Fig. A.7.
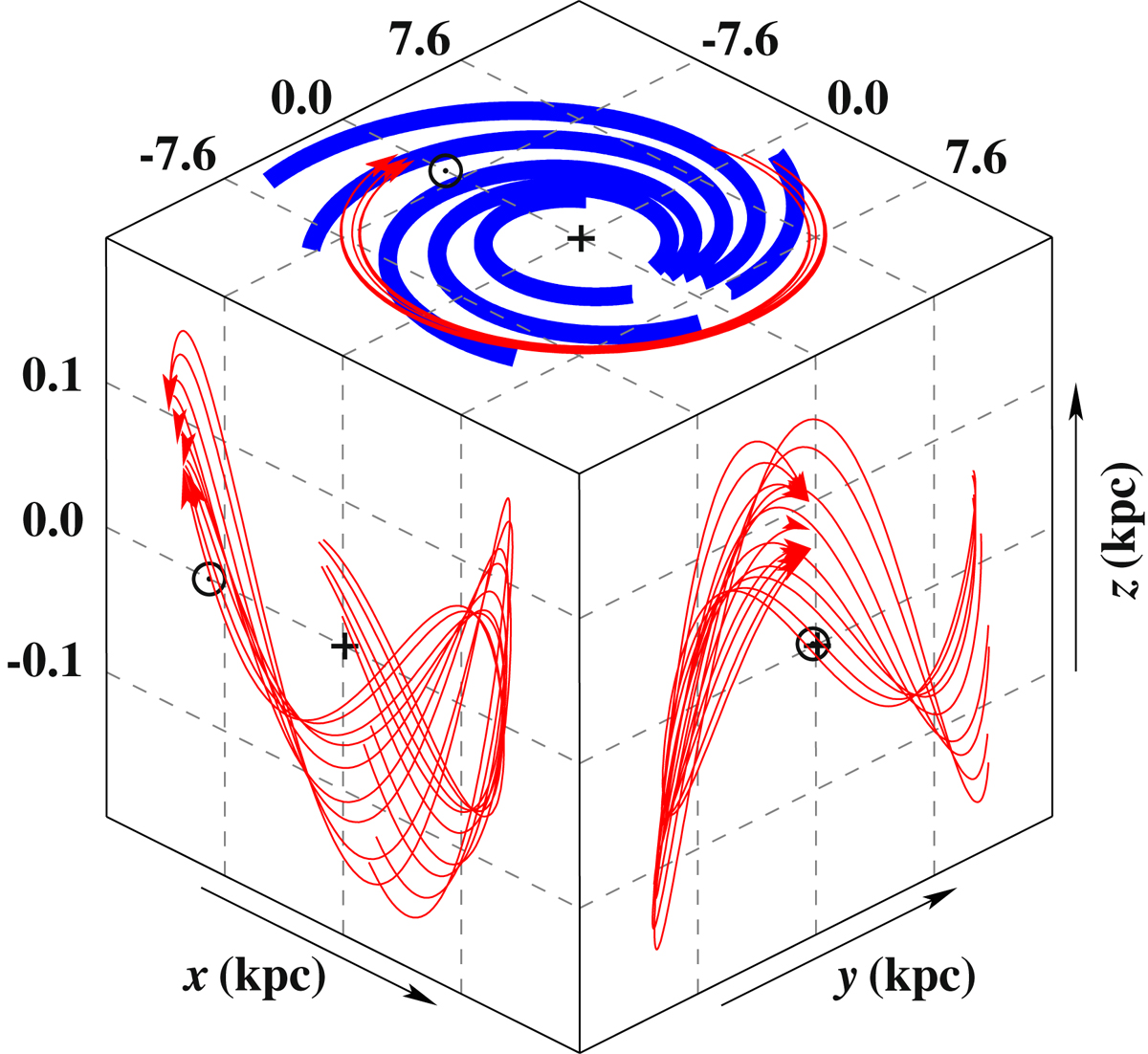
Three-dimensional orbit of LS V+22 25 in a Galactic Cartesian coordinate system in which the Galactic center (marked by a black +) lies at the origin, the Sun (marked by a black ⊙) is located on the negative x-axis, and the z-axis points to the Galactic north pole. The nine trajectories (red lines; arrows indicate the star’s current position) illustrate the effects of uncertainties in the parallax and proper motions from Gaia, and in the systemic radial velocity from Liu et al. (2019). These were computed back in time for 200 Myr using a standard three-component, axisymmetric model for the Galactic gravitational potential (see Irrgang et al. 2013 for details on the Milky Way mass model and on the orbit computations). The shape of the orbit (prograde, almost circular, small vertical oscillations) is typical for a thin-disk star (see, e.g., Pauli et al. 2006 for details on the properties of different kinematic groups). The thick blue solid lines schematically represent the loci of the spiral arms based on the polynomial logarithmic arm model of Hou & Han (2014). Interestingly, the current position of the star seems to be aligned with the Perseus spiral arm, which could be a possible sign of youth.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


