Fig. 4.
Download original image
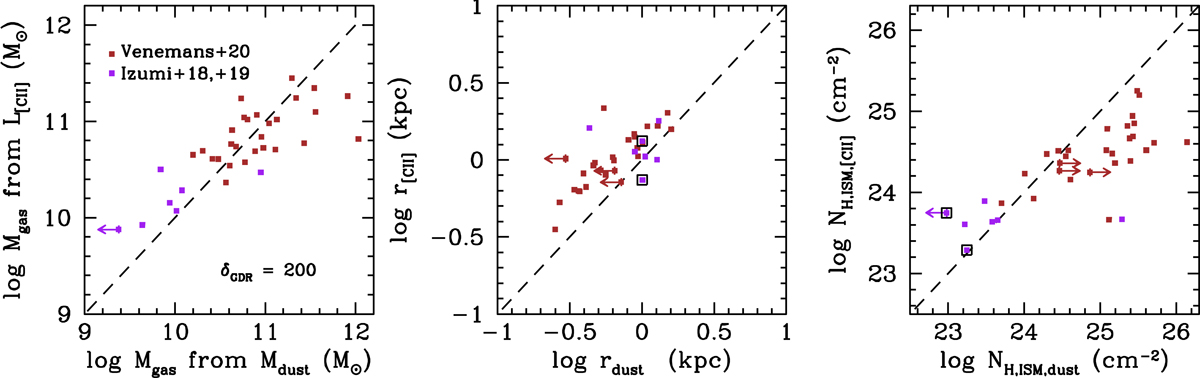
Comparison between ISM mass (left), size (center) and column density (right) as derived from [C II] and dust continuum observations for the z ∼ 6 QSO samples. The ISM masses derived with the two methods agree for δGDR = 200. The [C II]-based sizes are on average ∼1.5 times larger than the dust continuum sizes. The total ISM column densities are on average higher for the dust continuum method, owing to the smaller sizes measured. Three sources with upper limits to their continuum size in the Venemans et al. (2020) sample are marked with arrows in the central and right panels. One SHELLQs source is not detected in the continuum, and is shown with an arrow in the left and right panels. For this and for another source in the same sample (both marked with large open squares in the central and right panels), the size could not be estimated, so we assumed it equal to the median of the sample.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


