Fig. 2
Download original image
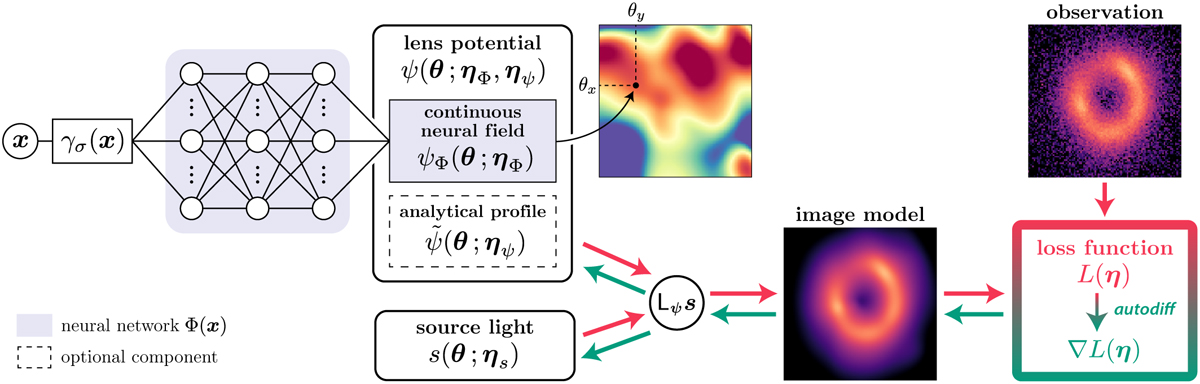
Flowchart of the proposed method. The lens potential is modeled with a continuous neural field that takes as input any position in the image plane and outputs the value of the lens potential at that position. Alternatively, an analytical profile (e.g., a SIE) models the smooth component of the lens potential, while the neural network captures deviations from that smooth component. The input coordinates are first passed through a Fourier feature mapping (γσ) to increase the dynamic range of the recovered features. The different model components follow Eq. (4) except for the blurring operator, omitted to avoid clutter. Since the model is fully differentiable, automatic differentiation is used to compute the exact gradient of the highly nonlinear loss function.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


