Fig. 4
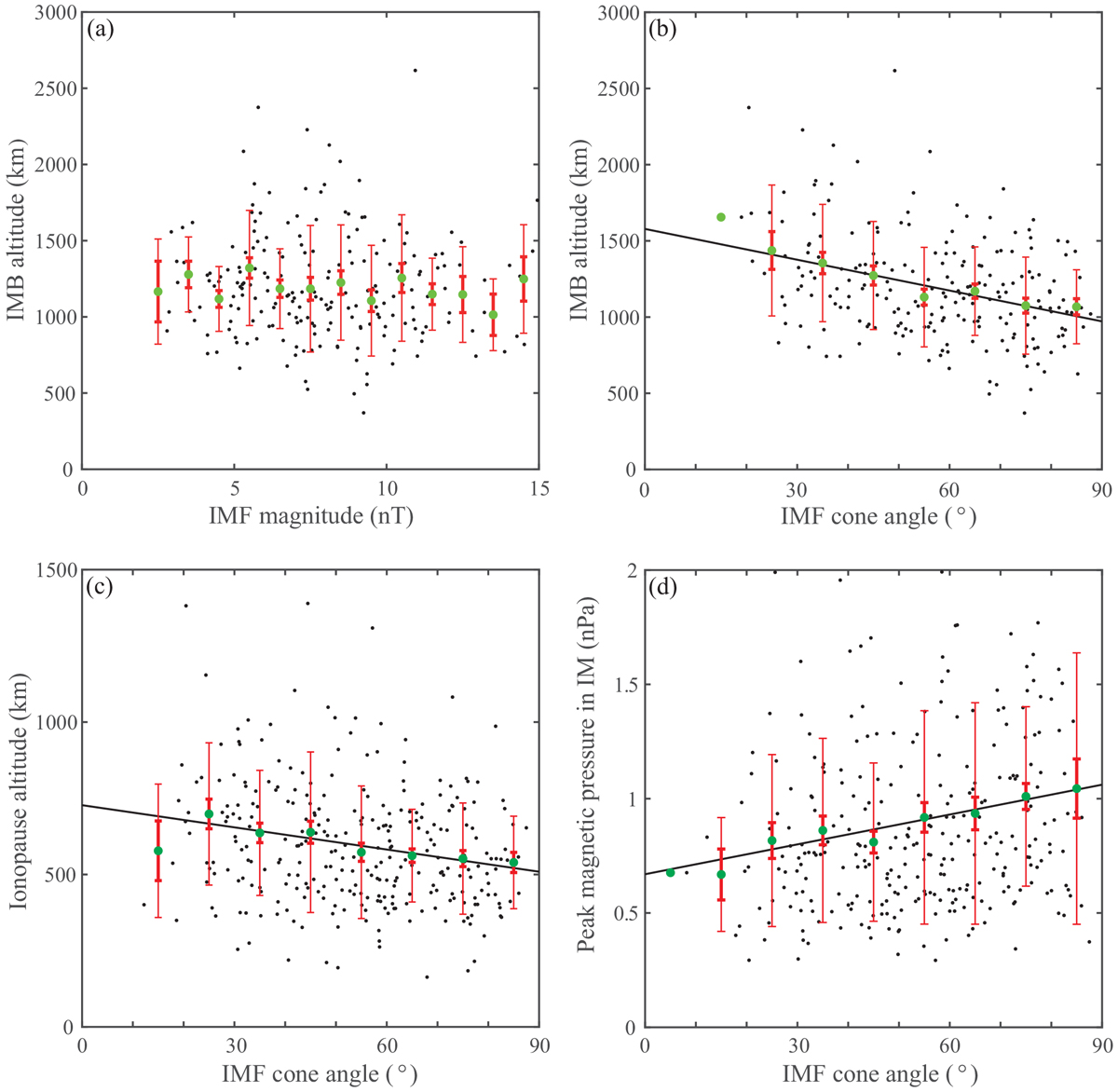
Dependence of Venusian IMB and ionopause altitude on the IMF. (a–b) Similar to Fig. 3, but the terminator IMB altitude is further normalized to the average SSN and average solar wind dynamic pressure. (c) The control of the IMF cone angle on the Venusian ionopause altitude normalized to the average solar wind dynamic pressure. (d) The control of the IMF cone angle on the peak value of the magnetic pressure in the induced magnetosphere (IM). Linear regressions (black line) were done to all of the data points (black points). The mean IMB altitude, the mean ionopause altitude and THE mean magnetic pressure in bins (green dots), the standard deviation in each bin (thin red error bars), and the standard error of the mean (thick red error bars) are shown. There is no correlation between the IMB altitude and the IMF magnitude (P-value > 0.01).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


