| Issue |
A&A
Volume 468, Number 1, June II 2007
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 103 - 112 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20066874 | |
| Published online | 26 March 2007 | |
Swift multi-wavelength observations of the bright flaring burst GRB 051117A
1
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Leicester, LE1 7RH, UK e-mail: mrg@star.le.ac.uk
2
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771, USA
3
Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802, USA
4
INAF-Osservatorio Astronomica di Brera, via Bianchi 46, 23807 Merate (LC), Italy
5
ASI Science Data Center, Via Galileo Galilei, 00044 Frascati, Italy
Received:
5
December
2006
Accepted:
15
March
2007
We report on the temporal and spectral characteristics of the early
X-ray emission from the Gamma Ray Burst 051117A as observed by Swift . The superb quality of the early X-ray light-curve and spectra of
this source, one of the brightest seen by the X-ray Telescope at such early
times, allows an unprecedented look at the spectral and temporal evolution of
the prompt and early afterglow emission for this GRB and allows us to place
stringent limits on the detection of lines. GRB 051117A displays a highly
complex light-curve, with an apparent initial slow decline of slope
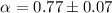 (
(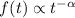 ) dominated by numerous
superposed flares of varying amplitude and duration. Between orbits 2 and 3,
the X-ray light-curve drops abruptly, highlighting the dominance of flaring
activity at early times, and indicating that the central engine for this burst
remains active for several kiloseconds after the initial explosion. The late
time slope (
) dominated by numerous
superposed flares of varying amplitude and duration. Between orbits 2 and 3,
the X-ray light-curve drops abruptly, highlighting the dominance of flaring
activity at early times, and indicating that the central engine for this burst
remains active for several kiloseconds after the initial explosion. The late
time slope (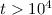 s) also decays relatively slowly with a powerlaw index
of
s) also decays relatively slowly with a powerlaw index
of 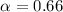 , breaking to a steeper slope of 1.1, 170 ks after the BAT
trigger. The X-ray light-curve at early times is characteristic of a noise
process, consisting of random shots superposed on an underlying powerlaw
decay, with individual shots well-modelled by a fast-rise and exponential
decay spanning a broad range in rise-times and decay rates. A temporal
spectral analysis of the early light-curve shows that the photon index and
source intensity are highly correlated with the spectrum being significantly
harder when brighter, consistent with the movement of the peak of the Band
function to lower energies following individual flares. The high quality
spectrum obtained from the first orbit of WT mode data, enables us to place a
, breaking to a steeper slope of 1.1, 170 ks after the BAT
trigger. The X-ray light-curve at early times is characteristic of a noise
process, consisting of random shots superposed on an underlying powerlaw
decay, with individual shots well-modelled by a fast-rise and exponential
decay spanning a broad range in rise-times and decay rates. A temporal
spectral analysis of the early light-curve shows that the photon index and
source intensity are highly correlated with the spectrum being significantly
harder when brighter, consistent with the movement of the peak of the Band
function to lower energies following individual flares. The high quality
spectrum obtained from the first orbit of WT mode data, enables us to place a
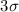 upper limit on the strength of any emission line features of
upper limit on the strength of any emission line features of 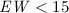 eV, assuming a narrow emission-line of 100 eV at the peak of the effective
area.
eV, assuming a narrow emission-line of 100 eV at the peak of the effective
area.
Key words: gamma rays: bursts / gamma rays: observations
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


