Fig. B.3
Download original image
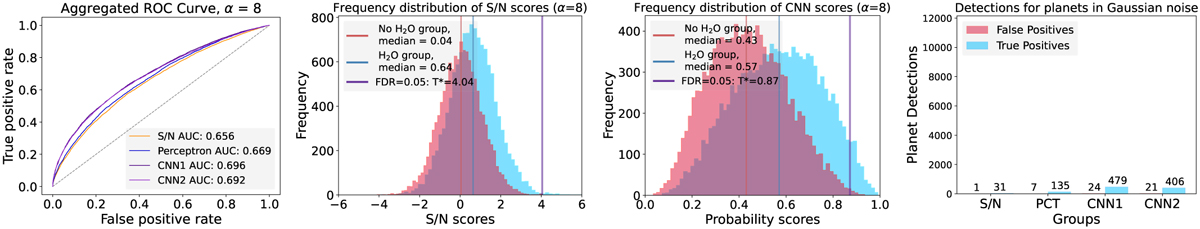
Tests conducted on planetary signals (H2O) embedded in idealistic simulated Gaussian noise. Left: ROC curves and AUC showing that neural networks are barely able to perform better than the S/N. Middle-Left and Middle-Right: Frequency distributions of aggregated scores assigned to the negative group (red) against the positive group (blue) for the S/N (left) and the CNN (right) in the presence of Gaussian noise. The CNNs are not able to separate the scores and improve conspicuity as well as in the case of non-Gaussian noise. Right: Classification predictions under a Gaussian noise regime, given a FDR≤ 5%. The use of MLCCS to extract signals becomes ineffective under Gaussian noise, as they are not able to extract more information than the S/N.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


