Fig. 2.
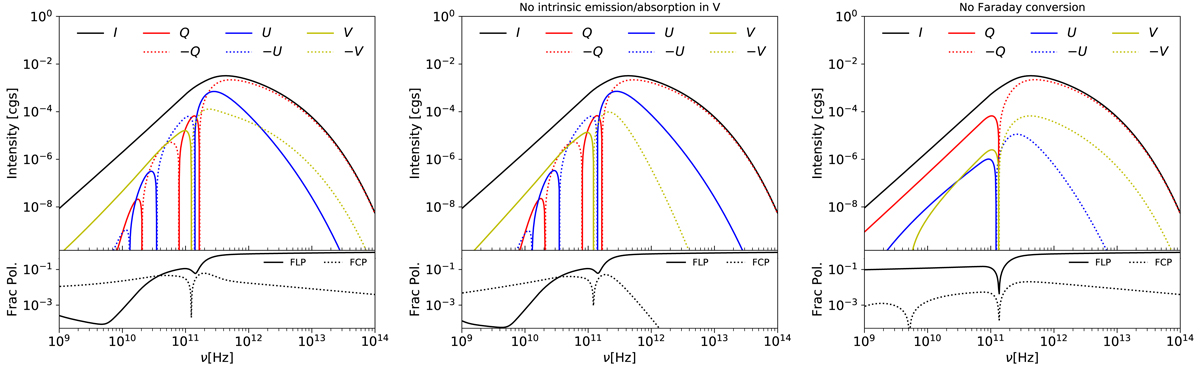
Left panel: spectral energy distribution of the Stokes parameters (I, Q, U, V, where I ≡ Iν is the specific intensity in cgs units [ergs s−1 cm−2 ster−1 Hz−1]) computed with the static background jet model described in Sect. 3.1 and the corresponding fractional linear and circular polarizations. Middle panel: same as the left panel, but assuming no emission/absorption in Stokes V (jV = aV = 0). Right panel: same as the left panel, but assuming no Faraday conversion (ρQ = 0). The flux in Stokes V (left panel) in the optically thick part of the spectrum is mainly produced by Faraday conversion. In the optically thin part of SED, Stokes V is due to intrinsic emission. In this jet model the spectra of fractional linear and circular polarization have steep and nearly flat spectral slope, respectively. When the values of Q, U, and V are negative, −Q, −U, and −V are plotted here.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


