Table 2
Power-law index of the result and model.
| Dataset and Mechanism | Index (γ1 )1 | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Observational Result | Previous Work | 0.38 – 0.9 | Plavchan & Bilinski (2013) |
| 1/3 ~ 0.33 | Mulders et al. (2015) | ||
| all multiple systems | 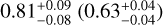 |
This Work | |
| Rp < Rgap (super-Earths) | 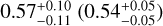 |
||
| Rp ≥ Rgap (sub-Neptunes) | 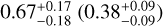 |
||
| mixed multiple systems | 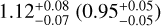 |
||
| Theoretical Model | Sublimation (active, α = 2)3 | 11/9 ∼ 1.22 | Liu et al. (2019) |
| Sublimation (passive, k = 2)4 | 1.0 | Dullemond et al. (2001) | |
| Sublimation (active, α = 1)3 | 7/9 ∼ 0.78 | Liu et al. (2019) | |
| Stellar Tides | 9/13 ∼ 0.69 | Jackson et al. (2009) | |
| Sublimation (passive, k = 1)4 | 0.5 | Dullemond et al. (2001) | |
| Co-rotation Radius | 1/3 ∼ 0.33 | Mulders et al. (2015) | |
| Planetary Tides | 3/13 ∼ 0.23 | Jackson et al. (2009) | |
Notes. 1The index represents the power-law relationship between the inner edge and stellar mass (γ1 ). 2To compare with the degree of metallicity correction presented in the observational results of this work, it is expressed here in the form: “γ1 in Eq. (8) (γ1 in Eq. (3))”. 3In the theoretical model of active dust sublimation, α represents the power-law index of the mass accretion rate scaling with stellar mass. 4In the theoretical model of passive dust sublimation, k represents the power-law index of the luminosity-mass dependence.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


