Fig. 1
Download original image
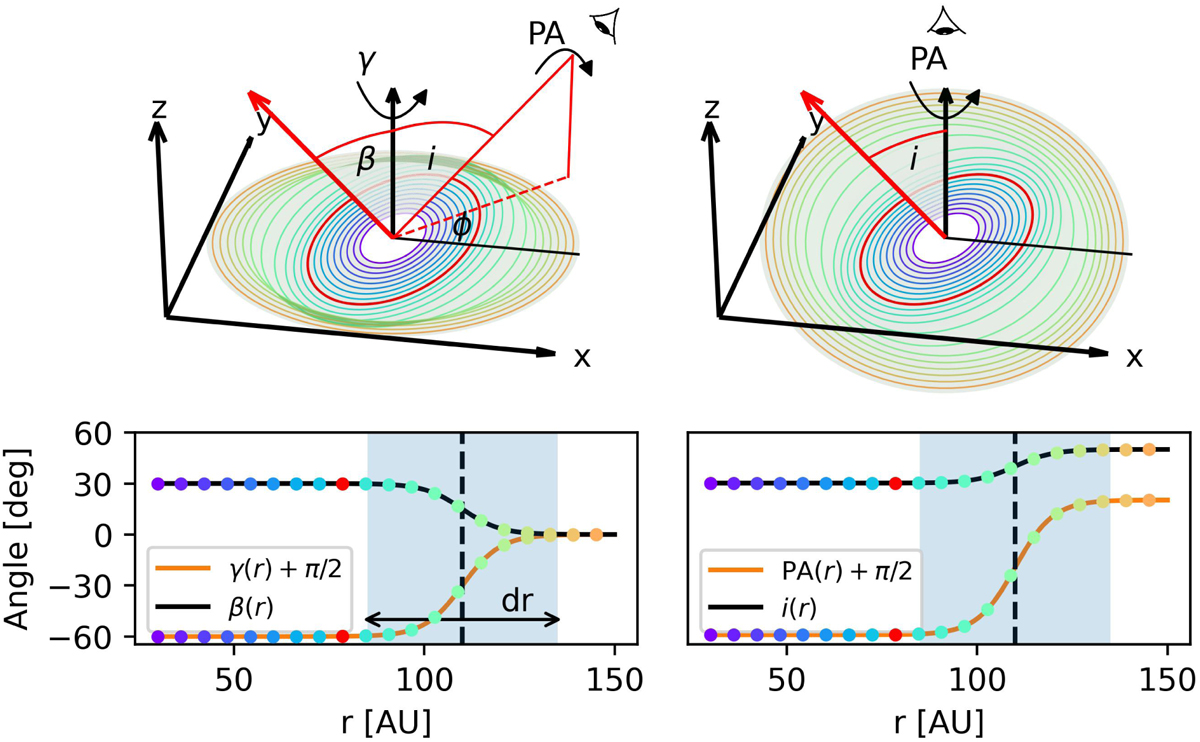
Geometrical representation of the warp models for each prescription. Left: disk-frame representation of the warp. The inner disk orientation is characterized by the angle β, representing the inclination with respect to the outer disk normal vector, and the twist angle γ denoting the rotation around the normal vector. The direction of the observer is defined through a rotation around the outer disk ɀ-axis by ϕ, and inclination i away from it, the camera is rotated by PA around the vector pointing toward the observer. Right: sky-frame representation of the warp. Each ring has an associated i and PA. The inclination is defined with respect to the ɀ-axis. The PA rotation is applied around the line-of-sight represented by the black arrow. On the bottom the respective profiles are plotted. The colored dots represent each ring position, the inflection point is demarcated by the black dashed line, and the rectangular region shows the transition width. We note that the angles shown are representative of the highlighted red ring, the red arrow is the normal vector to the surface defined by that ring.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


