Fig. B.1.
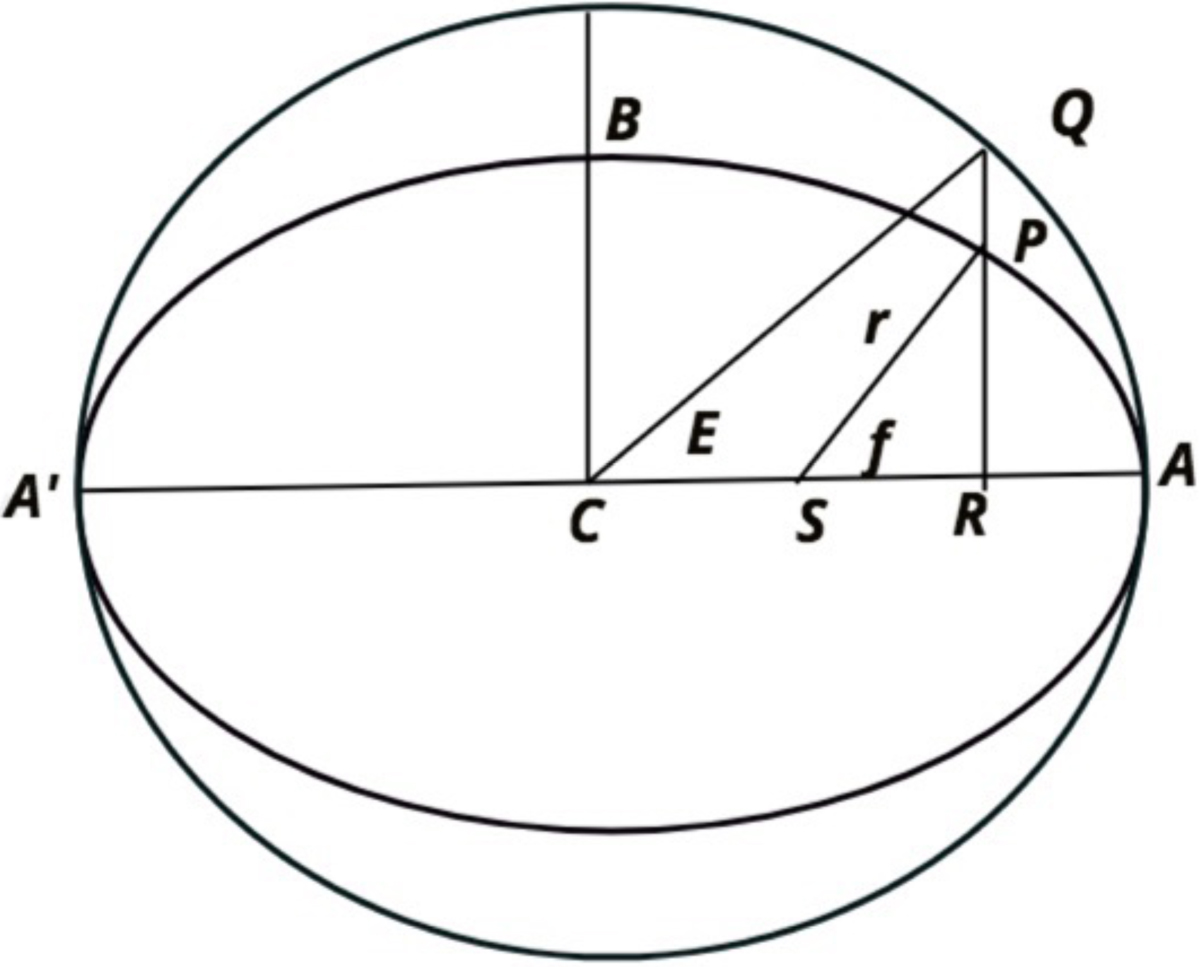
Scheme for deriving the relation between the true and mean anomaly. C is the common centre of the ellipse and the auxiliary circle. S is the focus of the ellipse. The semimajor and semiminor axes are CA = a and CB = b, respectively. The orbital postion of the object is P, its perpendicular projection on the semimiajor axis is R, and the intersection of PR and the auxiliary circle is Q. |SP|=r and CS = ae, where e is the eccentricity of ellipse. The angles ∠QCA and ∠PSA are the eccentric and the true anomaly, respectively. The radius of the auxiliary circle equals the orbital semimajor axis.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


