| Issue |
A&A
Volume 469, Number 2, July II 2007
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 663 - 669 | |
| Section | Stellar structure and evolution | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20066594 | |
| Published online | 24 April 2007 | |
GRB 050410 and GRB 050412: are they really dark gamma-ray bursts?
1
INAF - Istituto di Astrofisica Spaziale e Fisica Cosmica di Palermo, via Ugo La Malfa 153, 90146 Palermo, Italy e-mail: teresa.mineo@ifc.inaf.it
2
INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera, via E. Bianchi 46, 23807 Merate (LC), Italy
3
Penn State University, 525 Davey Lab, University Park, PA 16802, USA
4
ASI, Science Data Center, via G. Galilei, 00044 Frascati, Italy
5
NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771, USA
6
ASI, Unità Osservazione dell'Universo, Viale Liegi 26, 00198 Roma, Italy
7
Universities Space Research Association, 10211 Wincopin Circle, Suite 500, Columbia, MD, 21044-3432, USA
8
Department of Physics & Astronomy, University of Leicester, LE1 7RH, UK
9
Mullard Space Science Laboratory, University College of London, Holmbury St Mary, Dorking, Surrey RH5 6NT, UK
Received:
19
October
2006
Accepted:
17
April
2007
Aims.We present a detailed analysis of the prompt and afterglow emission of GRB 050410 and GRB 050412 detected by Swift for which no optical counterpart was observed.
Methods.We analysed data from the prompt emission detected by the Swift BAT and from the early phase of the afterglow obtained by the Swift narrow field instrument XRT.
Results.The 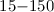 keV energy distribution of the GRB 050410 prompt
emission shows a peak energy at 53
keV energy distribution of the GRB 050410 prompt
emission shows a peak energy at 53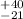 keV.
The XRT light curve of this GRB decays as a power law
with a slope of
keV.
The XRT light curve of this GRB decays as a power law
with a slope of  1.06 ± 0.04. The spectrum
is well reproduced by an absorbed power law with a spectral index
1.06 ± 0.04. The spectrum
is well reproduced by an absorbed power law with a spectral index
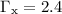 ± 0.4 and a low energy absorption
NH = 4
± 0.4 and a low energy absorption
NH = 4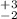
 1021 cm-2
which is higher than the Galactic value.
The
1021 cm-2
which is higher than the Galactic value.
The 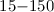 keV prompt emission in GRB 050412 is modelled with a hard
(Γ = 0.7 ± 0.2) power law.
The XRT light curve follows a broken power law with the first slope
keV prompt emission in GRB 050412 is modelled with a hard
(Γ = 0.7 ± 0.2) power law.
The XRT light curve follows a broken power law with the first slope
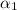 = 0.7 ± 0.4, the break time Tbreak = 254
= 0.7 ± 0.4, the break time Tbreak = 254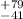 s and the second slope
s and the second slope 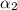 = 2.8
= 2.8 . The spectrum is fitted by a power law with
spectral index
. The spectrum is fitted by a power law with
spectral index 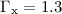 ± 0.2 which is absorbed at low energies by the
Galactic column.
± 0.2 which is absorbed at low energies by the
Galactic column.
Conclusions.The GRB 050410 afterglow light curve reveals the expected characteristics of the third component of the canonical Swift light curve. Conversely, a complex phenomenology was detected in the GRB 050412 because of the presence of the very early break. The light curve in this case can be interpreted as being the last peak of the prompt emission. The two bursts present tight upper limits for the optical emission, however, neither of them can be clearly classified as dark. For GRB 050410, the suppression of the optical afterglow could be attributed to a low density interstellar medium surrounding the burst. For GRB 050412, the evaluation of the darkness is more difficult due to the ambiguity in the extrapolation of the X-ray afterglow light curve.
Key words: gamma rays: bursts / X-rays: bursts / X-rays: individuals: GRB 050410 / X-rays: individuals: GRB 050412
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


