S 308 and other X-ray emitting bubbles around Wolf-Rayet stars
- Details
- Published on 25 January 2024
Vol. 681
6. Interstellar and circumstellar matter
S 308 and other X-ray emitting bubbles around Wolf-Rayet stars
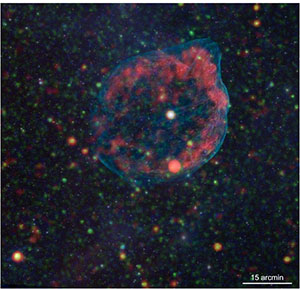
The role of massive stars in shaping their local environment is a continuing theme in the study of galactic star formation. Including stellar feedback in galactic models through the combined effects of wind mass loss and photoionization is physically challenging and, still, hypothetical, or at best loosely based on phenomenological prescriptions. Supernovae also bespeak the need of understanding the circumstellar medium to interpret the development of the energetics and spectra of some stripped systems. The eROSITA study of S 308, one of the Wolf-Rayet stars that have been targeted for X-ray and UV observations over the years, is the focus of this paper, but the sample includes other wind-shaped circumstellar environments (e.g., wind-blown bubbles). The energetics and dynamics are modeled using high-quality X-ray multiband imaging. This is a paradigmatic study and a harbinger of what is to come from the current sky-surveying high-energy satellites combined with ground-based data. Modelers of galactic evolution, supernovae, and gravitational wave progenitors will find much of interest in this paper.


