Fig. 1
Download original image
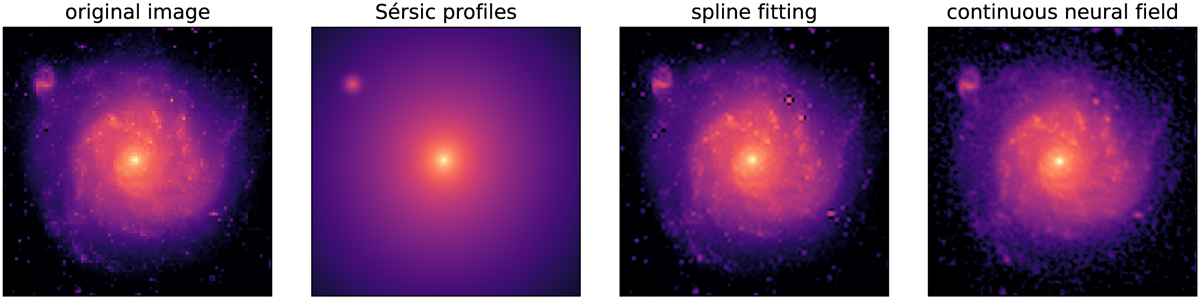
Examples of image representation methods, including the one used in this work. The left panel shows an HST observation of NGC 1309 featuring complex features such as spiral arms and a companion galaxy. The remaining panels show three representations of the original image, from the smoothest to the most complex, obtained by fitting the input image with an analytical model. The resolution of the models is in practice infinite, but here we simply choose one higher than the resolution of the original image. The second and third panels show a representation with two Sérsic profiles and a spline fit respectively. The fourth panel is the representation of the original image using a continuous neural field. This is obtained after optimizing (or 'training', but not in the conventional machine learning meaning) the weights of the neural network based on the pixel 2D coordinates and values of the input image. In this work, we are interested in spatial derivatives of the image (see Sect. 3.1), which we can compute analytically and efficiently from the neural field representation.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


