Fig. 2
Download original image
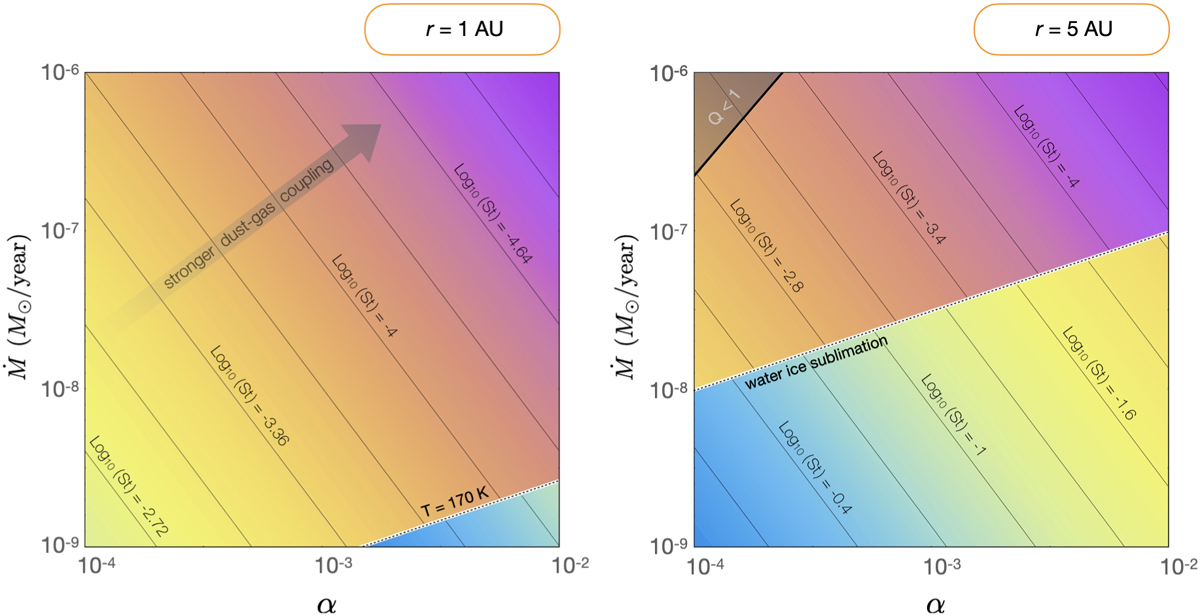
Stokes number attainable by dust grains at r = 1 AU (left panel) and r = 5 AU (right panel). Owing to the fragmentation barrier, solid grains within the disk cannot grow to an arbitrarily large size and disk turbulence acts as a limiting mechanism for particle growth. The inner regions of the disk are characterized by Stokes numbers on the order of St ~ 10−4, indicating very tight gas-dust coupling. Conversely, icy grains within the outer disk can reach Stokes numbers of order St ~ 10−1, implying diminished aerodynamic drag.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


