Fig. 10.
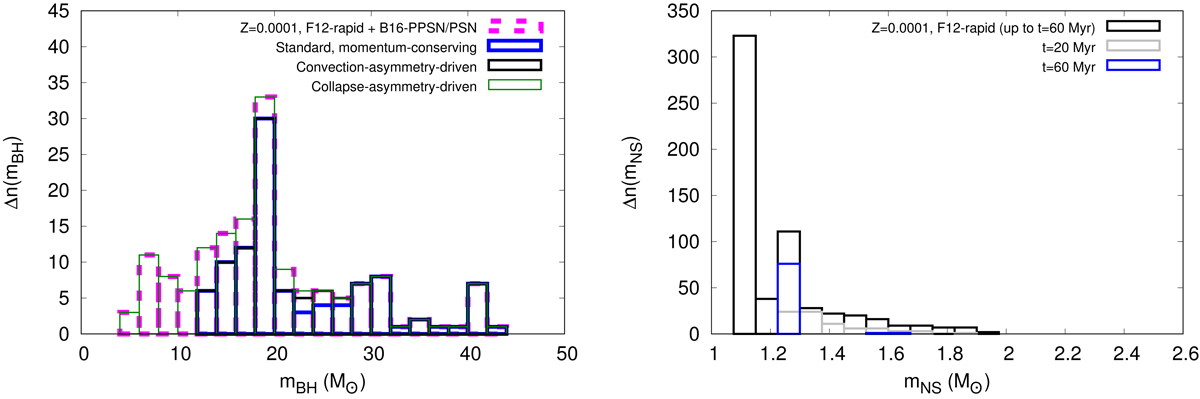
Left: comparison between the retained mass distribution of the BHs (inside a Mcl(0) ≈ 5 × 104 M⊙, rh(0) ≈ 2 pc, initially single-only stars model cluster; see also Fig. 8) for the various natal-kick prescriptions considered in this work (legends; see Sects. 3.1 and 3.2). The F12-rapid+B16-PPSN/PSN remnant-mass model (Sect. 2.2) and Z = 0.0001 is assumed. The dashed histogram represents the natal mass distribution of the BHs for these remnant-mass model and Z. No BHs are retained in such clusters in the neutrino-driven-kick case (Sect. 3.2.3; Fig. 9). In contrast, nearly all BHs are retained if the kicks are collapse asymmetry driven. Right: natal mass distribution of NSs for the F12-rapid(+B16-PPSN/PSN) remnant-mass model (black histogram). The retained mass distributions of the NSs for the collapse-asymmetry-driven kick model at t ≈ 20 Myr and 60 Myr are also shown (grey and blue histograms, respectively). The marginally escaping NSs at 20 Myr (Sect. 3.2.4; Fig. 9, bottom panel) are all depleted by 60 Myr when only the low-/zero-kicked ECS-NSs retain in the cluster.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


