Fig. 6
Download original image
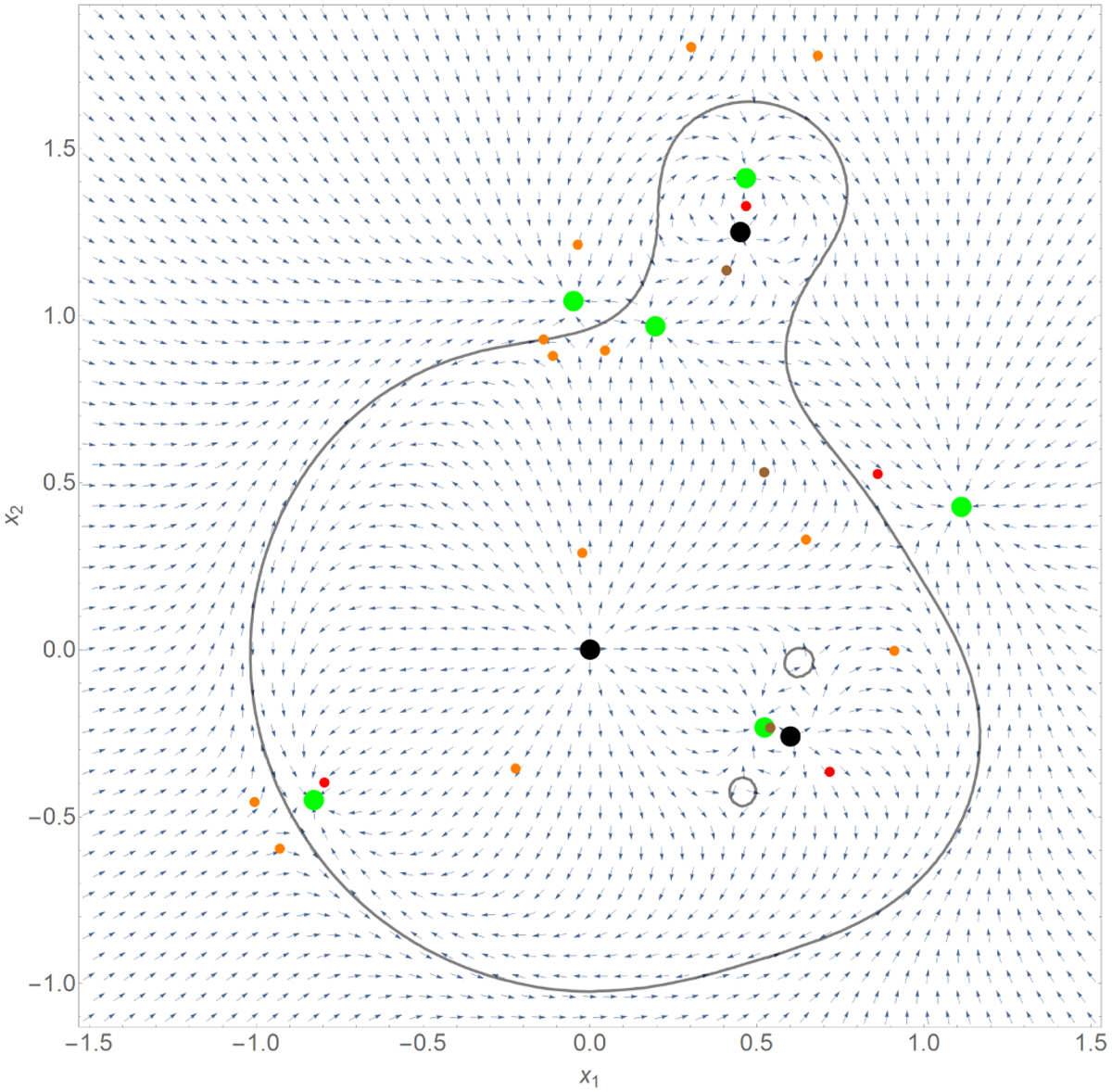
Solution search in the Nopoly algorithm. Here we have three lenses (black dots) with their critical curves in gray. The initial seeds based on image perturbations (Sect. 6.6.1) are the red dots. The seeds for central images (Sect. 6.6.2) are the brown dots. The vectors indicate the direction of displacement e as calculated by the Newton–Raphson method (18). Following the vector flow from the initial seeds, we find the images (green dots). For each image, we also calculate new seeds (orange dots) for possible partner images beyond the critical curves (Sect. 6.6.3). We note that the positive parity image on the right, the negative parity image on top and the negative parity image on the left are very close to the corresponding red seeds and are therefore immediately found. The remaining two negative parity images are caught starting from the brown seeds. At this point the positive parity image on the left would still be missing, but we see that the search for partner images starting from the nearby negative parity image places two orange seeds very close to this final image, which is eventually recovered.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


