| Issue |
A&A
Volume 449, Number 1, April I 2006
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 89 - 100 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20054457 | |
| Published online | 16 March 2006 | |
Swift observations of the prompt X-ray emission and afterglow from GRB050126 and GRB050219A
1
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Leicester, LE1 7RH, UK e-mail: mrg@star.le.ac.uk
2
INAF – Osservatorio Astronomica di Brera, via Bianchi 46, 23807 Merate, Italy
3
Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics, 525 Davey Lab., Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802, USA
4
Universita degli studi di Milano-Bicocca, P.za dell Scienze 3, 20126 Milano, Italy
5
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771, USA
6
Department of Physics, University of Nevada, BOX 454002, Las Vegas, NV 891, USA
7
ASI Science Data Center, via Galileo Galilei, 00044 Frascati, Italy
8
INAF – Instituto di Astrofisica Spaziale e Cosmica, via Ugo La Malfa 153, 90146, Palermo, Italy
9
Universities Space Research Association, 10211 Wincopin Circle, Suite 500, Columbia, MD, 21044-3432, USA
Received:
1
November
2005
Accepted:
23
November
2005
We report on the temporal and spectral characteristics of the early
X-ray emission from the Gamma Ray Bursts GRB050126 and GRB050219A as observed
by Swift . The X-ray light-curves of these 2 bursts both show
remarkably steep early decays (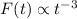 ), breaking to flatter
slopes on timescales of a few hundred seconds. For GRB050126 the burst shows
no evidence of spectral evolution in the 20–150 keV band, and the spectral
index of the γ-ray and X-ray afterglows are significantly different
suggesting a separate origin. By contrast the BAT spectrum of GRB050219A
displays significant spectral evolution, becoming softer at later times, with
Γ evolving toward the XRT photon index seen in the early X-ray
afterglow phase. For both bursts, the 0.2–10 keV spectral index pre- and
post-break in the X-ray decay light-curve are consistent with no spectral
evolution. We suggest that the steep early decline in the X-ray decay
light-curve is either the curvature tail of the prompt emission; X-ray flaring
activity; or external forward shock emission from a jet with high density
regions of small angular size (
), breaking to flatter
slopes on timescales of a few hundred seconds. For GRB050126 the burst shows
no evidence of spectral evolution in the 20–150 keV band, and the spectral
index of the γ-ray and X-ray afterglows are significantly different
suggesting a separate origin. By contrast the BAT spectrum of GRB050219A
displays significant spectral evolution, becoming softer at later times, with
Γ evolving toward the XRT photon index seen in the early X-ray
afterglow phase. For both bursts, the 0.2–10 keV spectral index pre- and
post-break in the X-ray decay light-curve are consistent with no spectral
evolution. We suggest that the steep early decline in the X-ray decay
light-curve is either the curvature tail of the prompt emission; X-ray flaring
activity; or external forward shock emission from a jet with high density
regions of small angular size (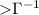 ). The late slope we associate
with the forward external shock.
). The late slope we associate
with the forward external shock.
Key words: gamma rays: bursts / gamma rays: observations / black hole physics
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


