Table 4
Outflow properties of the extended sample of galaxies.
| Object | log (MH2,OF)† |
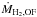 †
†
|
ROF | vOF,avg | vOF,max | log(τdep)† | log(Pkin,OF)† | (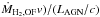 † † |
Refs. |
| [M⊙] | [M⊙ yr-1] | [kpc] | [km s-1] | [km s-1] | [yr] | [erg s-1] | |||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|
|
|||||||||
| IRAS F08572+3915 | 8.61 | 1210 | 0.82 | 800 | 1200 | 6.10 | 44.39 | 35 | 1 |
| IRAS F10565+2448 | 8.37 | 300 | 1.10 | 450 | 600 | 7.42 | 43.28 | 40 | 1 |
| IRAS 23365+3604 | 8.17 | 170 | 1.23 | 450 | 600 | 7.70 | 43.04 | 31 | 1 |
| Mrk 273 | 8.24 | 600 | 0.55 | 620 | 900 | 6.92 | 43.86 | 130 | 1 |
| IRAS F23060+0505 | ≤9.56 | ≤1500 | ≤4.05 | (550) | (1100) | ≥7.21 | ≤44.16 | ≤14 | 1 |
| Mrk 876 | ≤9.48 | ≤1830 | ≤3.55 | (700) | (1700) | ≥6.57 | ≤44.45 | ≤35 | 1 |
| I Zw 1 | ≤7.67 | ≤140 | (0.50) | (500) | (750) | ≥7.41 | ≤43.04 | ≤6 | 1 |
|
|
|||||||||
| Mrk 231 | 8.47 | 1050 | 0.60 | 700 | 1000 | 6.71 | 44.21 | 26 | 2 |
| NGC 1266 | 7.93 - 8.66 | 33–180 | 0.45 | 177 | 362 | 7.71–6.97 | 41.51–42.25 | 54–300 | 3 |
| M 82 | 8.08–8.25 | 12–18 | 0.80 | 100 | 230 | 7.56–7.38 | 40.58–40.75 | ≥650–≥980 | 4 |
| NGC 1377 | 7.29–8.03 | 14–76 | 0.20 | 110 | 140 | 7.29–6.56 | 40.73–41.46 | 34–190 | 5 |
| NGC 6240 | 8.61 | 800 | 0.65 | 400 | 500 | 6.96 | 43.61 | 25 | 6 |
| NGC 3256 | 7.34–7.51 | 11–16 | 0.50 | 250 | 425 | 8.64–8.48 | 41.34–41.50 | ≥560–≥810 | 7 |
| NGC 3628 | 7.36–7.54 | 4.5–6.7 | 0.40 | 50 | 110 | 8.88–8.70 | 39.55–39.72 | ≥690–≥1030 | 8 |
| NGC 253 | 6.32–6.50 | 4.2–6.3 | 0.20 | 50 | 100 | 7.53–7.35 | 39.52–39.70 | ≥870–≥1300 | 9 |
| NGC 6764 | 6.52–6.69 | 3.1–4.7 | 0.60 | 170 | 280 | 8.41–8.23 | 40.45–40.63 | 59–89 | 10 |
| NGC 1068 | 7.26 | 84 | 0.10 | 150 | 250 | 7.19 | 41.77 | 27 | 11 |
| IC 5063 | 7.37–8.10 | 23–127 | 0.50 | 300 | 450 | 7.48–6.75 | 41.82– 42.56 | 7–36 | 12 |
| NGC 2146 | 7.68–7.86 | 14–22 | 1.55 | 150 | 200 | 7.78–7.61 | 41.00–41.18 | ≥3300–≥4900 | 13 |
Notes. (1) Name; (2) mass of the molecular gas in the outflow; (3) molecular outflow mass-loss rate; (4) radius of the outflow extension; (5) average velocity of the outflow; (6) maximum velocity of the outflow; (7) depletion time-scale associated with the outflow; (8) kinetic power of the outflow; (9) outflow momentum rate relative to LAGN/c; (10) references for the molecular outflow measurements: 1 – this work; 2 – Cicone et al. (2012); 3 – Alatalo et al. (2011); 4 – Walter et al. (2002); 5 – Aalto et al. (2012b); 6 – Feruglio et al. (2013b); 7 – Sakamoto et al. (2006b); 8 – Tsai et al. (2012); 9 – Sakamoto et al. (2006a) and Bolatto et al. (2013); 10 – Leon et al. (2007); 11 – Krips et al. (2011); 12 – Morganti et al. (2013); 13 – Tsai et al. (2009).
For non-ULIRG galaxies we report two values of the outflow mass, outflow rate, depletion time, kinetic power, and momentum rate of the outflow (Cols. 2, 3, 7, 8, 9), obtained by adopting in one case the conservative CO-to-H2 conversion factor αCO(1 − 0) = 0.8, which was found to be appropriate for Mrk 231, and in the other case the same αCO(1 − 0) (Col. 6 in Table 3) as for estimating the total molecular gas mass in the same host galaxy (Col. 7 in Table 3). The two values of αCO yield respectively the lower and the higher estimates of MH2,OF, 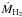 , and Pkin, and conversely for τdep (see also discussion in the text).
, and Pkin, and conversely for τdep (see also discussion in the text).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


