Fig. 1
Download original image
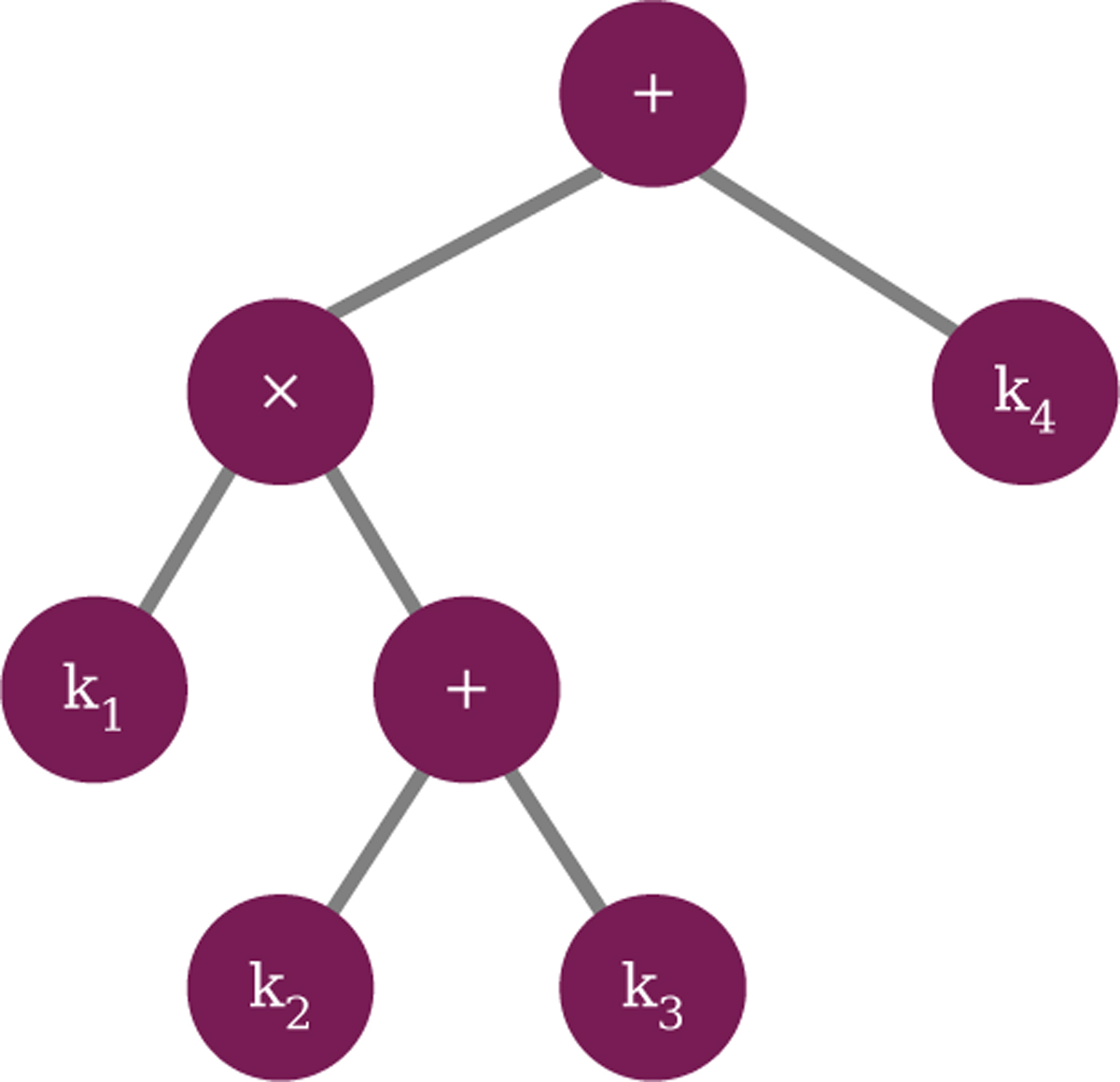
Example of a combinatorial kernel and its binary tree representation. The kernel, k, is described by a non-linear combination of four elementary kernels, k = k1 · (k2 + k3) + k4. This combination can be visualised as a binary tree, where the leaf nodes correspond to the elementary kernels (atoms), and the internal nodes represent operations.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


