| Issue |
A&A
Volume 449, Number 3, April III 2006
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 1281 - 1288 | |
| Section | Celestial mechanics and astrometry | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20054500 | |
| Published online | 24 March 2006 | |
Astrometric light-travel time signature of sources in nonlinear motion
I. Derivation of the effect and radial motion
Departament d'Astronomia i Meteorologia, Universitat de Barcelona, Av. Diagonal 647, 08028 Barcelona, Spain e-mail: anglada@am.ub.es
Received:
9
November
2005
Accepted:
6
December
2005
Context.Very precise planned space astrometric missions and recent
improvements in imaging capabilities require a detailed review of
the assumptions of classical astrometric modeling.Aims.We show that
Light-Travel Time must be taken into account in modeling the kinematics
of astronomical objects in nonlinear motion, even at stellar
distances.Methods.A closed expression to include Light-Travel Time in the
current astrometric models with nonlinear motion is provided. Using a
perturbative approach the expression of the Light-Travel Time signature
is derived. We propose a practical form of the
astrometric modelling to be applied in astrometric data reduction
of sources at stellar distances(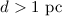 ).Results.We show that the
Light-Travel Time signature is relevant at
).Results.We show that the
Light-Travel Time signature is relevant at 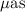 accuracy (or even
at mas) depending on the time span of the astrometric measurements.
We explain how information on the radial motion of a source can be
obtained. Some estimates are provided for
known nearby binary systemsConclusions.Given the obtained results,
it is clear that this effect must be taken into account in interpreting
precise astrometric measurements. The effect is particularly
relevant in measurements performed by the planned astrometric space missions
(GAIA, SIM, JASMINE, TPF/DARWIN). An objective criterion
is provided to quickly evaluate whether the Light-Travel Time modeling is
required for a given source or system.
accuracy (or even
at mas) depending on the time span of the astrometric measurements.
We explain how information on the radial motion of a source can be
obtained. Some estimates are provided for
known nearby binary systemsConclusions.Given the obtained results,
it is clear that this effect must be taken into account in interpreting
precise astrometric measurements. The effect is particularly
relevant in measurements performed by the planned astrometric space missions
(GAIA, SIM, JASMINE, TPF/DARWIN). An objective criterion
is provided to quickly evaluate whether the Light-Travel Time modeling is
required for a given source or system.
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


