Fig. 8.
Download original image
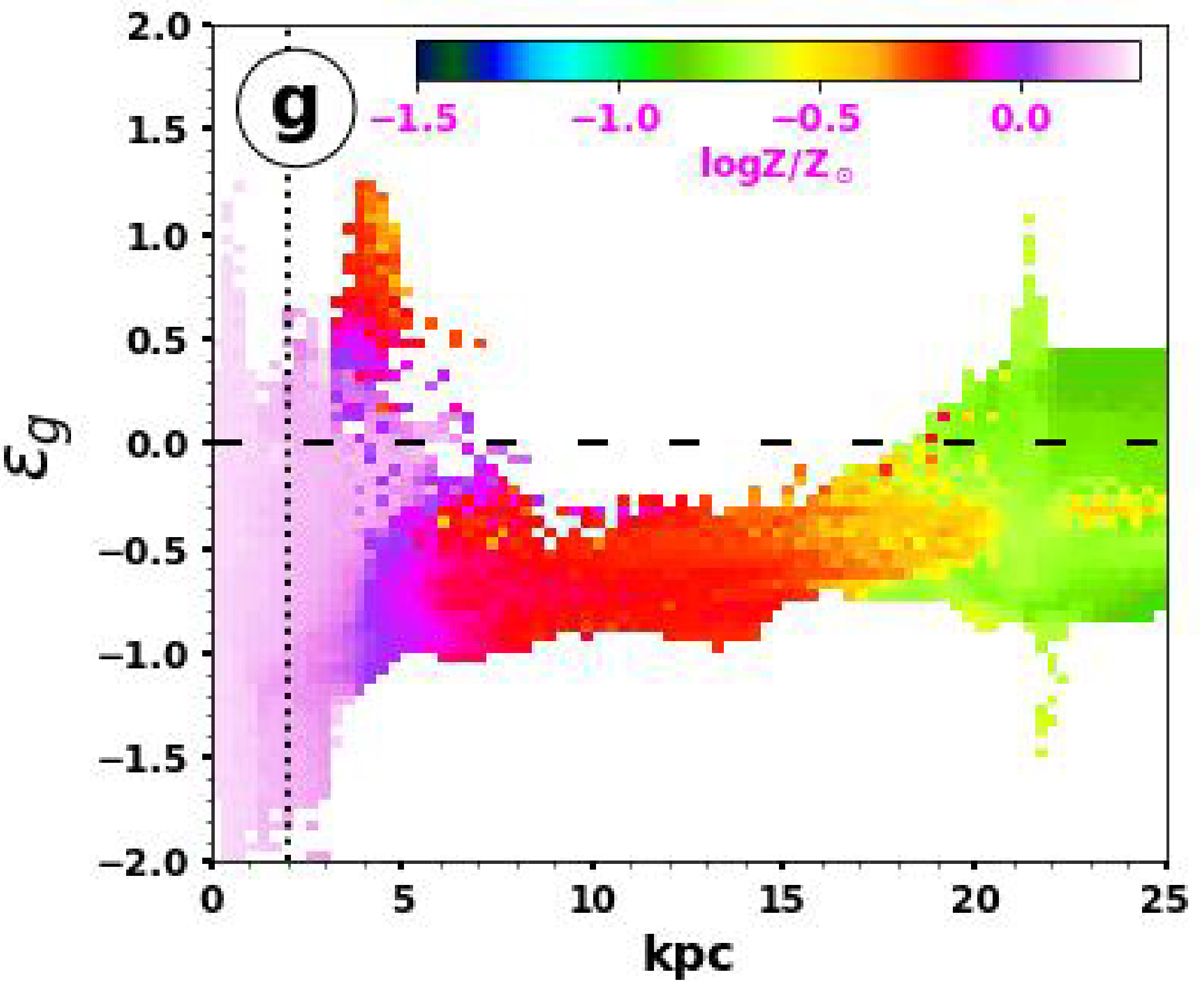
Variations of the gas circularity parameter ϵg with respect to the radial distance r and color coded according to the global gas metallicity at z = 0.33 (&#Xtextcircled;g). The gas in the satellite has a metallicy of log(Z/Z⊙) ∼ –0.85 (green) which is consistent with the metalicity of young stars displayed in Fig. A.2 (second line – fourth column). Then some of the gas of the satellite is accreted by G70 and is progressively enriched in metal as the radial distance decreases due to supernovae activity dominated by young stars in the central part. Consequently, the accreted gas reaches the galactic plane with a much higher metallicy and then forms stars that inherit the same high metallicity, consistent with trends found in Fig. A.2 at the same epoch.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


