Fig. 5.
Download original image
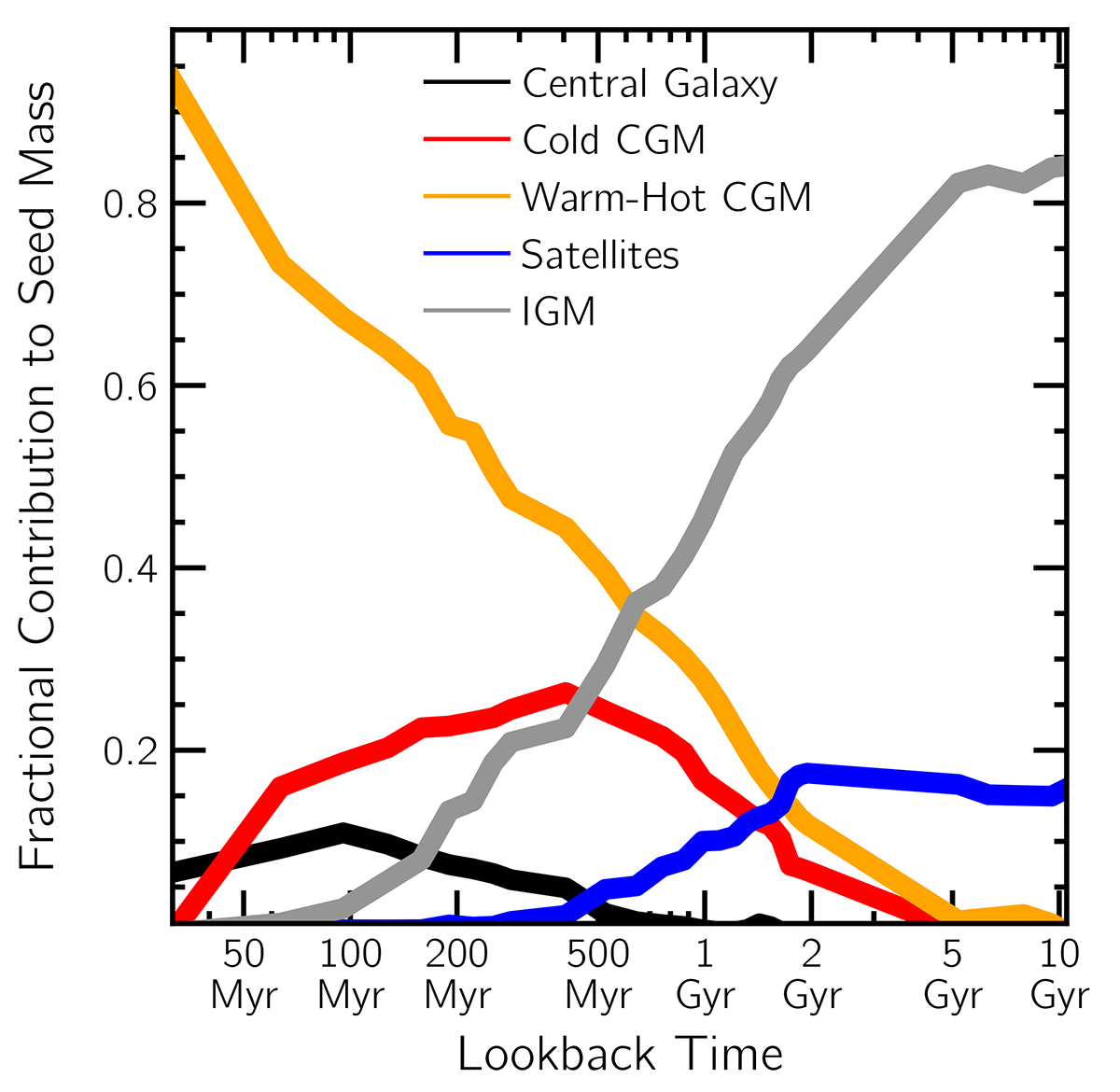
Dissecting the different sources of gas that seed the condensation of cold clouds out of the hot halo at z ∼ 0. On short timescales (≲500 Myr), the dissolution of past clouds into the hot phase, and the subsequent mixing, is the primary source, and it is also potentially stirred by outflows from the central galaxy into the CGM. Transitioning out into previous cosmic epochs as early as z ∼ 2 (tlookback ∼ 10.5 Gyr), the mass giving rise to these seeds was predominantly smoothly accreted from the IGM into the halo (∼85%), while clumpy accretion through satellites contributes the remaining ∼15%.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


