Fig. 4.
Download original image
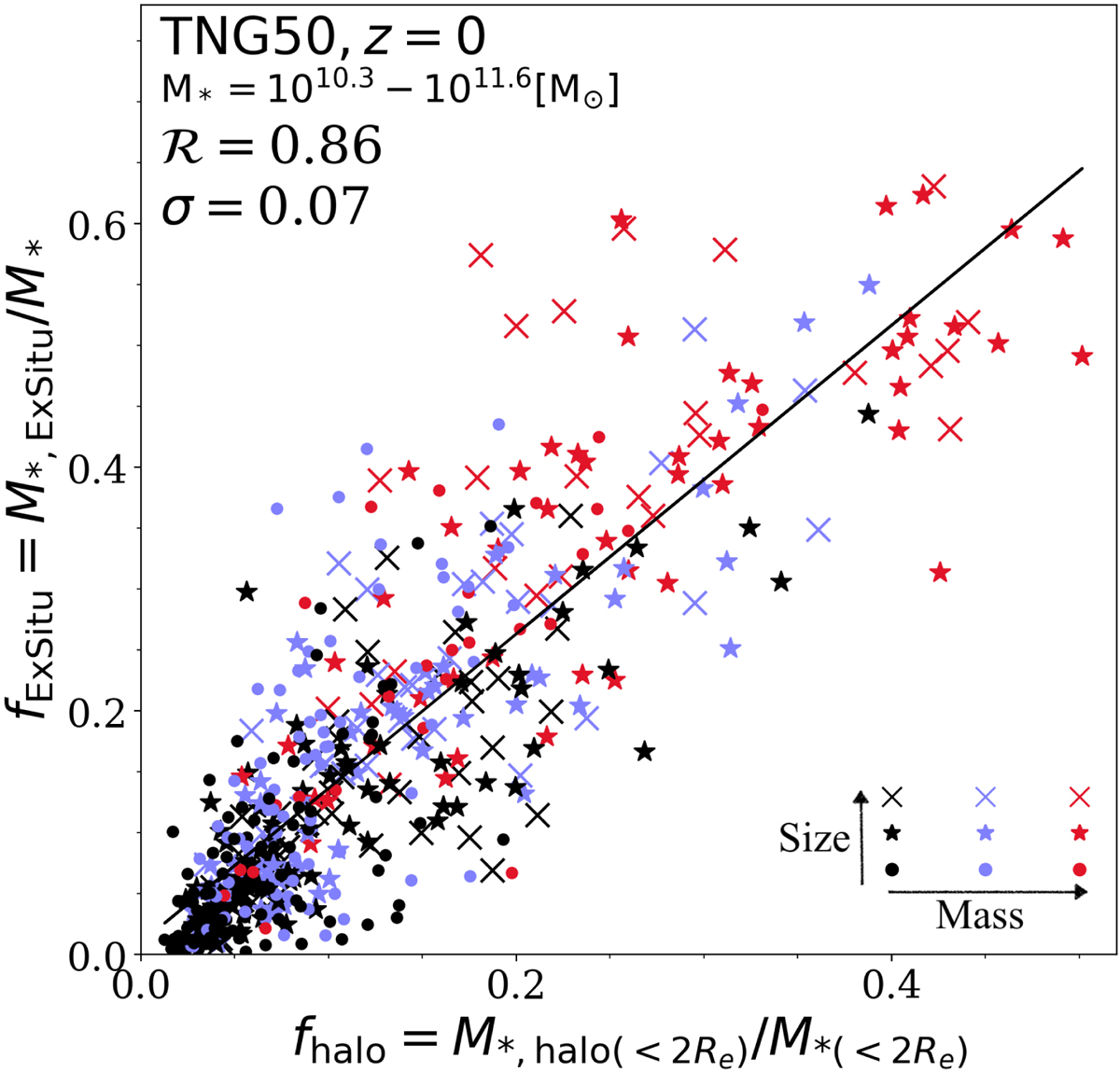
Connection between the hot inner stellar halo and the ex situ mass fraction according to TNG50. We show the mass fraction of the hot inner stellar halo compared to the total stellar mass within the maximum radius of rmax = 2 Re (fhalo = M*, halo(< 2 Re)/M*(< 2 Re)) versus the stellar ex situ fraction (fExSitu = M*, ExSitu/M*) for galaxies with M* > 1010.3 of TNG50 at z = 0. Here we exclude 37 objects identified with ongoing mergers or those with counter-rotating thin disks. Galaxies with size Re below, around, and above the average are indicated by dots, asterisks, and crosses, respectively: they are color coded based on stellar mass, with increasing stellar mass from black, to blue, to red. Galaxies with larger stellar masses and sizes exhibit systematically larger ex situ fractions as well as larger mass fractions in the hot inner stellar halo. The Pearson correlation coefficient ℛ(fhalo, fExSitu) = 0.86 of the whole sample is annotated. The black line is a linear fit to the data points, while the 1σ scatter of the data points against the linear fit is σ = 0.07.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


