Fig. 2
Download original image
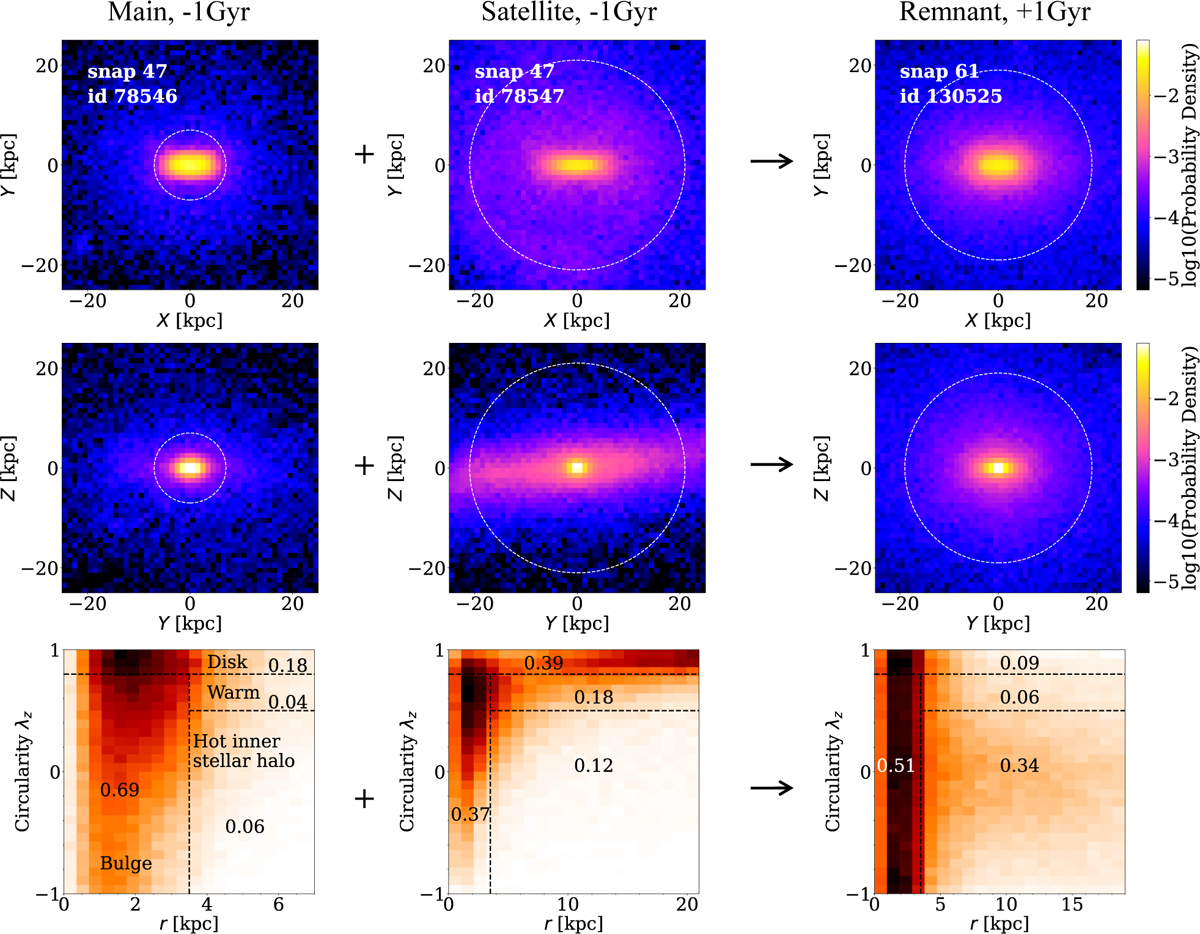
Decomposition of galaxy structure adopted in this paper. We show the main progenitor, the satellite, and the remnant galaxy of a merger pair as the same one shown in Fig. 1. The top and the middle row show galaxies image projected on the X–Y and Y–Z plane, corresponding to face-on view and edge-on view, respectively. Columns from left to right are the main galaxy, satellite galaxy and remnant galaxy, respectively, with snapshot and ID shown in each panel of the top row. The part enclosed by the white dotted circle indicates two times of half-mass radius. The bottom row displays corresponding stellar orbit distribution within the white dotted circle as well as decomposition method based on the phase space of λz versus r. The components of disk, warm, bulge, hot inner stellar halo, and the corresponding fractions are labeled in the panel. The merger destroys the disks of progenitor galaxies and causes an increase in the fraction of stars in the hot inner stellar halo of the remnant.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


