| Issue |
A&A
Volume 694, February 2025
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A297 | |
| Number of page(s) | 29 | |
| Section | Cosmology (including clusters of galaxies) | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202452551 | |
| Published online | 20 February 2025 | |
Simulating realistic self-interacting dark matter models including small and large-angle scattering
1
Physik Department T31, Technische Universität München James-Franck-Straße 1, D-85748 Garching, Germany
2
Fakultät für Physik, Universitäts-Sternwarte, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Scheinerstr. 1, D-81679 München, Germany
3
Excellence Cluster ORIGINS, Boltzmannstrasse 2, D-85748 Garching, Germany
⋆ Corresponding authors; cenanda.arido@tum.de, mathias.garny@tum.de, mfischer@usm.lmu.de
Received:
9
October
2024
Accepted:
8
January
2025
Context. Dark matter (DM) self-interactions alter matter distribution on galactic scales and alleviate tensions with observations. A feature of the self-interaction cross section is its angular dependence, which influences offsets between galaxies and DM halos in merging galaxy clusters. While algorithms for modelling mostly forward-dominated or mostly large-angle scatterings exist, incorporating realistic angular dependencies within N-body simulations remains challenging.
Aims. To efficiently simulate models with a realistic angle dependence, such as light mediator models, we developed, validated, and applied a novel method.
Methods. We combined existing approaches to describe small- and large-angle scattering regimes within a hybrid scheme. Below a critical angle, the scheme uses the effective description of small-angle scattering via a drag force combined with transverse momentum diffusion, while above the angle, it samples the dependence explicitly.
Results. We first verified the scheme using a test set-up with known analytical solutions, and we checked that our results are insensitive to the choice of the critical angle within an expected range. Next, we demonstrated that our scheme speeds up the computations by multiple orders of magnitude for realistic light mediator models. Finally, we applied the method to galaxy cluster mergers. We discuss the sensitivity of the offset between galaxies and DM to the angle dependence of the cross section. Our scheme ensures accurate offsets for mediator mass mϕ and DM mass mχ within the range 0.1v/c ≲ mϕ/mχ ≲ v/c, while for larger (smaller) mass ratios, the offsets obtained for isotropic (forward-dominated) self-scattering are approached. Here, v is the typical velocity scale. Equivalently, the upper condition can be expressed as 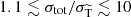 for the ratio of the total and momentum transfer cross sections, with the ratio being 1 (∞) in the isotropic (forward-dominated) limits.
for the ratio of the total and momentum transfer cross sections, with the ratio being 1 (∞) in the isotropic (forward-dominated) limits.
Key words: astroparticle physics / methods: numerical / galaxies: clusters: general / dark matter
© The Authors 2025
 Open Access article, published by EDP Sciences, under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Open Access article, published by EDP Sciences, under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article is published in open access under the Subscribe to Open model. Subscribe to A&A to support open access publication.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


