIC-MOS1 image from observation ID. 0152570101. We overplot on the image the radio contours derived from the MGPS-2 data in green and mark in red the position of the radio source J110149-610104 and the two XMM-Newton sources N and S. |
| In the text | |
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


