Fig. A.3.
Download original image
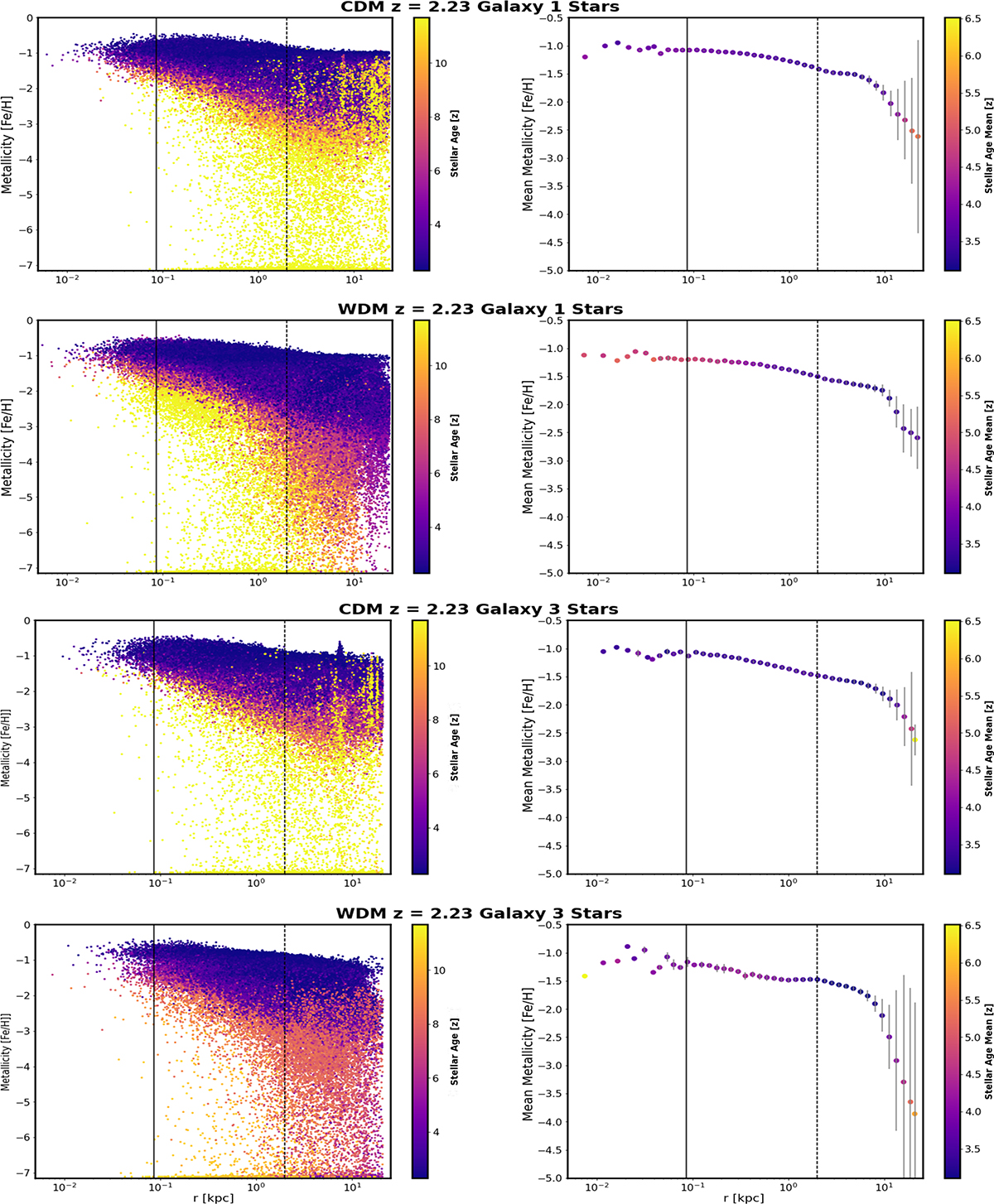
Left panel: 2D correlation of stellar distance vs. stellar metallicity. It is evident that metal-rich stars are predominantly located closer to the galactic center. This trend holds across all DM models, with a slight offset observed for ψDM. The data points are color-coded based on their stellar age, providing additional context. Right panel: 2D correlation of stellar spatial distribution vs. mean metallicity. The negative Spearman correlation coefficient indicates that older stars tend to be more metal-poor, while younger stars are more likely to be metal-rich. The data points are color-coded based on their mean stellar age, offering further insights. The vertical black line indicates the comoving limit, while the dashed line represents the ideal size of a core-halo structure.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


