Fig. 5
Download original image
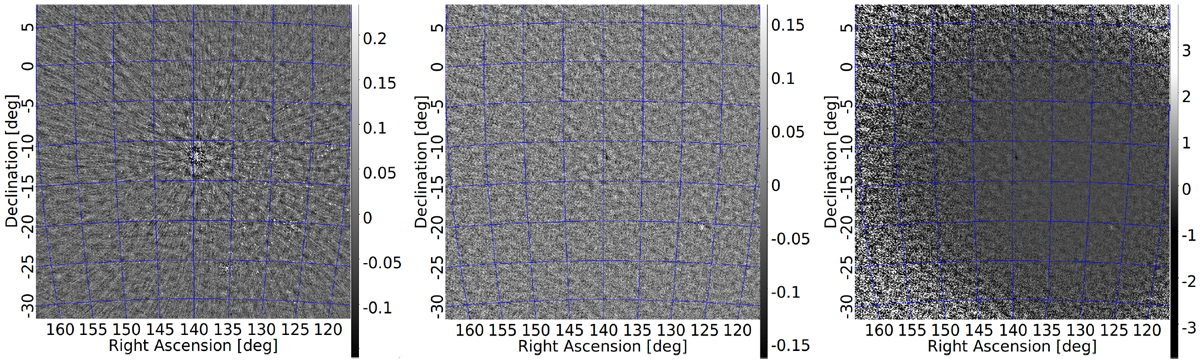
Example 0.5 s sky and difference images in X polarization (scale of the color bar is in Jy) used to calculate SEFD. Left: 0.5 s sky image. Center: difference between two consecutive 0.5 s images. Right: difference between two consecutive 0.5 s images corrected for the primary beam (divided by the primary beam in the X polarization). In order to calculate noise in every direction in the sky within the field of view (noise map), the standard deviation of the noise was calculated in small regions around each pixel in the difference image and divided by ![]() . These noise maps were later converted into SEFD using Eq. (29). The same procedure was applied to Y and is very similar to Stokes I polarizations (in this case the correction for the primary beam was more complex than the simple division by the corresponding primary beam).
. These noise maps were later converted into SEFD using Eq. (29). The same procedure was applied to Y and is very similar to Stokes I polarizations (in this case the correction for the primary beam was more complex than the simple division by the corresponding primary beam).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


