Fig. 4.
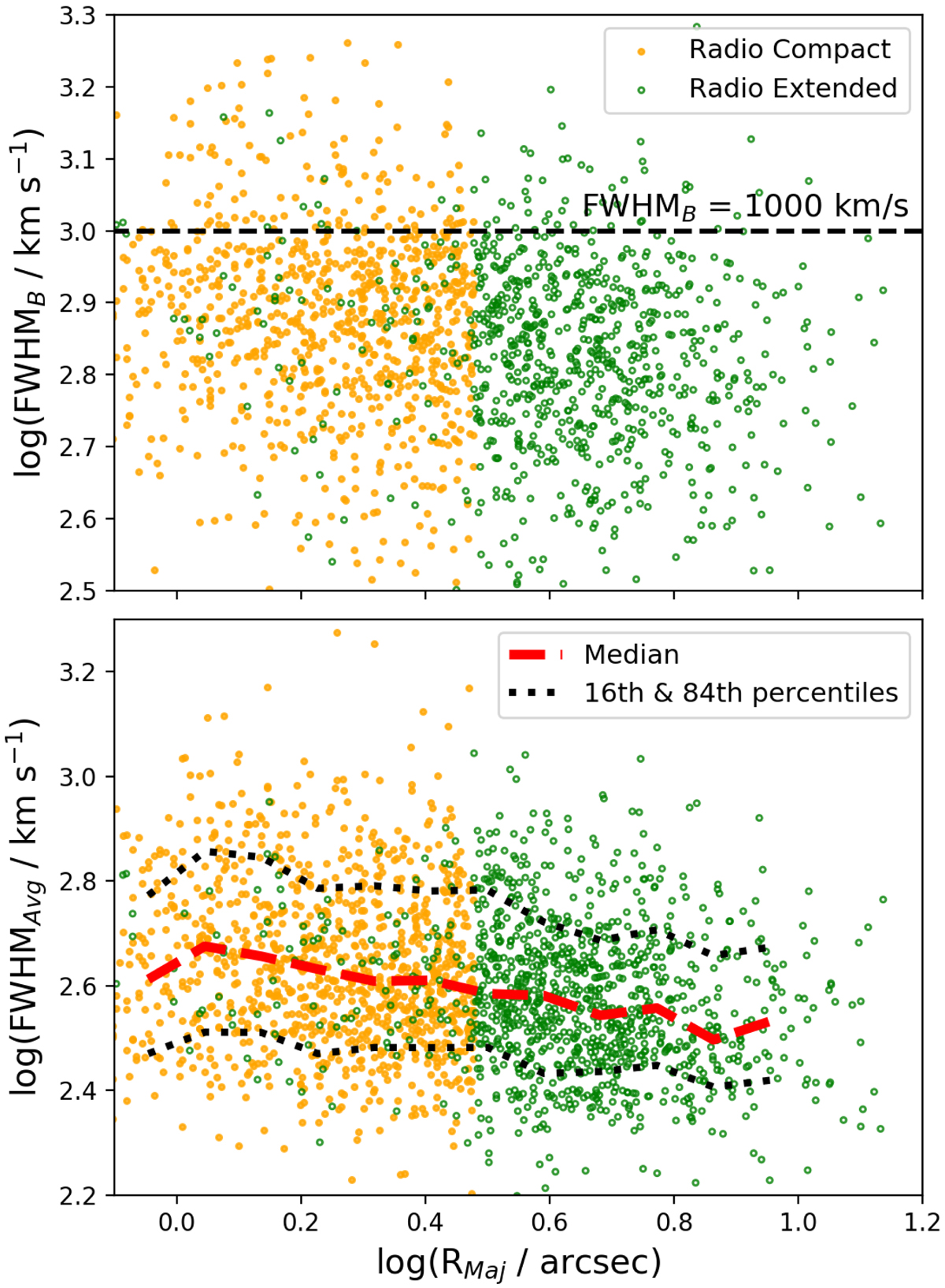
[O III] emission-line width vs. radio size, using two definitions: (1) the velocity width of the broadest [O III] emission-line component (FWHMB; top panel) and (2) the flux-weighted average velocity width of two emission-line components (bottom panel; FWHMAvg). Symbols are colour-coded as in Fig. 1 with the addition of the curve showing the running median (in 0.1 dex bins) and the corresponding 16th and 84th percentiles in the bottom panel. The small number of radio extended sources with apparently small sizes is due to extended radio structures beyond the core (see Sect. 3.2). We see a weak trend where the largest sources with ≈8 arcsec have a 0.1−0.2 dex smaller velocity widths on average than the smaller ≈1 arcsec sources. Compact radio sources are more likely to have the broadest emission-line components (e.g. FWHMB > 1000 km s−1; above the dashed line; Sect. 4.1).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


