Fig. 1.
Download original image
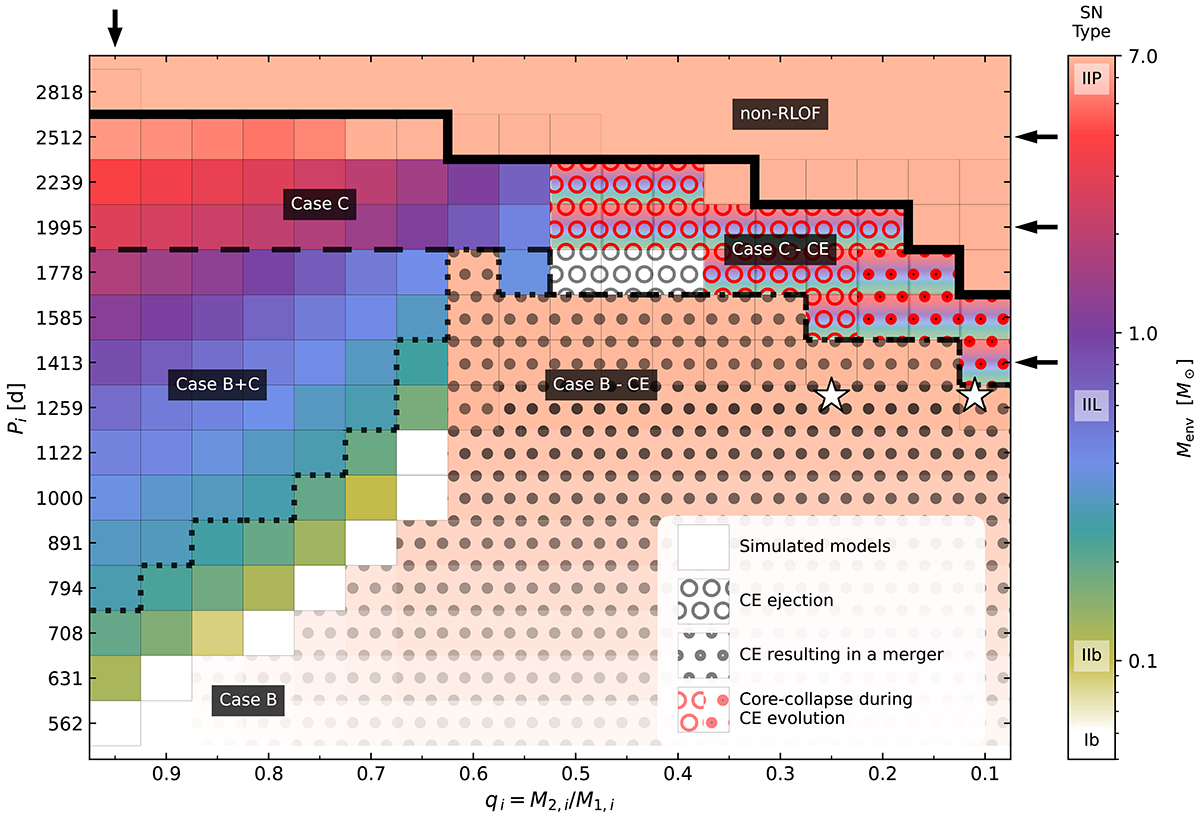
Initial orbital period Pi versus the initial mass ratio qi for the computed binary evolution models (squares), with a color-coding denoting the remaining envelope mass of the primary star at the time of its core collapse. The envelope mass can be used to indicate the anticipated SN type if no CSM interaction would occur (see color bar). The black lines separate systems without mass transfer (above the thick full-drawn), Case C (above the dashed line), Case B+C systems (above the dotted line), and pure Case B systems. where the latter is not investigated in the area in which no binary models are computed. The background pattern of circles indicates a likely CE evolution, where for wide, open circles the energy criterion implies that a CE ejection would be possible, and small filled circles imply the opposite. Here, symbols in red color indicate that the donor star’s core may collapse before the end of the common envelope phase is reached. As in this case, the pre-SN envelope structure is not well constrained, we give the corresponding squares multiple background colors, indicating the range of possibilities. The star symbols represent the multi-D models of Lau et al. (2022). Black arrows point out rows and columns in the plot for which data is displayed in Table 1.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


