Fig. 1
Download original image
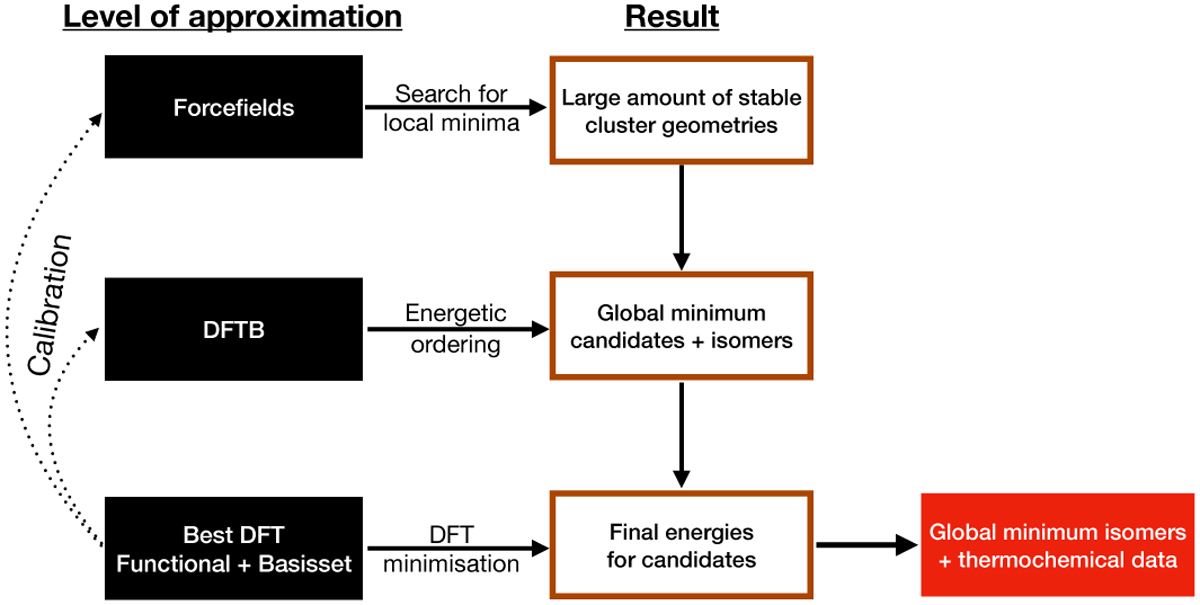
Hierarchical approach to determine global minimum candidate structures for clusters. (1) The geometries and binding energies of small clusters and isomers are used to calibrate the accuracy of the force field and DFTB methods. (2) A force-field description of interatomic interactions is used to locally optimise the geometries of a large number of generated clusters for each size N towards a potential energy minimum. (3) The geometries of these locally and semi-classically optimised cluster candidates are then further refined in a third step, using DFTB methods. This step optimises the geometries of the cluster candidates for the lowest possible potential energy. This provides an energetic ordering of the candidate geometries. (4) The energetically most favourable candidate geometries are then used as inputs for DFT calculations, resulting in the final and most accurate geometries, binding energies, and vibrational and rotational frequencies for each cluster within this approach.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


