| Issue |
A&A
Volume 652, August 2021
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A116 | |
| Number of page(s) | 10 | |
| Section | Catalogs and data | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202140889 | |
| Published online | 20 August 2021 | |
CARMENES input catalog of M dwarfs
VI. A time-resolved Ca II H&K catalog from archival data⋆
1
Department of Physics, Ariel University, Ariel 40700, Israel
e-mail: volkerp@ariel.ac.il
2
Hamburger Sternwarte, Universität Hamburg, Gojenbergsweg 112, 21029 Hamburg, Germany
3
Institut für Astrophysik, Georg-August-Universität, Friedrich-Hund-Platz 1, 37077 Göttingen, Germany
4
Centro de Astrobiología (CSIC-INTA), ESAC, Camino bajo del Castillo s/n, 28692 Villanueva de la Cañada, Madrid, Spain
5
Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung, Justus-von-Liebig-Weg 3, 37077 Göttingen, Germany
6
Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, 69117 Heidelberg, Germany
7
Institut de Ciències de l’Espai (ICE, CSIC), Campus UAB, C/Can Magrans s/n, 08193 Bellaterra, Spain
8
Institut d’Estudis Espacials de Catalunya (IEEC), 08034 Barcelona, Spain
9
Landessternwarte, Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg, Königstuhl 12, 69117 Heidelberg, Germany
10
Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (IAA, CSIC), Glorieta de la Astronomía 1, 18008 Granada, Spain
11
Departamento de Física de la Tierra y Astrofísica and IPARCOS-UCM (Instituto de Física de Partículas y del Cosmos de la UCM), Facultad de Ciencias Físicas, Universidad Complutense de Madrid, 28040 Madrid, Spain
Received:
25
March
2021
Accepted:
6
July
2021
Context. Radial-velocity (RV) jitter caused by stellar magnetic activity is an important factor in state-of-the-art exoplanet discovery surveys such as CARMENES. Stellar rotation, along with heterogeneities in the photosphere and chromosphere caused by activity, can result in false-positive planet detections. Hence, it is necessary to determine the stellar rotation period and compare it to any putative planetary RV signature. Long-term measurements of activity indicators such as the chromospheric emission in the Ca II H&K lines (RHK′) enable the identification of magnetic activity cycles.
Aims. In order to determine stellar rotation periods and study the long-term behavior of magnetic activity of the CARMENES guaranteed time observations (GTO) sample, it is advantageous to extract RHK′ time series from archival data, since the CARMENES spectrograph does not cover the blue range of the stellar spectrum containing the Ca II H&K lines.
Methods. We have assembled a catalog of 11 634 archival spectra of 186 M dwarfs acquired by seven different instruments covering the Ca II H&K regime: ESPaDOnS, FEROS, HARPS, HIRES, NARVAL, TIGRE, and UVES. The relative chromospheric flux in these lines, RHK′, was directly extracted from the spectra by rectification with PHOENIX synthetic spectra via narrow passbands around the Ca II H&K line cores.
Results. The combination of archival spectra from various instruments results in time series for 186 stars from the CARMENES GTO sample. As an example of the use of the catalog, we report the tentative discovery of three previously unknown activity cycles of M dwarfs.
Conclusions. We conclude that the method of extracting 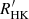 with the use of model spectra yields consistent results for different instruments and that the compilation of this catalog will enable the analysis of long-term activity time series for a large number of M dwarfs.
with the use of model spectra yields consistent results for different instruments and that the compilation of this catalog will enable the analysis of long-term activity time series for a large number of M dwarfs.
Key words: stars: activity / planetary systems / techniques: radial velocities / stars: late-type
Full Table 3 is only available at the CDS via anonymous ftp to cdsarc.u-strasbg.fr (130.79.128.5) or via http://cdsarc.u-strasbg.fr/viz-bin/cat/J/A+A/652/A116
© ESO 2021
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


