| Issue |
A&A
Volume 431, Number 3, March I 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 879 - 886 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20041541 | |
| Published online | 16 February 2005 | |
Q0957+561 revised: CO emission from a disk at z = 1.4*
1
I. Physikalisches Institut, University of Cologne, Zülpicherstr. 77, 50937 Köln, Germany e-mail: krips@ph1.uni-koeln.de
2
Institut de Radio Astronomie Millimétrique, 300 rue de la Piscine, 38406 Saint Martin d'Hères, France
3
Instituto de Estructura de la Materia (CSIC), Serrano 121, 28006 Madrid, Spain
4
Observatorio Astronómico Nacional (IGN), Apartado 112, 28800 Alcalá de Henares, Spain
Received:
28
June
2004
Accepted:
19
October
2004
Based on additional interferometric observations, we
reanalysed the CO(2-1) and 3 mm continuum emission of Q0957+561, a
lensed QSO at a redshift of 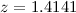 . The emission in the
CO(2-1) lines reveals a gas-rich host galaxy with a peculiar
double-peaked profile at one of the two lensed images. Our new
interferometric CO maps of the host galaxy agree well with HST images obtained by Keeton et al. (2000) and we thus argue that
the two velocity components arise from molecular gas in the disk
of the host galaxy. We also present new model calculations, all
in excellent agreement with recent time delay measurements and
simulations.
. The emission in the
CO(2-1) lines reveals a gas-rich host galaxy with a peculiar
double-peaked profile at one of the two lensed images. Our new
interferometric CO maps of the host galaxy agree well with HST images obtained by Keeton et al. (2000) and we thus argue that
the two velocity components arise from molecular gas in the disk
of the host galaxy. We also present new model calculations, all
in excellent agreement with recent time delay measurements and
simulations.
Key words: gravitational lensing / Galaxy: kinematics and dynamics / galaxies: quasars: individual: Q0957+561 / galaxies: high redshift / Galaxy: disk
© ESO, 2005
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


