| Issue |
A&A
Volume 516, June-July 2010
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A113 | |
| Number of page(s) | 6 | |
| Section | Astrophysical processes | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200913558 | |
| Published online | 22 July 2010 | |
Searching for spatial variations of α2/μ in the Milky Way
1
INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste, via G. B. Tiepolo 11,
34131 Trieste, Italy e-mail: lev@astro.ioffe.rssi.ru
2
Key Laboratory for Research in Galaxies and Cosmology,
Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, CAS, 80 Nandan Road, Shanghai 200030,
PR China
3
Ioffe Physical-Technical Institute,
Polytekhnicheskaya Str. 26, 194021 St. Petersburg, Russia
4
Hamburger Sternwarte, Universität Hamburg,
Gojenbergsweg 112, 21029 Hamburg, Germany
Received:
27
October
2009
Accepted:
2
April
2010
Aims. We probe the dependence of α2/μ on the ambient matter density by means of spectral observations in submm- and mm-wave bands.
Methods. A procedure is suggested for exploring
the value of F = α2/μ, where
μ = me/mp is the electron-to-proton mass ratio,
and α = e2/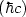 is the fine-structure constant.
The fundamental physical constants, which are measured in different physical environments of
high (terrestrial) and low (interstellar) densities of baryonic matter are
supposed to vary in chameleon-like scalar field models, which predict that
both masses and coupling constant may depend on the local matter density.
The parameter ΔF/F = (Fobs – Flab)/Flab
can be estimated from the radial velocity offset,
ΔV = Vrot – Vfs, between
the low-laying rotational transitions in carbon monoxide 13CO and
the fine-structure transitions in atomic carbon [C i].
A model-dependent constraint on Δα/α can be obtained from ΔF/F
using Δμ/μ independently measured from the ammonia method.
is the fine-structure constant.
The fundamental physical constants, which are measured in different physical environments of
high (terrestrial) and low (interstellar) densities of baryonic matter are
supposed to vary in chameleon-like scalar field models, which predict that
both masses and coupling constant may depend on the local matter density.
The parameter ΔF/F = (Fobs – Flab)/Flab
can be estimated from the radial velocity offset,
ΔV = Vrot – Vfs, between
the low-laying rotational transitions in carbon monoxide 13CO and
the fine-structure transitions in atomic carbon [C i].
A model-dependent constraint on Δα/α can be obtained from ΔF/F
using Δμ/μ independently measured from the ammonia method.
Results. Currently available radio astronomical datasets provide an upper limit on |ΔV| < 110 m s-1 (1σ). When interpreted in terms of the spatial variation of F, this gives |ΔF/F| < 3.7 × 10-7. An order of magnitude improvement in this limit will allow us to independently test a non-zero value of Δμ/μ = (2.2 ± 0.4stat ± 0.3sys) × 10-8, recently found with the ammonia method. Considering that the ammonia method restricts the spatial variation of μ at the level of |Δμ/μ| ≤ 3 × 10-8 and assuming that ΔF/F is the same in the entire interstellar medium, one obtains that the spatial variation of α does not exceed the value |Δα/α| < 2 × 10-7. Since extragalactic gas clouds have similar densities to those in the interstellar medium, the bound on Δα/α is also expected to be less than 2 × 10-7 at high redshift if no significant temporal dependence of α is present.
Key words: line: profiles / ISM: molecules / techniques: radial velocities / cosmology: observations
© ESO, 2010
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


