| Issue |
A&A
Volume 557, September 2013
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A12 | |
| Number of page(s) | 55 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201321221 | |
| Published online | 14 August 2013 | |
Online material
Appendix C: Tables and figures
We provide here:
-
the examples of the online tables of CDS: theoptical LC fit parameters(Tables C.1); the parameters of the optical/X-raySEDs fitted with a single power-law (Table C.2)and with a broken power-law (Table C.3); theX-ray spectrum fit parameters (Table C.4);redshifts and luminosity distances of the GRBs inour sample (Table C.5); the optical data used forthe SEDs (Table C.6);
-
the result of the F-test over the optical/X-ray SEDs to choose the better fit function (Table C.8);
-
the factors to convert magnitudes into flux densities (Table C.7);
-
the sample of the 165 GRBs with known redshift from which we started the data selection, with references to papers and GCNs whith optical data (Table C.9);
-
plots of the optical and X-ray LCs for the GRBs in our sample (Figs. C.1–C.9);
Optical LC fit parameters.
Parameters of the optical/X-ray SEDs fitted with a single power-law.
Parameters of the optical/X-ray SEDs fitted with a broken power-law.
Parameters of the X-ray spectrum fit.
Information on the GRBs in our sample.
Optical data used in the SED.
Conversion factors used to convert magnitude into flux density (Jy).
Result of the F-test over the optical/X-ray SEDs.
165 GRBs with redshift from the beginning of Swift observations in December 2004 until December 2011.
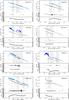 |
Fig. C.1
Comparison between optical and X-ray LCs. Top. Colored points: X-ray data. Dark color represents the excesses and light colors the continuum as calculated in M 13. Group A: blue/lightblue. Group B: red/orange. Group C: purple/magenta. Gray points: optical data. Black solid line: fit of the data. Gray solid line: components of the fit function used to fit the optical data. Middle. Ratio between the optical data and their fit function. The points have different colors when the optical data come from different filters. Bottom. Ratio between the X-ray flux and the optical flux. Hashed gray boxes: SED time intervals. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
 |
Fig. C.2
Comparison between optical and X-ray LCs. Color–coding as in Fig. C.1. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
 |
Fig. C.3
Comparison between optical and X-ray LCs. Color–coding as in Fig. C.1. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
 |
Fig. C.4
Comparison between optical and X-ray LCs. Color–coding as in Fig. C.1. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
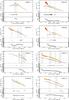 |
Fig. C.5
Comparison between optical and X-ray LCs. Color–coding as in Fig. C.1. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
 |
Fig. C.6
Comparison between optical and X-ray LCs. Color–coding as in Fig. C.1. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
 |
Fig. C.7
Comparison between optical and X-ray LCs. Color–coding as in Fig. C.1. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
 |
Fig. C.8
Comparison between optical and X-ray LCs. Color–coding as in Fig. C.1. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
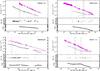 |
Fig. C.9
Comparison between optical and X-ray LCs. Color–coding as in Fig. C.1. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
 |
Fig. C.10
Optical/X-ray SEDs for GRBs belonging to Group A. Solid line: the fitting function. Dotted line: power-law (blue) or broken power-law (orange) fitting function. Light blue/blue lines stand for th power-law fitting functions. Red/orange lines correspond to the fitting function with the broken power-law. The distinction between the two different laws follows Table C.8. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
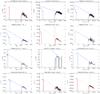 |
Fig. C.11
Optical/X-ray SEDs for GRBs belonging to Group A. Color–coding as in Fig. C.10. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
 |
Fig. C.12
Optical/X-ray SEDs for GRBs belonging to Group B. Color–coding as in Fig. C.10. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
 |
Fig. C.13
Optical/X-ray SEDs for GRBs belonging to Group B. Color–coding as in Fig. C.10. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
 |
Fig. C.14
Optical/X-ray SEDs for GRBs belonging to Group B. Color–coding as in Fig. C.10. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
 |
Fig. C.15
Optical/X-ray SEDs for GRBs belonging to Group B. Color–coding as in Fig. C.10. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
 |
Fig. C.16
Optical/X-ray SEDs for GRBs belonging to Group C. Color–coding as in Fig. C.10. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
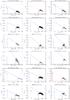 |
Fig. C.17
Optical/X-ray SEDs for GRBs belonging to Group C. Color–coding as in Fig. C.10. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
 |
Fig. C.18
Optical/X-ray SEDs for GRBs belonging to Group C. Color–coding as in Fig. C.10. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
© ESO, 2013
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


