Fig. 3
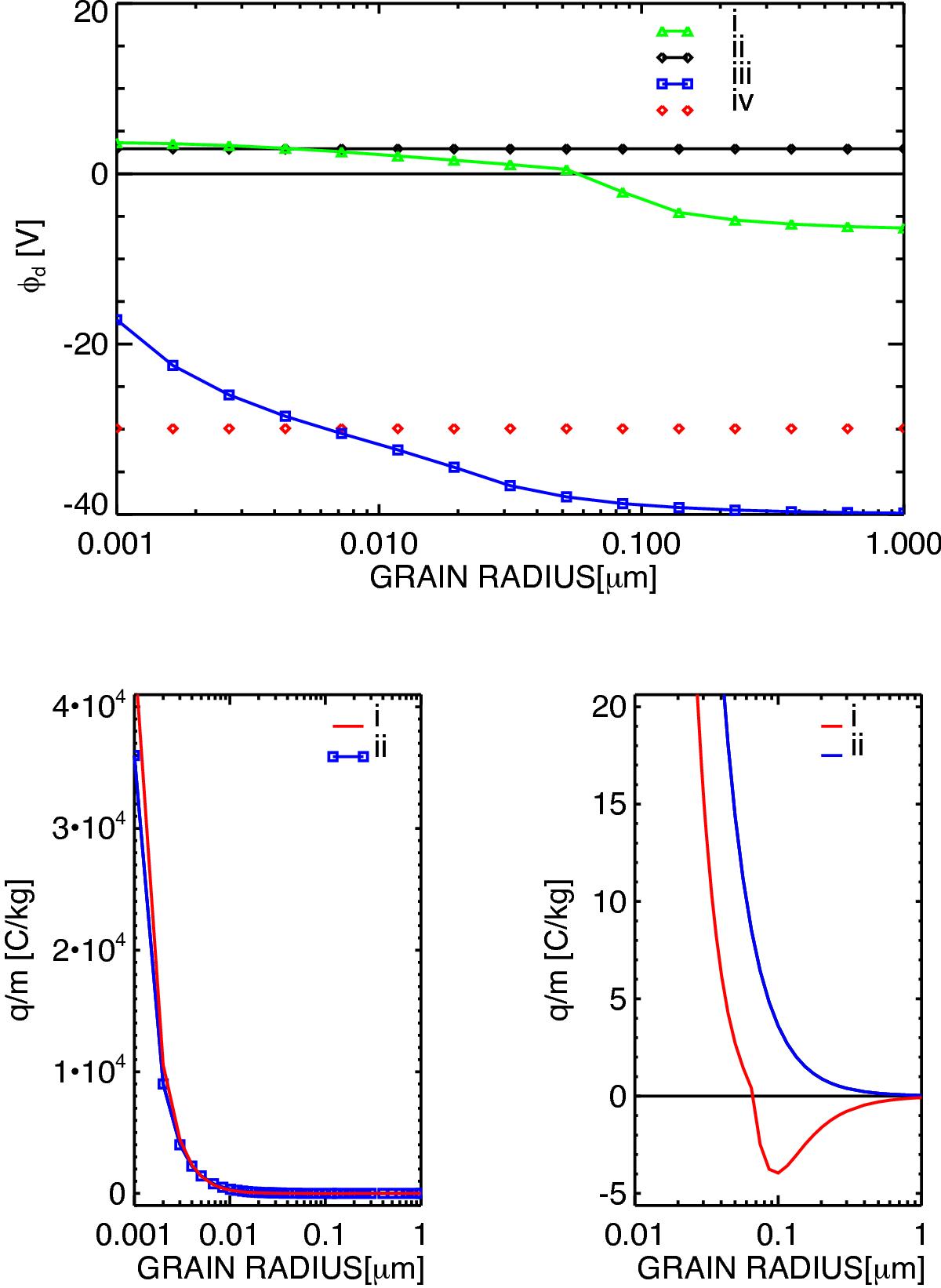
Top: dependence of the equilibrium surface potential φd(a) on grain radius a. Materials are NaCl (i); (ii) and silicate (iii); (iv) immersed in typical plasma conditions expected at r ~ 5.7RJ distance in the Jupiter system (see text). The results (i) and (iii) are obtained from the generalized Js model (7) and compared to results (ii) and (iv) using the Sternglass approximation for SEE ![]() . Bottom, left: dependence of the charge-to-mass ratio q/m on grain radius a for NaCl grains corresponding to the results (i) and (ii) in Fig. 3 (top). Bottom, right: zoom for small | q/m | emphasizing the existence of a size range where the new SEE model leads to a different polarity of the grains.
. Bottom, left: dependence of the charge-to-mass ratio q/m on grain radius a for NaCl grains corresponding to the results (i) and (ii) in Fig. 3 (top). Bottom, right: zoom for small | q/m | emphasizing the existence of a size range where the new SEE model leads to a different polarity of the grains.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.