Table 4
Physical properties derived for the 8 o’clock arc images A2 and A3.
| A2 | A3 | ||||
| Total | Main | Blob | Total | Reference | |
|
|
|||||
| Magnification factor μ | 5.0 ± 1.0 | 5.0 ± 1.0 | 11.7 ± 2.3 | 3.9 ± 0.8 | Sect. 3.2 |
| Half-light radius r1/2 (kpc) | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 0.53 ± 0.05 | 1.8 ± 0.2 | Sect. 3.2 |
| E(B − V)gasa | 0.30 ± 0.04 | 0.34 ± 0.10 | 0.23 ± 0.15 | 0.29 ± 0.09 | Sect. 4.2 |
| E(B − V)βb | 0.23 ± 0.10 | 0.16 ± 0.10 | Sect. 4.2 | ||
| E(B − V)starsc,d | 0.19 ± 0.04 | Sect. 4.1 | |||
| 12 + log (O/H)N2e | 8.35 ± 0.19 | 8.39 ± 0.19 | 8.22 ± 0.25 | 8.46 ± 0.19 | Sect. 4.3 |
| ZN2/Z⊙f | 0.46 ± 0.20 | 0.50 ± 0.22 | 0.34 ± 0.20 | 0.59 ± 0.26 | Sect. 4.3 |
| 12 + log (O/H)Ne3O2g | >8.09 | >8.09 | >8.09 | >8.18 | Sect. 4.3 |
| SFRHα (M⊙ yr-1)h | 279 ± 45 | 207 ± 80 | 33 ± 19 | 239 ± 99 | Sect. 4.4 |
| SFRUV (M⊙ yr-1)i | 156 ± 110 | 198 ± 140 | Sect. 4.4 | ||
| SFRSED (M⊙ yr-1)d |
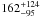
|
Sect. 4.1 | |||
| W0(Hα) (Å)j | 134 ± 67 | 89 ± 45 | 45 ± 23 | 139 ± 72 | Sect. 4.5 |
| W0(Hα) (Å)k | 187 ± 124 | 139 ± 115 | 51 ± 49 | 187 ± 152 | Sect. 4.5 |
| W0(Hβ) (Å)j | 30 ± 2 | 19 ± 3 | 11 ± 3 | 29 ± 3 | Sect. 4.5 |
| W0(Hβ) (Å)k | 47 ± 14 | 35 ± 22 | 13 ± 12 | 44 ± 23 | Sect. 4.5 |
| W0(Hα)SED (Å)d | 255 ± 95 | Sect. 4.1 | |||
| Age (Myr)d |
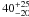
|
Sect. 4.1 | |||
| Mstars (109 M⊙)d |
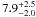
|
Sect. 4.1 | |||
| Mgas (109 M⊙)l | 20.9 ± 3.9 | 17.6 ± 5.6 | 2.2 ± 0.9 | 19.1 ± 6.4 | Sect. 4.6.1 |
| Mdyn,rot (109 M⊙)m | 16.0 ± 4.9 | 8.4 ± 2.7 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 20.2 ± 15.9 | Sect. 4.6.2 |
| Mdyn,disp (109 M⊙)n | 14.3 ± 4.5 | 12.6 ± 4.0 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | Sect. 4.6.2 | |
Notes. For A2 are listed the total values and the individual values corresponding to the main galaxy and the star-forming blob, as described in Sects. 3.2 and 3.3.
Stellar dust extinctions derived from the UV slopes, β, measured from the observed (V − I) colors (Table 1), following the prescriptions of Bouwens et al. (2009).
Stellar dust extinction derived from the SED modeling and corrected for the Galactic dust extinction, E(B − V)Gal = 0.056, at the position of the 8 o’clock arc (Schlegel et al. 1998).
Combined SED modeling results obtained with and without the treatment of nebular emission (continuum plus lines) and scaled to the Chabrier (2003) IMF. The predicted W0(Hα)SED comes, of course, only from SED models including the nebular emission.
Oxygen abundances derived from the N2 calibration from Pettini & Pagel (2004). The errors include the 0.18 dex systematic uncertainty in the N2 calibration zeropoint.
Gas-phase metallicities relative to the solar value of 12 + log (O/H)⊙ = 8.69 (Asplund et al. 2009).
Oxygen abundances derived from the Ne3O2 calibration from Nagao et al. (2006).
Star-formation rates computed from the Hα luminosity and corrected for dust extinction by E(B − V)gas values and for gravitational lensing by the magnification factor μ.
Star-formation rates computed from the UV continuum luminosity at the rest-frame wavelength of 1600 Å and corrected for dust extinction by E(B − V)stars values and for gravitational lensing by the magnification factor μ.
Rest-frame equivalent widths computed from the observed Balmer line and local continuum fluxes, assuming that the same dust extinction applies to the nebular and stellar emission.
Rest-frame equivalent widths computed from the dust-corrected Balmer line and local continuum fluxes, assuming that the gas-phase dust extinction, E(B − V)gas, applies to the nebular emission and the stellar dust extinction, E(B − V)stars, applies to the stellar continuum.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


