Fig. 9.
Download original image
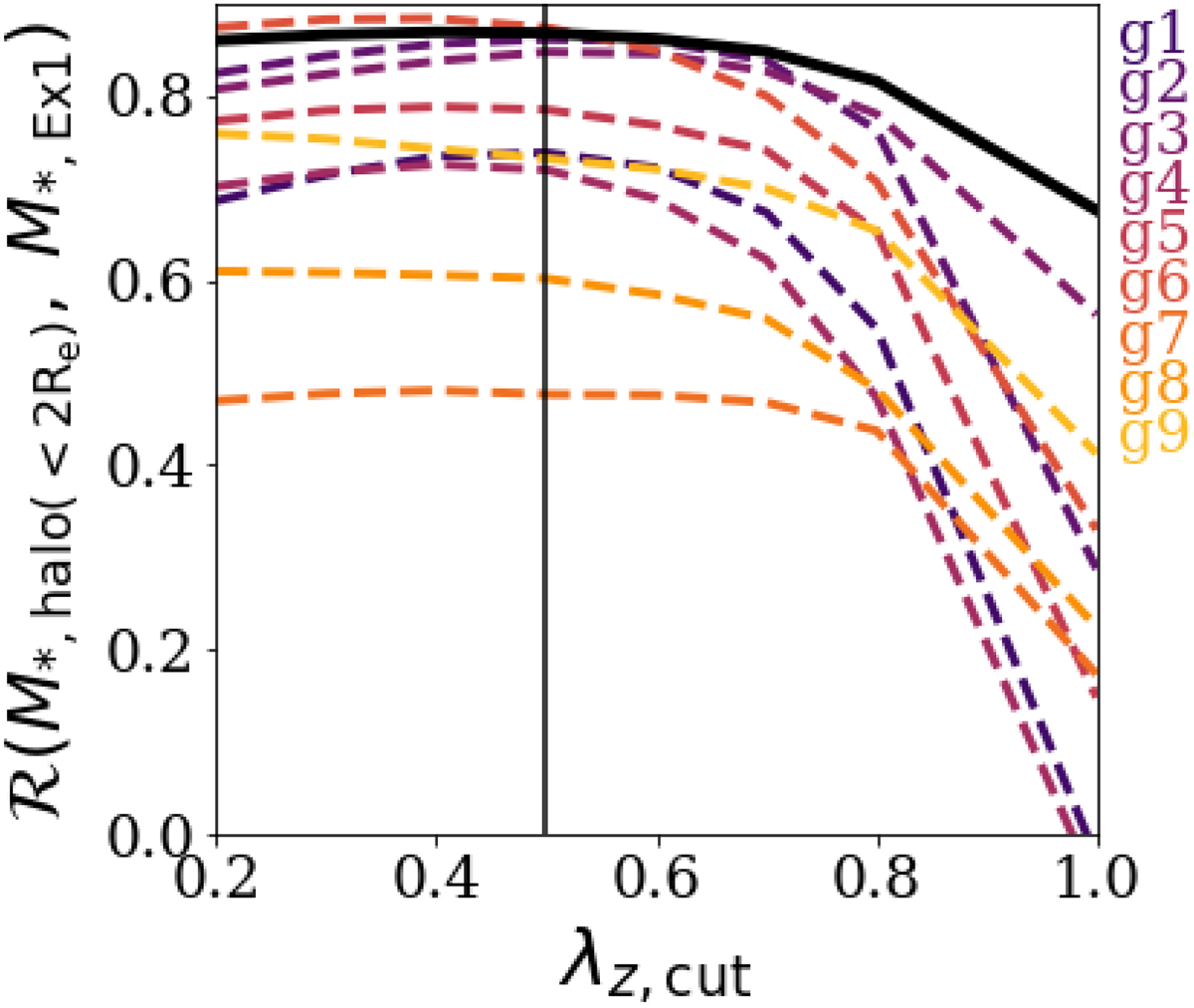
Dependence of the correlation between the masses of the most massive merger and of the hot inner stellar halo of a galaxy on the operational definition of the latter. We show the Pearson correlation coefficient between M*, Ex1 and M*, halo(r < 2 Re) as a function of λz, cut, the maximum level of orbital “coldness” adopted to define inner-halo stars. Namely, in the plot we adopt different definitions of hot inner stellar halo by imposing λz < λz, cut. Dashed curves in different colors indicate galaxies in subsamples g1–g9, and the solid black curve indicates galaxies of the whole sample.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


